Difference between revisions of "Radiographic Interpretation of Dental Traumatic Injuries - Small Animal"
m (Text replace - "[[Enamel Organ#" to "[[Tooth - Anatomy & Physiology#") |
|||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
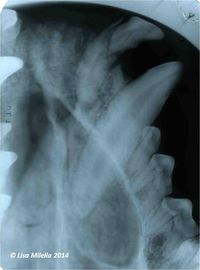
[[File:Tooth root fracture.jpg|200px|right|thumb|Root fracture]] | [[File:Tooth root fracture.jpg|200px|right|thumb|Root fracture]] | ||
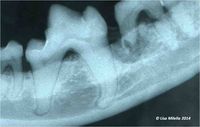
[[File:Tooth root fracture 2.jpg|200px|right|thumb|Root fracture]] | [[File:Tooth root fracture 2.jpg|200px|right|thumb|Root fracture]] | ||
| − | [[Intra-Oral Radiography - Small Animal|Dental radiographs]] are made to assess traumatic injuries to the [[:Category:Teeth - Anatomy & Physiology|teeth]], [[ | + | [[Intra-Oral Radiography - Small Animal|Dental radiographs]] are made to assess traumatic injuries to the [[:Category:Teeth - Anatomy & Physiology|teeth]], [[Tooth - Anatomy & Physiology#Alveolar Bone|alveolar bone]], [[Skull and Facial Muscles - Anatomy & Physiology#Mandible (mandibula)|mandible]], [[Skull and Facial Muscles - Anatomy & Physiology#Maxilla|maxilla]], and temporomandibular junction (TMJ). Depending on the injuries, skull radiographs and computed tomography (CT) scans may be recommended for a complete evaluation of all injuries.<br><br> |
| − | Traumatic injuries often lead to [[ | + | Traumatic injuries often lead to [[Tooth - Anatomy & Physiology#Root|root]] fractures, loss of the tooth [[Tooth - Anatomy & Physiology#Crown|crown]], and retention of the tooth root. Radiographs are made to identify persistent [[Tooth - Anatomy & Physiology#Root|roots]] and any associated pathology. A [[Tooth - Anatomy & Physiology#Crown|crown]] fracture that exposes the [[Tooth - Anatomy & Physiology#Pulp|pulp]] chamber will result in [[Endodontic Conditions - Small Animal|endodontic disease]]. When this occurs, the extent of pathology should be evaluated with a dental radiograph. Blunt trauma may result in damage to the pulp without fracturing the tooth. A dental radiograph should be made of any tooth that is discolored from pulp haemorrhage.<br><br> |
Root fractures with or without concurrent crown fractures occur secondary to trauma and affect the prognosis and treatment of the tooth.<br><br> | Root fractures with or without concurrent crown fractures occur secondary to trauma and affect the prognosis and treatment of the tooth.<br><br> | ||
[[Intra-Oral Radiography - Small Animal|Intra-oral radiographs]] of the mandible and maxilla are useful to determine the extent of jaw fractures and the involvement of tooth roots without superimposition of other structures. Intra-oral radiographs also allow proper treatment planning to avoid further damage to tooth structures during the repair of jaw fractures. | [[Intra-Oral Radiography - Small Animal|Intra-oral radiographs]] of the mandible and maxilla are useful to determine the extent of jaw fractures and the involvement of tooth roots without superimposition of other structures. Intra-oral radiographs also allow proper treatment planning to avoid further damage to tooth structures during the repair of jaw fractures. | ||
Revision as of 13:19, 2 November 2014
Interpretation of Traumatic Injuries
Dental radiographs are made to assess traumatic injuries to the teeth, alveolar bone, mandible, maxilla, and temporomandibular junction (TMJ). Depending on the injuries, skull radiographs and computed tomography (CT) scans may be recommended for a complete evaluation of all injuries.
Traumatic injuries often lead to root fractures, loss of the tooth crown, and retention of the tooth root. Radiographs are made to identify persistent roots and any associated pathology. A crown fracture that exposes the pulp chamber will result in endodontic disease. When this occurs, the extent of pathology should be evaluated with a dental radiograph. Blunt trauma may result in damage to the pulp without fracturing the tooth. A dental radiograph should be made of any tooth that is discolored from pulp haemorrhage.
Root fractures with or without concurrent crown fractures occur secondary to trauma and affect the prognosis and treatment of the tooth.
Intra-oral radiographs of the mandible and maxilla are useful to determine the extent of jaw fractures and the involvement of tooth roots without superimposition of other structures. Intra-oral radiographs also allow proper treatment planning to avoid further damage to tooth structures during the repair of jaw fractures.
| This article was written by Lisa Milella BVSc DipEVDC MRCVS. Date reviewed: 14 August 2014 |
| Endorsed by WALTHAM®, a leading authority in companion animal nutrition and wellbeing for over 50 years and the science institute for Mars Petcare. |