Difference between revisions of "Brachyspira pilosicoli"
| (10 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{OpenPagesTop}} | ||
{{Taxobox | {{Taxobox | ||
|name =''Brachyspira pilosicoli'' | |name =''Brachyspira pilosicoli'' | ||
| Line 5: | Line 6: | ||
|order =Spirochaetales | |order =Spirochaetales | ||
|family =Brachyspiraceae | |family =Brachyspiraceae | ||
| − | |genus =Brachyspira | + | |genus =[[:Category:Brachyspira and Serpulina|Brachyspira]] |
|species =''B. pilosicoli'' | |species =''B. pilosicoli'' | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | ==Introduction== |
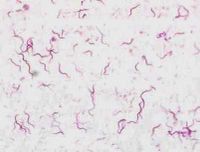
| + | [[File:Brachyspira pilosicoli.jpg|200px|right|thumb|Figure 1: ''Brachispira pilosicoli'' in culture, stained by Gram stain.]] | ||
| + | '''''Brachyspira pilosicoli''''' is a Gram-negative, spiral shaped bacterium. It is an anaerobic [[Spirochaetes|spirochaete]], closely related to ''[[Brachyspira hyodysenteriae]]''. The bacterium is loosely coiled and is 6-11µm long (Figure 1). It is only weakly haemolytic in contrast to ''B. hyodysenteriae''. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The bacterium may have '''8-12 internalised flagellae''', inserted at either pole of the cell between the inner and outer membranes. The outer membrane contains '''lipopolysaccharide''' (endotoxin). This pathogen can also cause '''zoonotic''' disease in people. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Lifecycle== | ||
| + | Infection of ''B.pilosicoli'' is acquired via '''ingestion of contaminated faeces'''. Once in the Alimentary tract, the spiral rotating motion allows the bacterium to move through the mucus in the intestine and thus reach and invade its target cells in the large intestine. The organism remains '''infective for long periods in organic matter''' but is '''inactivated by sunlight'''. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The pathogen has been isolated from '''dogs, birds, mice and humans'''. Dogs are thought to be a source of infection for people. | ||
| − | + | ==Diseases== | |
| − | + | ''B. pilosicoli'' is the cause of '''[[Porcine Intestinal Spirochaetosis|porcine intestinal spirochaetosis]]''' which is a much milder disease than the [[Swine Dysentery|swine dysentery]] caused by ''[[Brachyspira hyodysenteriae]]''. | |
| − | + | The presence of the spirochaetes in diarrhoeal faeces is not itself diagnostic because related, but non-pathogenic, species may be present. | |
| − | The | ||
| − | == | + | ==Pathogenesis== |
| + | The '''attachment''' of ''B. pilosicoli'' to epithelial cells of colonic mucosa causes oedema, shedding of epithelial cells, haemorrhage and leucocyte infiltration and leading to '''malabsorption'''. The invasion of goblet cells can also lead to '''secretory [[diarrhoea]]'''. | ||
| − | + | '''Toxins and proteins''' released by B. pilosicoli have '''haemolytic and cytotoxic effects'''. Its membranous '''LPS''' also contains an endotoxin (lipid A). | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | {{Learning |
| − | [[ | + | |literature search= [http://www.cabdirect.org/search.html?rowId=1&options1=AND&q1=%22Brachyspira+pilosicoli%22&occuring1=title&rowId=2&options2=AND&q2=&occuring2=freetext&rowId=3&options3=AND&q3=&occuring3=freetext&x=42&y=14&publishedstart=yyyy&publishedend=yyyy&calendarInput=yyyy-mm-dd&la=any&it=any&show=all ''Brachyspira pilosicoli'' publications] |
| + | |flashcards = [[Brachyspira pilosicoli Flashcards|''B. pilosicoli'' Flashcards]] | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | ==References== | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
| + | Hirsh, D. C., Maclachan, N. J., Walker, R. L (2004) '''Veterinary Microbiology 2nd ed.'''. Pp:131-133. ''Wiley-Blackwell, London''. | ||
| − | + | {{CABI source | |
| + | |datasheet = [http://www.cabi.org/ahpc/?compid=3&dsid=91832&loadmodule=datasheet&page=2144&site=160 ''Brachyspira pilosicoli''] | ||
| + | |date =11 June 2011 | ||
| + | }} | ||
<br><br><br> | <br><br><br> | ||
| − | |||
| + | {{Andrew Rycroft | ||
| + | |date = January 4, 2012}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{OpenPages}} | ||
| − | + | [[Category:Brachyspira_and_Serpulina]] | |
| − | [[Category:Brachyspira_and_Serpulina]][[Category:Pig Bacteria]] | + | [[Category:Pig Bacteria]] |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Zoonoses]] |
| + | [[Category:CABI Expert Review Completed]][[Category:CABI AHPC Pages]] | ||
Latest revision as of 12:32, 17 August 2012
| Brachyspira pilosicoli | |
|---|---|
| Phylum | Spirochaetes |
| Class | Spirochaetes |
| Order | Spirochaetales |
| Family | Brachyspiraceae |
| Genus | Brachyspira |
| Species | B. pilosicoli |
Introduction
Brachyspira pilosicoli is a Gram-negative, spiral shaped bacterium. It is an anaerobic spirochaete, closely related to Brachyspira hyodysenteriae. The bacterium is loosely coiled and is 6-11µm long (Figure 1). It is only weakly haemolytic in contrast to B. hyodysenteriae.
The bacterium may have 8-12 internalised flagellae, inserted at either pole of the cell between the inner and outer membranes. The outer membrane contains lipopolysaccharide (endotoxin). This pathogen can also cause zoonotic disease in people.
Lifecycle
Infection of B.pilosicoli is acquired via ingestion of contaminated faeces. Once in the Alimentary tract, the spiral rotating motion allows the bacterium to move through the mucus in the intestine and thus reach and invade its target cells in the large intestine. The organism remains infective for long periods in organic matter but is inactivated by sunlight.
The pathogen has been isolated from dogs, birds, mice and humans. Dogs are thought to be a source of infection for people.
Diseases
B. pilosicoli is the cause of porcine intestinal spirochaetosis which is a much milder disease than the swine dysentery caused by Brachyspira hyodysenteriae.
The presence of the spirochaetes in diarrhoeal faeces is not itself diagnostic because related, but non-pathogenic, species may be present.
Pathogenesis
The attachment of B. pilosicoli to epithelial cells of colonic mucosa causes oedema, shedding of epithelial cells, haemorrhage and leucocyte infiltration and leading to malabsorption. The invasion of goblet cells can also lead to secretory diarrhoea.
Toxins and proteins released by B. pilosicoli have haemolytic and cytotoxic effects. Its membranous LPS also contains an endotoxin (lipid A).
| Brachyspira pilosicoli Learning Resources | |
|---|---|
 Test your knowledge using flashcard type questions |
B. pilosicoli Flashcards |
 Search for recent publications via CAB Abstract (CABI log in required) |
Brachyspira pilosicoli publications |
References
Hirsh, D. C., Maclachan, N. J., Walker, R. L (2004) Veterinary Microbiology 2nd ed.. Pp:131-133. Wiley-Blackwell, London.

|
This article was originally sourced from The Animal Health & Production Compendium (AHPC) published online by CABI during the OVAL Project. The datasheet was accessed on 11 June 2011. |
| This article has been expert reviewed by Prof Andrew Rycroft BSc (Hons), PhD, C.Biol., FSB, FRCPath Date reviewed: January 4, 2012 |
Error in widget FBRecommend: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt66217ffd3aae25_88325000 Error in widget google+: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt66217ffd467343_94512557 Error in widget TwitterTweet: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt66217ffd4bf8b1_65577671
|
| WikiVet® Introduction - Help WikiVet - Report a Problem |