Spermatogenesis and Spermiation - Anatomy & Physiology
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
BACK TO REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
BACK TO MALE REPRODUCTIVE TRACT
Introduction
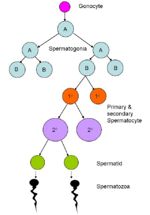
Unlike the female production of gametes which occurs entirely before birth with gamete maturation occurring in a pulsatile fashion after puberty, male individuals produce gametes continuously from puberty onwards for the rest of their reproductive lives and the release of the gametes is constant. Spermatogenesis is the process of producing sperm, and it occurs in three phases:
- Proliferative phase
- Meiotic phase
- Differentiation phase / spermiogenesis
The Spermatogenic Cycle
- Spermatogenesis occurs in the Seminipherous tubules of the testes.
- Sertoli cells found within the seminipherous tubules play a vital role in the production of gametes. Sertoli cells are support cell within the seminipherous tubules. They are anchored to the basement membrane and reach all the way to the lumen of the tubules. The junctional complexes between neighbouring sertoli cells make up the ‘’’blood-testes barrier’’’ which prevents autoimmune reactions against haploid spermatids and spermatozoa by providing an immunologically privileged site. The blood-testes barrier splits the seminipherous epithelium into two main sections; the basal compartment where spermatogonia develop and the adluminal compartment where spermatocytes, spermatids and spermatozoa develop.
- Spermatogenesis occurs in three phases:
- Proliferation - Spermatogonia undergo many mitotic divisions in order to maintain the spermatogonia population in order for spermatogenesis to be continuously producing sperm.
- Meiosis -
- Differenciation -
Hormonal Control of Spermatogenesis
The production of sperm is controlled by hormones influencing sertoli cells rather than sperm cells directly. Hormonal control is via the two gonadotrophins Luteinising hormone (LH) and follicle stimulating hormone (FSH).
- LH acts on the interstitial Leydig cells stimulating them to produce the androgen testosterone.
- FSH acts on the Sertoli cells within the seminipherous tubules stimulating production of Androgen Binding Protein as well as Inhibin