Difference between revisions of "Parotid Gland - Anatomy & Physiology"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | == | + | ==Overview== |
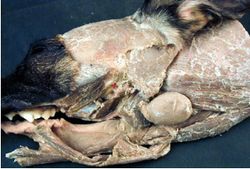
| − | [[Image:Parotid & Mandibular Salivary Gland.jpg|thumb|right| | + | [[Image:Parotid & Mandibular Salivary Gland.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Parotid Salivary Gland - Copyright Nottingham 2008]] |
| − | |||
| − | + | The parotid salivary gland produces a [[Serous Salivary Gland - Anatomy & Physiology|serous]] secretion. It is moulded around the base of the [[Ear - Anatomy & Physiology#Outer Ear|auricular cartilage]] of the ear. It is enclosed within facial covering. | |
| − | + | Trabeculae divide the gland into lobules. Major ducts run within trabeculae and merge to form a single duct. The duct opens in the vestibule opposite the 4th upper premolar (Not all species). | |
| − | + | The parotid gland is innervated by the '''glossopharyngeal nerve''' ([[Cranial Nerves - Anatomy & Physiology|CN IX]]) via the trigeminal branch. ([[Cranial Nerves - Anatomy & Physiology|CN V]]) | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Development== | ==Development== | ||
| − | + | There is an intercalated duct and cuboidal cells. This becomes a striated duct, the cuboidal cells develop with mitochondria in the base. The duct develops into an interlobular duct. The cells become stratified columnar cells. The stratified squamous epithelium then becomes continuous with the epithelium lining of the [[Oral Cavity Overview - Anatomy & Physiology|oral cavity]]. | |
| − | + | ==Species Differences== | |
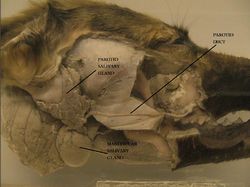
| + | [[Image:Parotid Duct.jpg|thumb|right|250px|Parotid Duct (Dog) - Copyright RVC]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
===Carnivores=== | ===Carnivores=== | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | There is some mucous secretion in the cat and dog. The duct is superficial in the dog. The duct runs across masseter muscle in carnivores. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
===Herbivores=== | ===Herbivores=== | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | It is a larger gland with a higher flow rate in herbivores to lubricate and soften the food. The duct is superficial in small ruminants. The parotid gland extends rostrally over the masseter muscle, ventrally to the angle of the jaw and caudally towards the atlantal fossa. The duct runs ventrally in herbivores below the [[Skull and Facial Muscles - Anatomy & Physiology#Mandibule (mandibula)|mandible]] (facial groove in horses) before entering the [[Oral Cavity Overview - Anatomy & Physiology|oral cavity]] at the rostral margin of the masseter muscle. | |
| − | + | ===Equine=== | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | The gland overlies the [[Ear - Anatomy & Physiology#Equine Gutteral Pouch|gutteral pouch]]. | |
| − | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| − | |||
| − | [[Oral_Cavity_-_Anatomy_%26_Physiology_-_Flashcards#Salivary_Glands_Flashcards|Salivary Glands Flashcards]] | + | ==Links== |
| + | |||
| + | '''Test yourself with the [[Oral_Cavity_-_Anatomy_%26_Physiology_-_Flashcards#Salivary_Glands_Flashcards|Salivary Glands Flashcards]]''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Click here for information on[[Parotid Gland - Histology|histology]]''' | ||
| − | + | '''Video links:''' | |
| − | |||
[http://stream2.rvc.ac.uk/Anatomy/canine/head_neck/Pot0258.mp4 Pot 258 Lateral section through the head of a dog] | [http://stream2.rvc.ac.uk/Anatomy/canine/head_neck/Pot0258.mp4 Pot 258 Lateral section through the head of a dog] | ||
[[Category:Salivary Glands - Anatomy & Physiology]] | [[Category:Salivary Glands - Anatomy & Physiology]] | ||
| − | [[Category:To Do - | + | [[Category:To Do - AimeeHicks]] |
Revision as of 09:22, 15 September 2010
Overview
The parotid salivary gland produces a serous secretion. It is moulded around the base of the auricular cartilage of the ear. It is enclosed within facial covering.
Trabeculae divide the gland into lobules. Major ducts run within trabeculae and merge to form a single duct. The duct opens in the vestibule opposite the 4th upper premolar (Not all species).
The parotid gland is innervated by the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) via the trigeminal branch. (CN V)
Development
There is an intercalated duct and cuboidal cells. This becomes a striated duct, the cuboidal cells develop with mitochondria in the base. The duct develops into an interlobular duct. The cells become stratified columnar cells. The stratified squamous epithelium then becomes continuous with the epithelium lining of the oral cavity.
Species Differences
Carnivores
There is some mucous secretion in the cat and dog. The duct is superficial in the dog. The duct runs across masseter muscle in carnivores.
Herbivores
It is a larger gland with a higher flow rate in herbivores to lubricate and soften the food. The duct is superficial in small ruminants. The parotid gland extends rostrally over the masseter muscle, ventrally to the angle of the jaw and caudally towards the atlantal fossa. The duct runs ventrally in herbivores below the mandible (facial groove in horses) before entering the oral cavity at the rostral margin of the masseter muscle.
Equine
The gland overlies the gutteral pouch.
Links
Test yourself with the Salivary Glands Flashcards
Click here for information onhistology
Video links: