Difference between revisions of "Enzootic Pneumonia - Calves"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
**Partial alveolar collapse distal to the compression | **Partial alveolar collapse distal to the compression | ||
**Alveolar exudate contains a mixture of inflammatory cells | **Alveolar exudate contains a mixture of inflammatory cells | ||
| − | **Slight thickening of the alveolar walls with lymphocytes[[Category:Cattle | + | **Slight thickening of the alveolar walls with lymphocytes[[Category:Cattle]] |
[[Category:Respiratory_Bacterial_Infections]] | [[Category:Respiratory_Bacterial_Infections]] | ||
[[Category:To_Do_-_Caz]] | [[Category:To_Do_-_Caz]] | ||
Revision as of 20:32, 26 July 2010
| This article is still under construction. |
- Range of infectious agents together with managemental and environmental stress cause damage to the respiratory tract
- Causes unthriftiness in animals < 6 months old
- Usually the primary pathogen is a virus, secondary pathogens are bacteria and mycoplasmas
- Pathogens:
- Mycoplasmas
- Mycoplasmal bronchitis and pneumonia of calves is an important component of the syndrome of enzootic pneumonia
- On its own causes Mycoplasmal ("Cuffing") pneumonia responsible for bronchitis and bronchiolitis and bronchointerstitial pneumonia
- It is thought to pick up host antigens in order to prevent recognition by the body defences as foreign
- In uncomplicated mycoplasma infection, the lesions are generally mild and consist of patchy red/purple areas of atelectasis in the cranio-ventral lung lobes
- More confluent areas can develop with an underlying bronchointestitial pneumonia and resulting atelectasis
- M. bovis
- Most pathogenic
- Widespread lymphofollicular accumulations which contain germinal centres develop more slowly
- These lesions can result in narrowing of the bronchiolar lumina - this is the classical lesion of ‘cuffing pneumonia’
- M. dispar
- Ureaplasma sp.
- Viruses
- Bovine respiratory syncytial virus (BRSV) - can be primary, causes suppression of pulmonary immune response
- Parainfluenza- 3 (PI3) - can be primary, causes suppression of pulmonary immune response
- Bovine viral diarrhoea virus (BVDV) - suppression of pulmonary immune response
- Adenoviruses
- Calf coronavirus
- Bovine herpes viruses
- Bacteria
- Mycoplasmas
- All transmitted by aerosol and direct contact
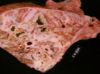
- Gross pathology:
- Consolidation of the cranioventral areas which increases in volume with duration
- On cut surface, exudate in the main airway of affected lobules with thickening of the surrounding connective tissue
- Micro pathology:
- Substantial lymphoid tissue around the airways
- Even to proper follicle formation, some of which may be large enough to compress the lumen
- Mixed cell exudate in the airway lumen
- Partial alveolar collapse distal to the compression
- Alveolar exudate contains a mixture of inflammatory cells
- Slight thickening of the alveolar walls with lymphocytes