Difference between revisions of "Type I Hypersensitivity"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 59: | Line 59: | ||
===Examples of Type I hypersensitivity=== | ===Examples of Type I hypersensitivity=== | ||
| − | * Allergy - WikiBlood|Atopy | + | * [[Allergy - WikiBlood|Atopy]] |
| − | * Allergy - WikiBlood|Flea allergic dermatitis | + | * [[Allergy - WikiBlood|Flea allergic dermatitis]] |
| − | * Allergy - WikiBlood|Sweet itch | + | * [[Allergy - WikiBlood|Sweet itch]] |
Revision as of 15:36, 29 August 2008
|
|
Introduction
- Also known as IgE-mediated or anaphylactic hypersensitivity.
- Ranges from mild cases, such as hayfever, to life-threatening reactions, such as bee-stings.
- Antigens that induce a type I reaction are known as allergens.
- Generally affects face, eyes, nose and feet
- IgE has a high affinity to IgE receptors on mast cells and basophils, and so binds these receptors.
Common allergens which elict a type I hypersensitivity reaction:
- Proteins : Foreign serum
- Plant pollens : Rye grass, ragweed, timothy grass, birch trees
- Drugs : Penicillin, sulphonamides, local anaesthetics, salicylates
- Foods : Nuts, seafood, eggs, milk
- Insect products : Bee venom, wasp venom, dust mites faeces, flea saliva
Mechanism
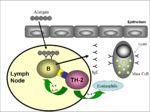
1. Initial antigen exposure sensitises immune system (Image 1):
- Allergen exposure causes IgE production.
- IgE coat mast cells by binding to Fc receptors.
- Mast cells are now sensitised to this particular allergen.
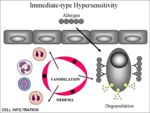
2. Subsequent exposure to the specific allergen (Image 2):
- mast cells degranulation.
- basophils with IgE receptors are recruited and also degranulate.
Mast cells secrete mediators:
- The release of inflammatary cytokines which can cause the dog to become itchy.
- Steroid mediators, e.g. prostaglandins and leukotriens
1. Chemoattractants (attracts mainly neutrophils but also eosinophils, |monocytes and basophils and plasma) 2. Vasoactive and inflammatory peptides (e.g. histamine and serotonin) which causes acute contraction of smooth muscle fibres
- If the allergen is inhaled (locally) it can lead to bronchoconstriction.
3. Mucus production - due to the release of mast cell proteases 4. Vasodilation (leads to redness and heat). 5. Oedema (from leaky blood vessels).
3. The late phase response:
- Mediated by eosinophils.
- Takes longer (several hours) as the eosinophils are mobilised from the bone marrow.