Difference between revisions of "Avian Intestines - Anatomy & Physiology"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m (Text replace - "[[The Gizzard - Anamtomy & Physiology|" to "[[Gizzard - Anatomy & Physiology|") |
|||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
*The inestines occupy the caudal part of the body | *The inestines occupy the caudal part of the body | ||
| − | *Contacts the reproductive organs and [[ | + | *Contacts the reproductive organs and [[Gizzard - Anatomy & Physiology|gizzard]] |
*The small intestine is long and relatively uniform in shape and size | *The small intestine is long and relatively uniform in shape and size | ||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
*There is no demarcation between the [[Jejunum - Anatomy & Physiology|jejunum]] and the [[Ileum - Anatomy & Physiology|ileum]] | *There is no demarcation between the [[Jejunum - Anatomy & Physiology|jejunum]] and the [[Ileum - Anatomy & Physiology|ileum]] | ||
[[Image:Duodenum Avian Anatomy.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Anatomy of the Avian Duodenum and Pancreas - RVC 2008]] | [[Image:Duodenum Avian Anatomy.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Anatomy of the Avian Duodenum and Pancreas - RVC 2008]] | ||
| − | *The [[Duodenum - Anatomy & Physiology|duodenum]] passes caudally over the [[ | + | *The [[Duodenum - Anatomy & Physiology|duodenum]] passes caudally over the [[Gizzard - Anatomy & Physiology|gizzard]] then loops back towards the stomach where it joins the [[Jejunum - Anatomy & Physiology|jejunum]] |
| − | **Arises from the right dorsal aspect of the [[ | + | **Arises from the right dorsal aspect of the [[Gizzard - Anatomy & Physiology|gizzard]] |
**Loop lies ventral on the abdominal floor | **Loop lies ventral on the abdominal floor | ||
**The [[Pancreas - Anatomy & Physiology|pancreas]] lies within the loops | **The [[Pancreas - Anatomy & Physiology|pancreas]] lies within the loops | ||
Revision as of 16:39, 7 September 2010
Structure
- The inestines occupy the caudal part of the body
- Contacts the reproductive organs and gizzard
- The small intestine is long and relatively uniform in shape and size
- The duodenum passes caudally over the gizzard then loops back towards the stomach where it joins the jejunum
- Jejunum
- Loose coils around the mesentery
- Thin walls so content appears green
- Suspended from the dorsal wall of the abdomen by the mesentery
- Ileum
- Begins opposite the apices of the caeca or at the vitelline diverticula
- Suspended from the dorsal wall of the abdomen by the mesentery
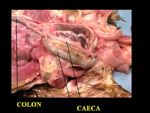
- A short colon
- The colon lies ventral to the synsacrum and opens into the cloaca
- Runs ventral to the vertebrae
- Terminates in the coprodeum
- Amino acids and glucose can be absorbed
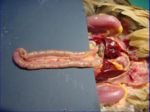
- 2 caeca from the ileocaecal junction run with the ileum caudally
- Blind sacs about 16-18cm long
- Extend towards the liver then fold back on themselves
- Mesentery runs between the caeca then on towards the ileum
- Often contain dark coloured material
- 3 parts of each caeca
- Bacterial breakdown of cellulose occurs
- Antiperistaltic movements transport chyme
- Caeca emptied a few times per day
- Unlike mammals, there are no lacteals in the epithelium
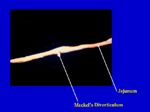
Vitelline Diverticula
- Small outgrowth on the jejunum
- Former connection will yolk sac
- Also called Meckel's diverticulum
Function
- See small intestine
Vasculature
- See small intestine
Innervation
- See small intestine
Lymphatics
- Patches of lymphoid nodules are present in Peyer's Patches
- Most abundant in the duodenum
- No mesenteric lymph nodes
Histology
Species Differences
- Duck and goose have several loops of 'U' shaped jejunum
- Pigeons have a circular mass of jejunum with inner and outer turns
- Long caeca in turkey and chicken
- Pigeons and song birds have short caeca
- Parrots do not have caeca
- The dorsal and ventral lobes of the pancreas are connected dorsally in poultry
Test Yourself with the Avian Alimentary System Flashcards
Avian Alimentary Tract Flashcards