Difference between revisions of "Avian Intestines - Anatomy & Physiology"
m (Text replace - "Category:To Do - Review" to "Category:To Do - AP Review") |
|||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
Patches of lymphoid nodules are present in '''[[Peyer's Patches - Anatomy & Physiology|Peyer's Patches]]'''. They are most abundant in the '''[[Duodenum - Anatomy & Physiology|duodenum]]'''. There are no mesenteric lymph nodes. | Patches of lymphoid nodules are present in '''[[Peyer's Patches - Anatomy & Physiology|Peyer's Patches]]'''. They are most abundant in the '''[[Duodenum - Anatomy & Physiology|duodenum]]'''. There are no mesenteric lymph nodes. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Histology== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Caeca | ||
| + | **Serous coat has nerve plexuses | ||
| + | **Columnar epithelium and goblet cells | ||
| + | **Smooth muscle in folds at base | ||
| + | **Caecal sphincter at proximal part containing a lot of lymphoid tissue (caecal tonsil) | ||
| + | **Middle section has thin walls and appears green | ||
| + | **The bulbous blind ends have thicker walls | ||
| + | |||
| + | *See [[Small Intestine - Anatomy & Physiology#Histology|small intestine]] | ||
==Species Differences== | ==Species Differences== | ||
| Line 54: | Line 66: | ||
'''Click here for more information on the [[:Category:Large Intestine - Anatomy & Physiology|Large Intestine - Anatomy & Physiology]]''' | '''Click here for more information on the [[:Category:Large Intestine - Anatomy & Physiology|Large Intestine - Anatomy & Physiology]]''' | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Category:Small Intestine - Anatomy & Physiology]] | [[Category:Small Intestine - Anatomy & Physiology]] | ||
[[Category:Avian Alimentary System - Anatomy & Physiology]] | [[Category:Avian Alimentary System - Anatomy & Physiology]] | ||
[[Category:To Do - AimeeHicks]][[Category:To Do - AP Review]] | [[Category:To Do - AimeeHicks]][[Category:To Do - AP Review]] | ||
Revision as of 18:24, 10 December 2010
Structure
The inestines occupy the caudal part of the body. They contact the reproductive organs and the gizzard. The small intestine is long and relatively uniform in shape and size. There is no demarcation between the jejunum and the ileum.
The duodenum passes caudally over the gizzard then loops back towards the stomach where it joins the jejunum. It arises from the right dorsal aspect of the gizzard. The loop lies ventral on the abdominal floor and the pancreas lies within the loops. 3 pancreatic ducts and one bile duct enter the caudal duodenum at a common papila.
Jejunum
The jejunum has loose coils around the mesentery. It has thin walls so its content appears green. It is suspended from the dorsal wall of the abdomen by the mesentery.
Ileum
The ileum begins opposite the apices of the caeca or at the vitelline diverticula. It is suspended from the dorsal wall of the abdomen by the mesentery .
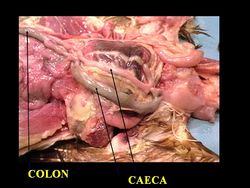
colon
The short colon lies ventral to the synsacrum and opens into the cloaca. It runs ventral to the vertebrae and terminates in the coprodeum. Amino acids and glucose can be absorbed here.
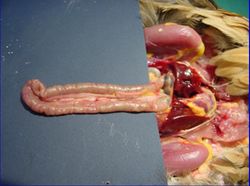
2 caeca from the ileocaecal junction run with the ileum caudally. They are blind sacs, about 16-18cm long. They extend towards the liver then fold back on themselves. The mesentery runs between the caeca then on towards the ileum. It often contains dark coloured material. There are 3 parts of each caeca. It is where the bacterial breakdown of cellulose occurs. Antiperistaltic movements transport chyme and the caeca are emptied a few times per day. Unlike mammals, there are no lacteals in the epithelium.
Vitelline Diverticula
The vitelline diverticula is a small outgrowth on the jejunum. It is the former connection with the yolk sac. It is also called Meckel's diverticulum.
Function
Vasculature
Innervation
Lymphatics
Patches of lymphoid nodules are present in Peyer's Patches. They are most abundant in the duodenum. There are no mesenteric lymph nodes.
Histology
- Caeca
- Serous coat has nerve plexuses
- Columnar epithelium and goblet cells
- Smooth muscle in folds at base
- Caecal sphincter at proximal part containing a lot of lymphoid tissue (caecal tonsil)
- Middle section has thin walls and appears green
- The bulbous blind ends have thicker walls
- See small intestine
Species Differences
The duck and goose have several loops of 'U' shaped jejunum. Pigeons have a circular mass of jejunum with inner and outer turns. A long caeca is present in the turkey and chicken. Pigeons and song birds have a short caeca. Parrots do not have caeca. The dorsal and ventral lobes of the pancreas are connected dorsally in poultry.
Links
Test Yourself with the Avian Alimentary Tract Flashcards
Click here for information on the Small Intestine - Anatomy & Physiology
Click here for more information on the Large Intestine - Anatomy & Physiology