Difference between revisions of "Blastocyst Embryonic Development - Anatomy & Physiology"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Pre-Implantation Development == | == Pre-Implantation Development == | ||
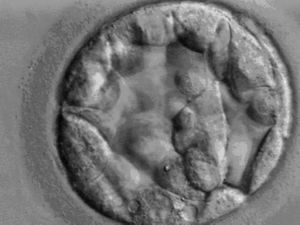
[[Image:Blastocyst.jpg|thumb|right|300px|Blastocyst - Courtesy of Wikimedia Commons]] | [[Image:Blastocyst.jpg|thumb|right|300px|Blastocyst - Courtesy of Wikimedia Commons]] | ||
| − | + | Once sperm has entered the the '''oocyte''', an '''ootid''' is formed. At an early stage the ootid will contain male and female '''pronuclei''' along with the first and second '''polar bodies'''. Fusion of the male and female '''pronuclei''' will result in a single '''diploid nucleus''' or '''syngamy'''. Once this '''syngamy''' has occurred, the '''zona pellucida''' then develops into an imprenetrable layer that prevents polyspermy and so polyploidy. Once the '''zona pellucida''' has developed, the ootid is now referred to as a '''zygote''' (diploid) and will begin undergoing mitotic divisions via a '''cleavage''' process that will begin to give rise to daughter cells called '''blastomeres'''. These cleavage divisions will begin to produce a 4-celled embryo and then an 8-celled embryo. | |
| − | + | <br /> | |
| − | + | <br /> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
* These cells are totipotent and divide asynchronously. | * These cells are totipotent and divide asynchronously. | ||
* After the 8-celled stage, a ball of cells is formed. This stage is referred to as a '''morula'''. | * After the 8-celled stage, a ball of cells is formed. This stage is referred to as a '''morula'''. | ||
Revision as of 16:02, 18 January 2011
Pre-Implantation Development
Once sperm has entered the the oocyte, an ootid is formed. At an early stage the ootid will contain male and female pronuclei along with the first and second polar bodies. Fusion of the male and female pronuclei will result in a single diploid nucleus or syngamy. Once this syngamy has occurred, the zona pellucida then develops into an imprenetrable layer that prevents polyspermy and so polyploidy. Once the zona pellucida has developed, the ootid is now referred to as a zygote (diploid) and will begin undergoing mitotic divisions via a cleavage process that will begin to give rise to daughter cells called blastomeres. These cleavage divisions will begin to produce a 4-celled embryo and then an 8-celled embryo.
- These cells are totipotent and divide asynchronously.
- After the 8-celled stage, a ball of cells is formed. This stage is referred to as a morula.
- Tight junctions form between outer cells of the morula.
- Gap junctions form between inner cells of the morula.
- Thus, two groups of cells are created within the morula.
- Outer cells pump sodium into the intracellular spaces and water follows osmotically.
- Fluid begins to accumulate within the morula.
- Cells of the morula continue to divide and a blastocyst develops, consisting of:
- Inner cell mass (ICM)
- Blastocoele cavity
- Single layer of trophoblast cells
- As fluid accumulates, the outer cells become flattened and a cavity known as the blastocoele is formed.
- Gap junctions connecting the inner cells of the morula enable them to polarise as a group.
- As a result, two separate cellular components emerge - the inner cell mass and the trophoblasts.
- Blastocyst continues mitosis.
- Fluid accumulates to fill the blastocoele and pressure within the embryo increases.
- Concurrent with growth and fluid accumulation is the production of proteolytic enzymes by trophoblastic cells.
- Enzymes weaken the zona pellucida.
- Blastocyst begins to contract and relax causing intermittent pressure pulses on the zona pellucida.
- Zona pellucida ruptures with the development of a small fissure just large enough for the blastocyst to squeeze out.
- Blastocyst 'hatches' from the zona pellucida.
- Rodent, Dog, Cat, Primate: 8 days after fertilization
- Ungulates: 12 days after fertilization.
- Blastocyst free-floating within the uterus, totally dependent on the uterine environment for survival.