Difference between revisions of "Adaptive Immunity to Viruses"
(Created page with "thumb|200px|right|'''''' '''Humoral''' *Production of '''neutralising antibody''' *'''Antibody-dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC)''' [[Immuno...") |
|||
| (14 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[Image: | + | {{OpenPagesTop}} |
| + | [[Image:virusimmunity.jpg|350px|right]] | ||
| + | ==Humoral== | ||
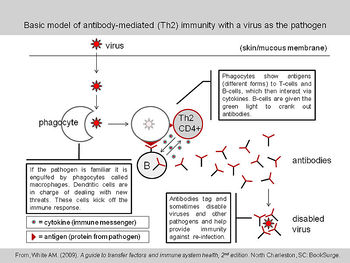
| + | The humoral response to viruses involves the production of '''neutralising antibody''' and '''Antibody-dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC)'''. [[Immunoglobulins|Antibody]]-labelled cells can be targeted by [[Lymphocytes#Natural Killer (NK) cells|NK Cells]] as another defence against viral infection. The antibody produced against viral protein can attach to infected cells during their budding phase, which effectively labels them for [[Lymphocytes#Natural Killer (NK) cells|NK]] targeting. [[Lymphocytes#Natural Killer (NK) cells|NK]] cells express Fcγ receptors with which to detect such cells. Once activated, they release a host of enzymes to induce apoptosis of the budding cell. | ||
| − | + | ==Cell-Mediated== | |
| − | + | The cell-mediated response to viruses involves [[Lymphocytes#Cytotoxic CD8+|CD8<sup>+</sup> T-cell]] mediated killing of virus infected cells. They are the main cells involved in the immune response to '''intracellular''' virus infection. Viruses are detected by the recognition of [[Major Histocompatability Complexes#MHC I|MHC I]]-peptide complex and infected cells are killed by apoptosis. Perforin and granzymes activate the caspase cascade and Fas-ligand triggers the Fas-mediated apoptosis pathway. Cytotoxic [[Cytokines|cytokines]] (especially TNF-α & TNF-β lymphotoxin) act on TNF receptors to induce programmed cell death. | |
| − | |||
| − | [[ | ||
| − | + | <br><br> | |
| − | + | {{Jim Bee 2007}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | {{OpenPages}} | |
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Adaptive Immune System]] |
Latest revision as of 16:16, 2 July 2012
Humoral
The humoral response to viruses involves the production of neutralising antibody and Antibody-dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC). Antibody-labelled cells can be targeted by NK Cells as another defence against viral infection. The antibody produced against viral protein can attach to infected cells during their budding phase, which effectively labels them for NK targeting. NK cells express Fcγ receptors with which to detect such cells. Once activated, they release a host of enzymes to induce apoptosis of the budding cell.
Cell-Mediated
The cell-mediated response to viruses involves CD8+ T-cell mediated killing of virus infected cells. They are the main cells involved in the immune response to intracellular virus infection. Viruses are detected by the recognition of MHC I-peptide complex and infected cells are killed by apoptosis. Perforin and granzymes activate the caspase cascade and Fas-ligand triggers the Fas-mediated apoptosis pathway. Cytotoxic cytokines (especially TNF-α & TNF-β lymphotoxin) act on TNF receptors to induce programmed cell death.
| Originally funded by the RVC Jim Bee Award 2007 |
Error in widget FBRecommend: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt665697768e9794_60743872 Error in widget google+: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt665697769353f3_44701877 Error in widget TwitterTweet: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt66569776994ce0_84374848
|
| WikiVet® Introduction - Help WikiVet - Report a Problem |