Leishmania
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |
- Leishmania spp. are intracellular parasites of macrophages
- Are closely related to Trypanosoma spp.
- Cause diseases in humans, dogs and wild animals
- Present in southern Europe, Africa, Asia and south America
- Can cause both cutaneous and visceral diseases
Recognition
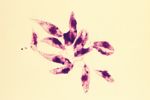
- Ovoid shaped
- Possesses a rod-shaped kinetoplast
- Has a rudimentary flagellum which does not project beyond the cell margin
- After the amastigote has transformed into a promastigote inside the sand fly, the kinetoplast is situated in the posterior of the body
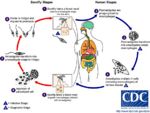
Life Cycle
- Transmitted by blood sucking sand flies
- Phlebotomus spp. in the Old World
- Lutzomyia spp. in the New World
- The amastigote (morphological form) is found in vertebrate macrophages
- Multiplies and migrates to insect proboscis
- Inoculated during feeding
- Can be transmitted percutaneously if sand fly crushed on skin
- Invades macrophages and reverts to amastigote
- Multiplies by binary fission
Pathogenesis
- Infection of vertebrate host
- Produces foci of proliferating Leishmania-infected macrophages in skin (cutaneous) or internal organs (visceral)
- Very long incubation period
- Months to years
- Many infected dogs are asymptomatic
- Visceral form causes chronic wasting condition
- Generalised eczema
- Loss of hair around eyes producing 'spectacle' effect
- Intermittent fever
- Generalised lymphadenopathy
- Generalised eczema
- Long periods of remission followed by recurrence of clinical signs is not uncommon in infections
- Involved in skin infections
Epidemiology
- Disease dependent on sand fly vectors
- E.g. Common in dogs around the Mediterranean coast, foci around southern Europe and around Madrid
- Reservoirs of infection
- E.g. Wild animals such as rodents and stray dogs
- Mechanisms of transmission
- sand fly bite
- Rarely through direct contact
- Leishmaniasis in British dogs
- Susceptible to infection if exposed whilst abroad in endemic areas as have no immunity
- No sand flies in Britain but dogs have become infected whilst in contact with infected imported animals
Diagnosis
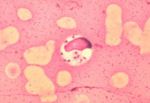
- Demonstrate Leishmania organisms
- In skin scraping or smears
- In joint fluid, lymph node or bone marrow biopsies
Treatment and Control
- Chemotherapy
- Prolonged treatment, expensive, suppresses infection
- Does not cure infection
- Prevent sand flies biting
- Collars, sprays containing insecticide with repellent effect
- Destruction of infected and stray dogs
- Sand flies biting infected dogs may spread the disease to other dogs, humans and wildlife
- There is a slight possibility of transmission to humans by direct contact
In dogs
- disseminated disease of the monocyte-macrophage system
- protozoa; genus Leishmania
- increased travel means clinincal disease may be acquired in endemic areas but now presents to veterinarians in non-endemic areas
- lymph node aspirates contain macrophages with organisms