Difference between revisions of "Trachea - Anatomy & Physiology"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
The cervical part of the trachea lies generally in the median position, although this varies slightly depending on the position of the head. | The cervical part of the trachea lies generally in the median position, although this varies slightly depending on the position of the head. | ||
The thoracic part of the trachea crosses the aortic arch, thus it's positioning is moved slightly to the right at this level. | The thoracic part of the trachea crosses the aortic arch, thus it's positioning is moved slightly to the right at this level. | ||
| + | |||
The trachea bifurcates to form the two [[Bronchi and bronchioles - Anatomy & Physiology|bronchi]] at the level of the 4th-6th inter[[Ribs and Sternum - Anatomy & Physiology#Costae|costal]] space. | The trachea bifurcates to form the two [[Bronchi and bronchioles - Anatomy & Physiology|bronchi]] at the level of the 4th-6th inter[[Ribs and Sternum - Anatomy & Physiology#Costae|costal]] space. | ||
Revision as of 17:31, 14 August 2008
|
|
Introduction
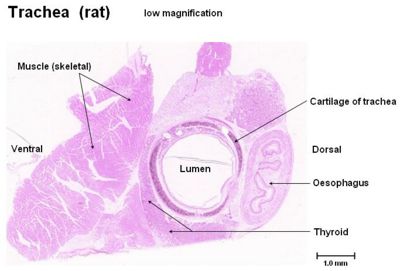
The trachea is the tube linking the cricoid cartilage of the larynx to the bronchi, forming part of the conducting system which transports air from the external environment to the lungs. The oesophagus lies dorsally to the trachea. The cervical part of the trachea lies generally in the median position, although this varies slightly depending on the position of the head. The thoracic part of the trachea crosses the aortic arch, thus it's positioning is moved slightly to the right at this level.
The trachea bifurcates to form the two bronchi at the level of the 4th-6th intercostal space.
Structure
- The trachea contains numerous rings of hyaline cartilage which are C-shaped, being dorsally incomplete, connected to eachother by elastic connective tissue. The ends of the incomplete rings are joined by smooth muscle - Trachealis muscle.
- The structural conformation of the trachea prevents collapse due to traction forces, whilst allowing it to adjust in length and diameter as the neck moves and the diaphragm contracts.
- The trachea's walls are made up of a number of layers: Inner Mucosa, Fibrocartilaginous middle layer, and and adventitia (in the neck) or serosa (in the thorax).
- The inner mucosa contains glands which produce mucus. This mucus traps debris and is constantly moved upwards towards the pharynx where it is swallowed. This mechanism is known as the Muco-Ciliary escalator.
Function
- Transporting air for respiration from the larynx to the bronchi.
Histology
Species Differences
- In the Dog and Cat the C-Shaped rings are joined by muscle which is placed externally, rather than internally as is normal for the other species.
- In avian species the trachea is composed of tightly stacked rings of cartilage, which are complete with no dorsal space. They overlap considerably.
Links
The Syrinx- avian vocalisation
References
- Dyce, K.M., Sack, W.O. and Wensing, C.J.G. (2002) Textbook of Veterinary Anatomy. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Saunders.