Difference between revisions of "Hypothalamus - Anatomy & Physiology"
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{OpenPagesTop}} | ||
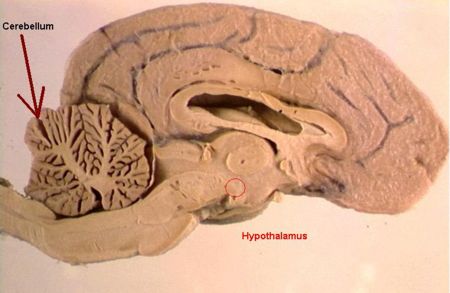
[[Image:Canine Brain CS showing Hypothalamus1.jpg|thumb|right|450px|'''Canine Brain Cross Section''' ''Courtesy of BioMed Image Archive'']] | [[Image:Canine Brain CS showing Hypothalamus1.jpg|thumb|right|450px|'''Canine Brain Cross Section''' ''Courtesy of BioMed Image Archive'']] | ||
== Hypothalamus == | == Hypothalamus == | ||
| Line 73: | Line 74: | ||
==Negative Feedback== | ==Negative Feedback== | ||
| − | |||
The Hypothalamus works along with the Pituitary and it's target glands by [[Negative Feedback - Anatomy & Physiology|negative feedback.]] | The Hypothalamus works along with the Pituitary and it's target glands by [[Negative Feedback - Anatomy & Physiology|negative feedback.]] | ||
| − | [[Image:HypothalamicPituitaryAxis.jpg| | + | [[Image:HypothalamicPituitaryAxis.jpg|center|thumb|250px|<small><center>'''Schematic Diagram of the Hypothalamic Pituitary Axis</center></small>]] |
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Links== | ==Links== | ||
| − | <big>'''Hypothalamus Differences in the Male and Female - Anatomy & Physiology'''</big> | + | <big>'''[[Hypothalamus Differences in the Male and Female - Anatomy & Physiology|Hypothalamus Differences in the Male and Female]]'''</big> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | {{Learning | ||
| + | |flashcards = [[Hypothalamus_Flash_Cards_- Anatomy & Physiology|Hypothalamus Flashcards]] | ||
| + | |full text = [http://www.cabi.org/cabdirect/FullTextPDF/2008/20083156739.pdf ''' Role of catecholamines in regulation of hypothalamo pituitary ovarian axis: a review.''' Phogat, J. B.; Umed Singh; Inderjeet Singh; College of Veterinary Sciences, Haryana Agricultural University, Hisar, India, Haryana Veterinarian, 2007, 46, pp 1-7, many ref.] | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | {{OpenPages}} | ||
[[Category:Endocrine System - Anatomy & Physiology]] | [[Category:Endocrine System - Anatomy & Physiology]] | ||
Revision as of 13:16, 29 June 2012
Hypothalamus
The hypothalamus is a small area in the ventral diencephalon of the forebrain, in the floor of the third ventricle, and is a functional link between the nervous and endocrine systems.
The hypothalamus controls most of the endocrine glands within the body, largely through stimulation of the Pituitary Gland by secretion of neurohormones. It is a vital regulator of homeostasis, including Thermoregulation.
Nuclei
| Nuclei | Function |
|---|---|
| Paraventricular | Production of Oxytocin and ADH |
| Supraoptic | Production of Oxytocin and ADH |
| Suprachiasmatic | Circadian Rhythm
Biological Clock |
| Lateral | Arousal |
| Arcuate | Energy |
| Mammilary | Wakefulness |
| Ventromedial | Feeding centre |
| Dorsomedial | Feeding, drinking and regulates body weight |
Inputs
The hypothalamus recieves direct inputs via specific receptors. It also recieves indirect inputs from the blood and nerves.
Direct Inputs via Receptors:
- Thermoreceptors: Neurons in the anterior hypothalamus respond to heat by initiating peripheral vasodilation and sweating. Neurons in the posterior hypothalamus respond to cold by initiating shivering, piloerection and peripheral vasoconstriction. These mechanisms are part of the Thermoregulation system.
- Osmoreceptors: respond to an increase in blood osmolarity by releasing Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) from the Supraoptic Nucleus which is then secreted by the posterior pituitary and acts to retain water at the kidneys. It also stimulates neurons in the thirst centre in the lateral hypothalamus in an attempt to increase water intake.
- Energy Balance: Neurons in the arcuate nucleus sense blood glucose and hormones. Leptin causes satiety, ghrelin stimulates appetite.
Indirect Inputs from bloodstream include information about:
- Temperature
- Osmotic Pressure
- Hormone concentrations - including Leptin, Cortisol, Oestrogens, Progesterone, Androgens, T3.
Indirect Neural Inputs:
- Uses Visceral and somatic sensory neurons, the Limbic System and the Reticular Activating System.
Outputs
- Biological Clock - Light sensed by retina causes stimulation of neurons leading the the suprachiasmatic nucleus which stimulates the Pineal Gland as a result.
- Secretory Neurons - ADH and Oxytocin are released by the Supraoptic and Paraventricular nuclei cell bodies. The axons descend into the Posterior Pituitary gland, where they terminate in blood vessels releasing the hormone directly into circulation. Thus the posterior pituitary acts as a storage site and is not a true endocrine gland.
- Hypothalamic Hormones - the hypothalamus releases hormones which have an activating or inhibitory effect on their target organ, hence they are named Releasing or Inhibitory Hormones respectively.
Releasing Hormones:
- Thyrotropin Releasing Hormone (TRH)
- Growth Hormone Releasing Hormone (GH-RH)
- Gonadotrophin Releasing Hormone (GnRH)
- Corticotropin Releasing Hormone (CRH)
- Prolactin Releasing Hormone (PRL-RH)
Inhibitory Hormones:
- Growth Hormone Inhibiting Hormone aka Somatostatin (GH-IH)
- Gonadotrophin Inhibiting Hormone (GnIH)
- Dopamine (PRL-IH)
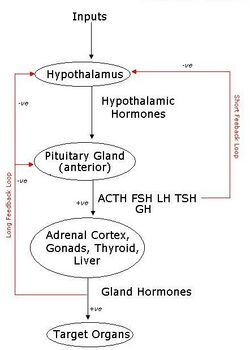
Negative Feedback
The Hypothalamus works along with the Pituitary and it's target glands by negative feedback.
Links
Hypothalamus Differences in the Male and Female
| Hypothalamus - Anatomy & Physiology Learning Resources | |
|---|---|
 Test your knowledge using flashcard type questions |
Hypothalamus Flashcards |
 Full text articles available from CAB Abstract (CABI log in required) |
Role of catecholamines in regulation of hypothalamo pituitary ovarian axis: a review. Phogat, J. B.; Umed Singh; Inderjeet Singh; College of Veterinary Sciences, Haryana Agricultural University, Hisar, India, Haryana Veterinarian, 2007, 46, pp 1-7, many ref. |
Error in widget FBRecommend: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt66235ddab314d4_88372435 Error in widget google+: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt66235ddab66ee0_38537113 Error in widget TwitterTweet: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt66235ddab95858_11534556
|
| WikiVet® Introduction - Help WikiVet - Report a Problem |