Difference between revisions of "Avian Hard Palate"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (18 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | {{OpenPagesTop}} | |
| − | |||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
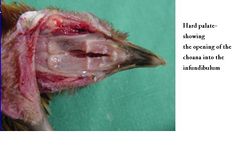
| − | The avian hard palate contains a slit-like opening called the choanal opening which communicates with the | + | The avian hard palate contains a slit-like opening called the '''choanal opening''' which communicates with the nasal pharynx. Air travels through the choanal opening into the '''infundibulum''', then dorsally into the '''auditory tubes'''. |
| − | [[Image:Choana and Infundibulum Avain.jpg|thumb|right| | + | [[Image:Choana and Infundibulum Avain.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Anatomy of the Avian Hard Palate showing the Choanal opening into the Infundibulum - RVC 2008]] |
==Structure and Function== | ==Structure and Function== | ||
| − | + | There are several rows of caudally facing '''[[Tongue - Anatomy & Physiology#Types of Papillae|conical]] papillae'''. A long, narrow, median slit in the [[Pharynx - Anatomy & Physiology|pharynx]] marks the '''infundibulum'''. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Histology== | ==Histology== | ||
| − | + | There are numerous [[Salivary Glands - Anatomy & Physiology|salivary glands]] present in the '''submucosa'''. Salivary secretions are mainly mucous with some amylase. The hard palate has a thick layer of '''stratified squamous epithelium'''. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | ==Links== | ||
| − | + | Click here for more information on the '''[[Hard Palate|hard palate]]'''. | |
| − | [[The Avian Alimentary Tract - Anatomy & Physiology - Flashcards| | + | {{Template:Learning |
| + | |flashcards = [[The Avian Alimentary Tract - Anatomy & Physiology - Flashcards|The avian alimentary tract]] | ||
| + | }} | ||
| − | [[ | + | {{OpenPages}} |
| + | [[Category:Avian Alimentary System - Anatomy & Physiology]] | ||
| + | [[Category:A&P Done]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:24, 28 June 2012
Introduction
The avian hard palate contains a slit-like opening called the choanal opening which communicates with the nasal pharynx. Air travels through the choanal opening into the infundibulum, then dorsally into the auditory tubes.
Structure and Function
There are several rows of caudally facing conical papillae. A long, narrow, median slit in the pharynx marks the infundibulum.
Histology
There are numerous salivary glands present in the submucosa. Salivary secretions are mainly mucous with some amylase. The hard palate has a thick layer of stratified squamous epithelium.
Links
Click here for more information on the hard palate.
| Avian Hard Palate Learning Resources | |
|---|---|
 Test your knowledge using flashcard type questions |
The avian alimentary tract |
Error in widget FBRecommend: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt6621798927a542_48061584 Error in widget google+: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt662179892af9e7_82451006 Error in widget TwitterTweet: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt662179893088b2_10490540
|
| WikiVet® Introduction - Help WikiVet - Report a Problem |