Black Leg
Also known as: Blackquarter
Introduction
A bacterial disease affecting cattle and sheep caused by Clostridium chauvoei. Spores pass through the wall of the GI tract and via the bloodstream enter the muscle and liver where they then lie latent. This results in oedematous and crepitant swelling of the muscles. Under the correct conditions (usually anaerobic following injury) they germinate and bacilli grow. Toxins damage the capillaries causing a severe necrotising myositis.
Signalment
In cattle it is typically beef breeds who are affected particularly animals in good health and good body condition. More frequently occurs in cattle between 6-24 months old but can affect animals of any age. In some animals lesions occur following muscle trauma, which is thought to activate latent spores in the muscle.
In sheep, cases typically occur following some form of injury such as shearing cuts, docking or castration.
Tends to affect animals in the summer months.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is made on clinical signs and muscle biopsy.
History and Clinical Signs
The bacteria can cause rapid toxaemia resulting in sudden death, however, if clinical signs do occur these can include toxaemia, pyrexia, depression, pulmonary oedema, circulatory collapse lameness and swollen hot muscles which later become cool as necrosis occurs.
Pathology
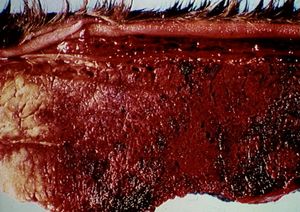
Affected muscle is black, dry, infiltrated with small bubbles, distended by serous or serosanguinous exudate and often has a rancid smell. The lesions can be present in any muscle including the tongue or diaphragm and it is not unusual to find clumps of gram positive bacteria in affected muscle. Often in sheep, lesions are deep and quite small. Suspected cases can be confirmed using demonstration of C. chauvoei in diseased muscle using the fluorescent antibody test on smears produced from the primary lesion.
Treatment
Vaccination can prevent black leg in cattle and sheep. In the face of an outbreak all susceptible animals should be treated with penicillin and vaccinated.
Prognosis
Poor, clinical cases can be treated with penicillin however this is rarely successful.
Literature Search
Use these links to find recent scientific publications via CAB Abstracts (log in required unless accessing from a subscribing organisation).
Blackleg publications
References
Merck & Co (2008) The Merck Veterinary Manual (Eighth Edition) Merial
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |