Difference between revisions of "Pituitary Growth Hormone - Anatomy & Physiology"
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
*Acromegaly | *Acromegaly | ||
| − | For information on these diseases, see [[Pituitary Gland - Pathology|Pituitary Pathology]]. | + | For information on these diseases, see [[:Category:Pituitary Gland - Pathology|Pituitary Pathology]]. |
[[Category:Endocrine System - Anatomy & Physiology]] | [[Category:Endocrine System - Anatomy & Physiology]] | ||
Revision as of 14:28, 21 February 2011
Pituitary Growth Hormone
Growth Hormone, also known as Somatotropin is a hormone produced by the Somatotropes of the anterior pituitary gland.
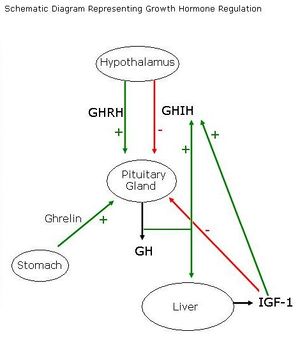
Regulation of GH secretion is complex. The Hypothalamus produces the stimulatory Growth Hormone Releasing Hormone (GHRH) and the inhibitory Growth Hormone Inhibitory Hormone (GHIH) also known as Somatostatin, which have their effects directly on the anterior pituitary gland.
Ghrelin, from the stomach stimulates the pituitary gland to secrete further GH.
Negative feedback occurs directly, with increased GH levels causing the hypothalamus to secrete GHIH to inhibit further GH secretion. In addition, negative feedback occurs via the liver. GH causes the liver to secrete IGF-1 which directly decreases GH secretion from the pituitary, and also acts on the hypothalamus to secrete GHIH to further decrease secretion.
Actions
- Rapid Catabolic Actions resulting in Hyperglycaemia
- Insulin antagonism
- Increased lipolysis
- Increased gluconeogenesis
- Decreased glucose transport across the cell membrane
- Slower, longer lasting hypertrophic actions mostly mediated by IGF-1 = GROWTH
- Increased protein synthesis and chondrogenesis
Associated Diseases
- Pituitary Dwarfism
- Acromegaly
For information on these diseases, see Pituitary Pathology.