Difference between revisions of "Linguatula serrata"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | <categorytree mode=pages>Parasites</categorytree> | + | <categorytree mode=pages style="float:right; clear:right; margin-left:1ex; border:1px solid gray; padding:0.7ex; background-color:white;">Parasites</categorytree> |
| + | |||
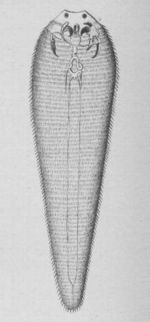
[[Image:Linguatula taenioides.jpg|right|thumb|150px|Copyright Cooper Curtice (Washington, Government Printing Office, 1890) Wikimedia Commons]] | [[Image:Linguatula taenioides.jpg|right|thumb|150px|Copyright Cooper Curtice (Washington, Government Printing Office, 1890) Wikimedia Commons]] | ||
*Also known as the tongue worm | *Also known as the tongue worm | ||
Revision as of 22:25, 6 April 2010
- Also known as the tongue worm
- A highly specialised arthropod
Recognition
- Tongue-like appearance
- Expanded anteriorly
- Adults are over 10cm in length
- Females measure between 30-130mm in length
- Males measure up to 20mm in length
- Transversely striated
Life cycle
- Life cycle takes 6 months
- Adults inhabit the nasal passages of dogs and sometimes cats
- Eggs are expelled by coughing and sneezing or are passed out with the faeces
- Herbivorous intermediate hosts ingest the eggs
- Eggs hatch in the herbivore intestine
- Larvae migrate to the mesenteric lymph nodes and encyst to become infective nymphs
- Cysts measure 1mm in diameter
- When a dog eats infected uncooked viscera the life cycle is completed
- Infective nymphs migrate from the viscera during chewing and crawl up into the nasal cavity via the soft palate
- Infective nymphs mature to adults in the nasal cavities and can survive for a year in the final host
Pathogenesis
- Causes rhinitis
- Heavy infection leads to coughing, sneezing and nasal discharge