Difference between revisions of "Echinococcus multilocularis"
| (28 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{OpenPagesTop}} |
| − | + | {{Taxobox | |
| − | {{ | + | |kingdom =Animalia |
| − | | | + | |phylum =Platyhelminthes |
| − | | | + | |class =[[:Category:Cestodes|Cestoda]] |
| − | | | + | |sub-class =Eucestoda |
| − | | | + | |order =[[:Category:Cyclophyllidea|Cyclophyllidea]] |
| − | | | + | |super-family = |
| − | | | + | |family =[[:Category:Taeniidae|Taeniidae]] |
| + | |sub-family = | ||
| + | |genus =Echinococcus | ||
| + | |species =''E. multilocularis'' | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | + | Also known as: '''''Dwarf fox tapeworm | |
| − | == | + | ==Overview== |
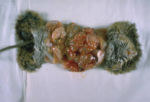
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:Rat infected with E. multilocularis.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Rat infected with ''E. multilocularis'' - Dr. I. Kagan]] |
| − | + | ''E. multilocularis'' is not present in the UK but is endemic in central Europe and North America. It is zoonotic and so presents a major health problem in Europe (including Switzerland where urban foxes are now infected) having spread from 4 countries in the 1980s to being found in 12 countries now. This has been attributed to the anti-rabies campaign which has increased the number of foxes which are commonly found as the definitive host. Humans can act as intermediate hosts if eggs are ingested causing the formation of hydatid cysts in the liver, these rapidly invade the liver and are inoperable. | |
| − | '' | ||
| + | ==Characteristics== | ||
| + | ''E. mulitlocularis'' is a relatively small tapeworm between 2-4mm as an adult.<br> | ||
| + | '''Scolex''' | ||
| + | *2 rows of hooks | ||
| + | *4 suckers | ||
| + | '''Proglottid''' | ||
| + | *Between 3 - 5 segments in total | ||
| + | *Terminal proglottid forms 1/2 the length of the mature worm | ||
| + | *1 proglottid shed per week | ||
| + | *Has single genital pore | ||
| + | '''Eggs''' | ||
| + | *200-300 eggs per mature proglottid | ||
| + | *30-40μm in diameter | ||
| + | *Striated shell | ||
| + | *Hooks visible on oncosphere | ||
| − | === Life-Cycle | + | ==Life Cylce== |
| − | The | + | ''E. multilocularis'' has a typical [[Cyclophyllidea Life-Cycle|cestode life cycle]] involving the formation of a metacestode cyst in the intermediate host before developing to adulthood in the definitive host. The definitive host for ''E. multilocularis'' is most commonly the dog, though it has also been seen in the cat. Epidemiologically the most important definitive host in the spread of the disease is the fox. ''E. multilocularis'' mainly uses small rodents such as voles, mice and rats as an intermediate host, forming multilobular hydatid cysts in the liver of the host. The short life span of the intermediate host species is the reason for the rapid growth of the cyst, even in longer lived host like humans. This is the stage that generally causes pathology in the host animal and can be fatal. |
| − | + | ==Epidemiology== | |
| − | + | ''E. mulitilocularis'' is found throughout the northern hemisphere, originally its primary range was the tundra of northern Russia and eastern Europe. The prevalence of this worm is increasing to encompass many urban areas which increases the risk of zoonotic infection. The parasites definitive host in the wild is the red fox and the arctic fox. In North America and Europe there is an increasing presence of red foxes in urban and suburban areas, this increases the risk of infection of both humans and pets. The disease it causes is called Alveolar Hydatid Disaese. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | ==Treatment and Control== | |
| + | Control involves treatment of definitive hosts, dogs and cats, with anthelmintics in order to remove adult worms from the host. The treatment of intermediate host pets (and humans) is not routine and can be dangerous as due to the infiltrative nature of the hydatid cyst and its metastatic ability. Surgical removal of the cyst is therefore not advisable. | ||
| − | + | {{Learning | |
| − | + | |flashcards = [[Cestodes_Flascards|Cestode Flashcards]] | |
| − | + | |literature search =[http://www.cabdirect.org/search.html?rowId=1&options1=AND&q1=%22Echinococcus+multilocularis%22&occuring1=title&rowId=2&options2=AND&q2=&occuring2=freetext&rowId=3&options3=AND&q3=&occuring3=freetext&publishedstart=2000&publishedend=yyyy&calendarInput=yyyy-mm-dd&la=any&it=any&show=all&x=43&y=8 ''Echinococcus multilocularis'' publications since 2000] | |
| − | + | }} | |
| − | === | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | === | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | === | ||
| − | '' | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | {{review}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | {{OpenPages}} | ||
| + | [[Category:Taeniidae]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Zoonoses]] | ||
| − | + | [[Category:Expert_Review]] | |
| − | [[Category: | ||
Latest revision as of 15:00, 6 July 2012
| Echinococcus multilocularis | |
|---|---|
| Kingdom | Animalia |
| Phylum | Platyhelminthes |
| Class | Cestoda |
| Sub-class | Eucestoda |
| Order | Cyclophyllidea |
| Family | Taeniidae |
| Genus | Echinococcus |
| Species | E. multilocularis |
Also known as: Dwarf fox tapeworm
Overview
E. multilocularis is not present in the UK but is endemic in central Europe and North America. It is zoonotic and so presents a major health problem in Europe (including Switzerland where urban foxes are now infected) having spread from 4 countries in the 1980s to being found in 12 countries now. This has been attributed to the anti-rabies campaign which has increased the number of foxes which are commonly found as the definitive host. Humans can act as intermediate hosts if eggs are ingested causing the formation of hydatid cysts in the liver, these rapidly invade the liver and are inoperable.
Characteristics
E. mulitlocularis is a relatively small tapeworm between 2-4mm as an adult.
Scolex
- 2 rows of hooks
- 4 suckers
Proglottid
- Between 3 - 5 segments in total
- Terminal proglottid forms 1/2 the length of the mature worm
- 1 proglottid shed per week
- Has single genital pore
Eggs
- 200-300 eggs per mature proglottid
- 30-40μm in diameter
- Striated shell
- Hooks visible on oncosphere
Life Cylce
E. multilocularis has a typical cestode life cycle involving the formation of a metacestode cyst in the intermediate host before developing to adulthood in the definitive host. The definitive host for E. multilocularis is most commonly the dog, though it has also been seen in the cat. Epidemiologically the most important definitive host in the spread of the disease is the fox. E. multilocularis mainly uses small rodents such as voles, mice and rats as an intermediate host, forming multilobular hydatid cysts in the liver of the host. The short life span of the intermediate host species is the reason for the rapid growth of the cyst, even in longer lived host like humans. This is the stage that generally causes pathology in the host animal and can be fatal.
Epidemiology
E. mulitilocularis is found throughout the northern hemisphere, originally its primary range was the tundra of northern Russia and eastern Europe. The prevalence of this worm is increasing to encompass many urban areas which increases the risk of zoonotic infection. The parasites definitive host in the wild is the red fox and the arctic fox. In North America and Europe there is an increasing presence of red foxes in urban and suburban areas, this increases the risk of infection of both humans and pets. The disease it causes is called Alveolar Hydatid Disaese.
Treatment and Control
Control involves treatment of definitive hosts, dogs and cats, with anthelmintics in order to remove adult worms from the host. The treatment of intermediate host pets (and humans) is not routine and can be dangerous as due to the infiltrative nature of the hydatid cyst and its metastatic ability. Surgical removal of the cyst is therefore not advisable.
| Echinococcus multilocularis Learning Resources | |
|---|---|
 Test your knowledge using flashcard type questions |
Cestode Flashcards |
 Search for recent publications via CAB Abstract (CABI log in required) |
Echinococcus multilocularis publications since 2000 |
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |
Error in widget FBRecommend: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt66226a481e5261_39452560 Error in widget google+: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt66226a4821d756_83469007 Error in widget TwitterTweet: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt66226a4824bb91_64825905
|
| WikiVet® Introduction - Help WikiVet - Report a Problem |