Difference between revisions of "Theileria"
m (New page: {{review}} {{toplink |backcolour = |linkpage =Parasites |linktext =PARASITES |pagetype=Bugs |sublink1=Protozoa |subtext1=PROTOZOA }} <br>) |
|||
| (35 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{OpenPagesTop}} |
| − | {{ | + | {{Taxobox |
| − | | | + | |name = ''Theileria'' spp |
| − | | | + | |kingdom = Protista |
| − | | | + | |sub-kingdom = |
| − | | | + | |phylum = [[:Category:Protozoa|Protozoa]] |
| − | | | + | |super-class = |
| − | | | + | |class = |
| + | |sub-class = | ||
| + | |super-order = | ||
| + | |order = Piroplasmorida | ||
| + | |sub-order = | ||
| + | |super-family = | ||
| + | |family = Theileriidae | ||
| + | |sub-family = | ||
| + | |genus = Theileria | ||
| + | |species = ''Theileria parva'' and others | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | <br> | + | ==Introduction== |
| + | [[Image:Theileria parva life cycle.jpg|thumb|right|300px|''Theileria parva'' Life Cycle Diagram - Dennis Jacobs & Mark Fox RVC]] | ||
| + | [[File:Theileria_lifecycle.gif|thumb|200px|right|''Theileria'' Lifecycle]] | ||
| + | ''Theileria'' species are a group of '''[[Protozoa | protozoan]]''' pathogens causing severe '''lymphatic proliferative disease''' in cattle. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''''T. parva''''' is the species of most veterinary importance, affecting cattle in Central and Eastern Africa and is the cause of [[East Coast Fever | East Coast Fever]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Other species cause significant economic losses in the Mediterranean, Middle East and Northern Africa. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Lifecycle== | ||
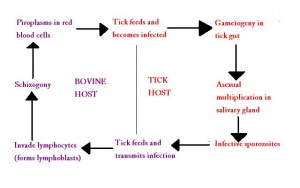
| + | ''Theileria'' are transmitted via the [[Haemaphysalis spp.|''Haemaphysalis'']] and [[Rhipicephalus spp.|''Rhipicephalus'']] species of '''[[Ticks|tick]] vectors'''. | ||
| + | |||
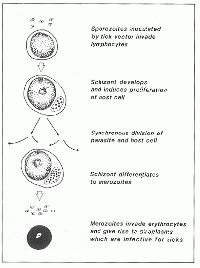
| + | '''Sporozoites''' enter '''mononuclear''' cells of the host and develop into '''trophozoites''' and multinucleate '''schizonts''' by '''asexual''' reproduction. This process stimulates proliferation of the host cells, allowing further multiplication of the parasite. The local '''[[Lymph Nodes - Anatomy & Physiology|lymph nodes]]''' are first infected. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Schizonts then '''disseminate''' through the '''[[:Category:Primary Lymphoid Tissue | lymphoid tissues]]''' before differentiating into '''merozoites'''. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The merozoites enter the '''[[Erythrocytes | erythrocytes]]''' and form '''piroplasms''' which are '''infective to ticks''' and capable of sexual reproduction. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Sexual reproduction occurs within the nymph and larval stages of the [[Ticks |tick]] and the final infective stage is present within the '''salivary glands''' and is transmitted to mammalian hosts when bloodfeeding. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Transmission in the tick is then '''[[Ticks#Disease Transmission|trans-stadial]]'''. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In endemic areas, '''endemic stability''' is often reached, in which most or all cattle may be infected and be carriers and most ticks are also infected, but young calves gain solid immunity from their immune dams and therefore rarely show clinical disease. This state however takes time to stabilise and will cause significant economic losses in the process. | ||
| + | |||
| + | For more information on ticks as vectors, see [[Tick Disease Transmission]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Pathogenesis== | ||
| + | [[Lymphocytes - Introduction|Lymphocytes]] are '''killed''' by invading protozoa and later in disease, '''lymphopoeisis''' is reduced and prevented. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Diseases== | ||
| + | <big><b>[[Theileriosis - Cattle |Bovine Theileriosis]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[East Coast Fever]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Babesiosis - Horse|Equine Babesiosis]]</b></big> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==''Theileria parva''== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''T. parva'' is primarily a parasite of '''African buffalo''' and the cause of '''[[Theileriosis - Cattle | Bovine Theileriosis]]''' and '''[[East Coast Fever]]'''. It may be transmitted by a wide range of [[Ticks |tick]] hosts although ''Rhipicephalus appeniculatus'' is the most importnat in the field. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The protozoa form '''rod shaped''' piroplasms within host [[Erythrocytes | erythrocytes]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Sheep and mice can also be infected. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==''Theileria annulata''== | ||
| + | Also Known As: '''''T. dispar'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''T. annulata'' is also a cause of [[Theileriosis - Cattle |Bovine Theileriosis]]. The parasite infects '''[[Macrophages |macrophages]]''' and '''[[B cells| B Lymphocytes]]''' forming '''round or oval''' piroplasma within host [[Erythrocytes | erythrocytes]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | It also infects sheep and yaks. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==''Theileria equi''== | ||
| + | ''Theileria equi'' (formerly ''Babesia equi'') and ''Babesia caballi'' cause [[Babesiosis - Horse|babesiosis in horses]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {{Learning | ||
| + | |flashcards = [[Piroplasmida_Flashcards|Piroplasmida Flashcards]] | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==References== | ||
| + | <references/> | ||
| + | {{CABI source | ||
| + | |datasheet = [http://www.cabi.org/ahpc/?compid=3&dsid=96673&loadmodule=datasheet&page=2144&site=160 Theileria] | ||
| + | |date = 4/06/2011 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | <br><br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Nick Lyons | ||
| + | |date = July 8, 2012}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{OpenPages}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Piroplasmida]] | ||
| + | [[Category:CABI Expert Review]][[Category:CABI AHPC Pages]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Nick Lyons reviewed]] | ||
Revision as of 17:35, 17 August 2012
| Theileria spp | |
|---|---|
| Kingdom | Protista |
| Phylum | Protozoa |
| Order | Piroplasmorida |
| Family | Theileriidae |
| Genus | Theileria |
| Species | Theileria parva and others |
Introduction
Theileria species are a group of protozoan pathogens causing severe lymphatic proliferative disease in cattle.
T. parva is the species of most veterinary importance, affecting cattle in Central and Eastern Africa and is the cause of East Coast Fever.
Other species cause significant economic losses in the Mediterranean, Middle East and Northern Africa.
Lifecycle
Theileria are transmitted via the Haemaphysalis and Rhipicephalus species of tick vectors.
Sporozoites enter mononuclear cells of the host and develop into trophozoites and multinucleate schizonts by asexual reproduction. This process stimulates proliferation of the host cells, allowing further multiplication of the parasite. The local lymph nodes are first infected.
Schizonts then disseminate through the lymphoid tissues before differentiating into merozoites.
The merozoites enter the erythrocytes and form piroplasms which are infective to ticks and capable of sexual reproduction.
Sexual reproduction occurs within the nymph and larval stages of the tick and the final infective stage is present within the salivary glands and is transmitted to mammalian hosts when bloodfeeding.
Transmission in the tick is then trans-stadial.
In endemic areas, endemic stability is often reached, in which most or all cattle may be infected and be carriers and most ticks are also infected, but young calves gain solid immunity from their immune dams and therefore rarely show clinical disease. This state however takes time to stabilise and will cause significant economic losses in the process.
For more information on ticks as vectors, see Tick Disease Transmission.
Pathogenesis
Lymphocytes are killed by invading protozoa and later in disease, lymphopoeisis is reduced and prevented.
Diseases
Theileria parva
T. parva is primarily a parasite of African buffalo and the cause of Bovine Theileriosis and East Coast Fever. It may be transmitted by a wide range of tick hosts although Rhipicephalus appeniculatus is the most importnat in the field.
The protozoa form rod shaped piroplasms within host erythrocytes.
Sheep and mice can also be infected.
Theileria annulata
Also Known As: T. dispar
T. annulata is also a cause of Bovine Theileriosis. The parasite infects macrophages and B Lymphocytes forming round or oval piroplasma within host erythrocytes.
It also infects sheep and yaks.
Theileria equi
Theileria equi (formerly Babesia equi) and Babesia caballi cause babesiosis in horses.
| Theileria Learning Resources | |
|---|---|
 Test your knowledge using flashcard type questions |
Piroplasmida Flashcards |
References

|
This article was originally sourced from The Animal Health & Production Compendium (AHPC) published online by CABI during the OVAL Project. The datasheet was accessed on 4/06/2011. |
| This article has been expert reviewed by Nick Lyons MA VetMB CertCHP MRCVS Date reviewed: July 8, 2012 |
Error in widget FBRecommend: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt662146a53f10b8_79133678 Error in widget google+: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt662146a542ad77_80182312 Error in widget TwitterTweet: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt662146a5460da6_18996957
|
| WikiVet® Introduction - Help WikiVet - Report a Problem |