Difference between revisions of "Gall Bladder - Anatomy & Physiology"
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
The gall bladder stores bile produced in the [[Liver - Anatomy & Physiology|liver]]. Bile is important in the digestion of lipids. | The gall bladder stores bile produced in the [[Liver - Anatomy & Physiology|liver]]. Bile is important in the digestion of lipids. | ||
| − | The gall bladder forms as an outgrowth of the bile duct, as a secondary hollow at the posterior edge of the original hepatic rudiment. The | + | The gall bladder forms as an outgrowth of the bile duct, as a secondary hollow at the posterior edge of the original hepatic rudiment. The '''cystic duct''' joins the common bile duct which enters the [[Duodenum - Anatomy & Physiology|duodenum]] at the major '''duodenal papillae''' (with the pancreatic duct) on the dorsal surface of the [[Duodenum - Anatomy & Physiology|duodenum]]. |
==Structure== | ==Structure== | ||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
'''Canine''' | '''Canine''' | ||
| − | The gall bladder lies opposite the 8th intercostal space. It has the | + | The gall bladder lies opposite the 8th intercostal space. It has the thinnest layers of tunica muscularis. |
'''Bovine''' | '''Bovine''' | ||
| − | The bovine gall bladder has the thickest layers of the tunica muscularis. | + | The bovine gall bladder has the thickest layers of the tunica muscularis. Sheep have a less projecting gall bladder than cows. The gallbladder lies against the 10th or 11th rib. |
'''[[Avian Digestive Tract - Anatomy & Physiology|Avian]]''' | '''[[Avian Digestive Tract - Anatomy & Physiology|Avian]]''' | ||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
[[Image:Guinea-pig Gallbladder Hsitology.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Histology of the Guinea-pig Gallbladder - Copyright RVC 2008]] | [[Image:Guinea-pig Gallbladder Hsitology.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Histology of the Guinea-pig Gallbladder - Copyright RVC 2008]] | ||
| − | The gall bladder has a highly folded '''mucosa'''. It has a reduced '''submucosa''' and no '''lamina muscularis'''. The gall bladder has a simple columnar epithelium and no present | + | The gall bladder has a highly folded '''mucosa'''. It has a reduced '''submucosa''' and no '''lamina muscularis'''. The gall bladder has a simple columnar epithelium and no glands present. |
==Links== | ==Links== | ||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
[[Category:Liver and Gall Bladder - Anatomy & Physiology]] | [[Category:Liver and Gall Bladder - Anatomy & Physiology]] | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:A&P Done]] |
Revision as of 17:43, 17 December 2010
Introduction
The gall bladder stores bile produced in the liver. Bile is important in the digestion of lipids.
The gall bladder forms as an outgrowth of the bile duct, as a secondary hollow at the posterior edge of the original hepatic rudiment. The cystic duct joins the common bile duct which enters the duodenum at the major duodenal papillae (with the pancreatic duct) on the dorsal surface of the duodenum.
Structure
The gall bladder lies between the right medial and quadrate lobes of the liver. It is partly attached and partly free.
Function
The gall bladder stores bile and concentrates bile by absorption through the folded mucosal wall.
Innervation
The gall bladder is innervated by parasympathetic nerves.
Species Differences
Equine Equine species have no gallbladder.
Rodents
There is no gallbladder in rats.
Canine
The gall bladder lies opposite the 8th intercostal space. It has the thinnest layers of tunica muscularis.
Bovine
The bovine gall bladder has the thickest layers of the tunica muscularis. Sheep have a less projecting gall bladder than cows. The gallbladder lies against the 10th or 11th rib.
Pigeons and parrots lack a gallbladder.
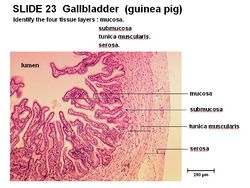
Histology
The gall bladder has a highly folded mucosa. It has a reduced submucosa and no lamina muscularis. The gall bladder has a simple columnar epithelium and no glands present.
Links
Test yourself with the Liver & Gall Bladder Flashcards
Click here for pathology of the Gall Bladder