|
|
| (12 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| − | ===Overview=== | + | {{frontpage |
| | + | |pagetitle =Campylobacter species |
| | + | |pagebody = <div style="text-align: left; direction: ltr; margin-left: 1em;"> |
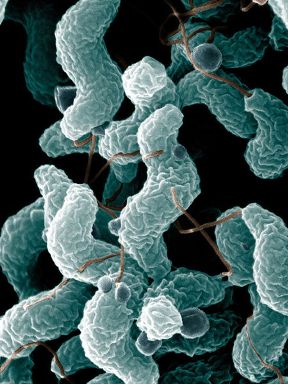
| | + | Campylobacter bacteria are Gram-negative organisms with a characteristic spiral appearance. They live on the mucosa of the intestinal and genital tract and can be commensals or pathogens. Enteric species can cause disease in humans and other species can cause infertility and abortion in cattle and sheep. |
| | + | </div> |
| | | | |
| − | *Live on mucosa of intestinal and genital tract and can be commensals or pathogens
| + | |contenttitle =Content |
| − | *Enteric species cause disease in humans
| + | |contentbody =<big><b> |
| − | *Other species cause infertility and abortion in cattle and sheep
| + | <categorytree mode=pages>Campylobacter species</categorytree> |
| − | *Excreted in faeces of birds, (''C. jejuni'' and ''C. lari'') as well as pigs contaminating water and food supplies
| + | </b></big> |
| − | *''C. fetus'' restricted to bovine prepucial mucosa
| + | |logo = Campylobacter logo.jpg |
| | + | }} |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| − | ===Characteristics===
| |
| | | | |
| − | *Curved, Gram negative rods
| + | [[Category:Bacterial Organisms]] |
| − | *Polar flagellum aids motility
| + | [[Category:Gram_negative_bacteria]] |
| − | *Daughter cells remain joined giving gull-wing or spiral appearance
| + | [[Category:Rods]] |
| − | *Microaerophilic
| |
| − | *Sensitive to drying
| |
| − | *Thermophilic species - ''C. jejuni, C. coli''
| |
| − | *Non-thermophilic species e.g. ''C. fetus''
| |
| − | *Grow on enriched selective media e.g. Skirrow agar in 1-10% carbon dioxide and 5-10% oxygen tension
| |
| − | *''C. jejuni'' requires increased temperatures for growth
| |
| − | *Many grow on MacConkey
| |
| − | *Oxidase positive, non-fermentative
| |
| − | *''C. fetus'' subspecies ''venerealis'' and subspecies ''fetus'' have small, round, smooth, translucent colonies
| |
| − | *''C. jejuni'' has small, flat, grey colonies with watery appearance
| |
| − | *Smears stained with dilute carbol fuschin for 4 minutes
| |
| − |
| |
| − | | |
| − | ===Pathogenesis and pathogenicity===
| |
| − | | |
| − | *''C. fetus'' subspecies ''fetus'' and subspecies ''venerealis'' possess a microcapsule (S layer) which resists phagocytosis and serum-mediated destruction and enhances survival in the genital tract
| |
| − | *Antigens of S layer undergoes antigenic shifts in ''C. fetus'' subspecies ''venerealis'', allowing persistence in the host
| |
| − | *''C. jejuni'' attaches and invades host enterocytes and produces enterotoxin-like substances
| |
| − | *Flagellae of ''C. jejuni'' required for colonisation
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | [[Campylobacter fetus subspecies venerealis]] | |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | ===''Campylobacter fetus'' subspecies ''fetus''===
| |
| − | | |
| − | *Sporadic abortion in cows and sheep
| |
| − | *10% of ovine abortions in the UK
| |
| − | *Enteric organism of sheep, goats and cattle; faecal-oral transmission
| |
| − | *Ingestion during last trimester of pregnancy causes a bacteraemia
| |
| − | *Bacteria reach the uterus
| |
| − | *Necrotic placentitis causes late abortion, still birth or weak lambs
| |
| − | *Sporadic abortion in cattle
| |
| − | *Aborted lambs may have round necrotic lesions on surface of liver
| |
| − | *Aborting ewes source of infection for vulnerable animals
| |
| − | *Up to 20% of flock may abort
| |
| − | *Solid immunity developed
| |
| − | *S layer immunodominant antigen
| |
| − | *Diagnosis: hepatic lesions in lambs; presence of organisms in foetal abomasum; isolation and identification
| |
| − | *Treatment/control: isolate aborting ewes; destroy placenta; move other ewes to clean pasture; vaccinate flock with bacterin during outbreak and prophylactically; chlortetracycline in feed in an outbreak
| |
| − | | |
| − | | |
| − | ===[[Intestine Pathogens - Pathology#Campylobacter jejuni|''Campylobacter jejuni'']]===
| |
| − | | |
| − | *Widespread on farms - hyperendemic
| |
| − | *Carried as commensals in intestines of cattle, sheep, dogs, wild birds and especially chickens
| |
| − | *Farm animals regularly exposed via faecal-oral route; maternal antibody protects while active immunity develops
| |
| − | *Animals with little exposure are very susceptible, e.g. humans, pets
| |
| − | *Most chicken carcasses contaminated, leading to food poisoning and enterocolitis in people from uncooked meat
| |
| − | *Colonisation, attachment and invasion of colonic enterocytes; toxin production
| |
| − | *Necrosis of colonic absorptive epithelial cells, erosion of mucosa, crypt abscesses, inflammatory infiltrate of [[Neutrophils - WikiBlood|neutrophils]] into mucosa causes colitis
| |
| − | *Enteritis and diarrhoea in susceptible dogs; treatment with enrofloxacin
| |
| − | *Causes abortion in ewes
| |
| − | *Usually asymptomatic infections in chickens and turkeys, but occasional outbreaks of avian hepatitis occur with decreased egg production, loss of condition, haemorrhage and necrosis of liver; phase contrast microscopy demonstrates curved rods in bile; in-feed dihydrostreptomycin sulphate in outbreak
| |
| − | *Implicated in [[Intestines Catarrhal Enteritis - Pathology#Undifferentiated Neonatal Calf Diarrhoea|undifferentiated neonatal calf diarrhoea]], a mixed viral enteritis in calves
| |
| − | [[Category:Bacteria]][[Category:Gram_negative_bacteria]] | |