Difference between revisions of "Adenoma"
| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
*May be difficult to distinguish from nodular hyperplasia | *May be difficult to distinguish from nodular hyperplasia | ||
*Single and larger nodules than normal [[Pancreas - Anatomy & Physiology|pancreas]] | *Single and larger nodules than normal [[Pancreas - Anatomy & Physiology|pancreas]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Learning | ||
| + | |flashcards = [[Cytology Q&A 07]] | ||
| + | }} | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 06:43, 9 August 2011
- Adenomas are unusual but may develop in oropharyngeal salivary tissue.
Intestinal adenoma
- An adenoma is a growth of glandular origin.
- Intestinal adenomas are found in both the small and large intestines.
- Intestinal adenomas usually grow into the lumen.
- These growths are bengin and polyp-like.
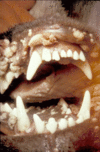
Tumours of the Perianal Area
Hepatoid Gland Tumours (Perianal Adenomas)
These tumours arise from the solid, modified sebaceous circumanal glands. They are the third most common tumour in intact male dogs, and arise more frequently in older dogs.
The tumour is under hormonal control. Hepatoid glands are also found at the tail head, prepuce and other skin sites, and tumours can also arise from there.
Clinical features
Adenomas occur alone or in number, as round, well-differentiated, freely-movable masses. Tumours can become ulcerated and secondarily infected. There can be signs of perianal pain and tenesmus.
Diagnosis
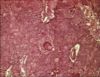
Cytology of the mass will reveal large hepatoid cells with a round, central nuclei, multiple nucleoli, and an abundant cytoplasm. There may be concurrent inflammation or haemorrhage. Cytology cannot distinguish adenomas from adenocarcinomas, and further investigations should be carried out if malignancy is suspected.
Treatment
Castration is the treatment of choice and 95% of tumours will regress. Administration of oestrogens or anti-androgens can also be considered, but side-effects of those hormones should not be forgotten. Surgical removal of the tumour may be necessary if it is large, or in females.
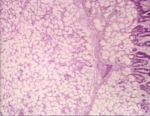
Hepatocytic
- seen mostly in sheep and cattle
Gross
- a single, pale, soft, often large nodule
- well demarcated from adjacent tissue, often with a noticeable capsule
Microscopically
- normal hepatocytic appearance
- no portal tracts within the mass
- a capsule surrounds the growth
Cholangiocellular - bile duct
- very rare
- reported in dogs and cats
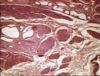
Pancreatic
Image of multifocal pancreatic adenoma in a dog from Cornell Veterinary Medicine
- Very rare
- May be difficult to distinguish from nodular hyperplasia
- Single and larger nodules than normal pancreas
| Adenoma Learning Resources | |
|---|---|
 Test your knowledge using flashcard type questions |
Cytology Q&A 07 |
References
Withrow, S. (2001) Small animal clinical oncology Elsevier Health Sciences
Morrison, W. (2002) Cancer in dogs and cats: medical and surgical management Teton NewMedia