Difference between revisions of "Small Mammals Q&A 18"
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| align="center" | [[File:Manson_logo.gif|90px|Mansonlogo]] | | align="center" | [[File:Manson_logo.gif|90px|Mansonlogo]] | ||
| − | | align="left" | This question was provided by [[:Category:Manson|Manson Publishing]] as part of the [[OVAL Project]]. See more [[Category: Small Mammals Q&A|Small Mammals questions]] | + | | align="left" | This question was provided by [[:Category:Manson|Manson Publishing]] as part of the [[OVAL Project]]. See more [[:Category: Small Mammals Q&A|Small Mammals questions]] |
|} | |} | ||
<br><br><br> | <br><br><br> | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
Hyperestrogenism occurs when an intact jill remains unbred and in oestrus for an extended period of time. The most prominent sign of oestrus is vulvar swelling. The effects of prolonged exposure to high levels of endogenous oestrogen are alopecia and bone marrow suppression. Signs include petechial hemorrhages on the skin and mucous membranes, pallor, lethargy and generalized weakness. | Hyperestrogenism occurs when an intact jill remains unbred and in oestrus for an extended period of time. The most prominent sign of oestrus is vulvar swelling. The effects of prolonged exposure to high levels of endogenous oestrogen are alopecia and bone marrow suppression. Signs include petechial hemorrhages on the skin and mucous membranes, pallor, lethargy and generalized weakness. | ||
| − | |l1= Hyperoestrogenism | + | |l1= Hyperoestrogenism - Ferret |
|q2= How would you treat these conditions? | |q2= How would you treat these conditions? | ||
|a2= Manage adrenocortical neoplasia with adrenalectomy of the affected gland(s) or mitotane therapy. | |a2= Manage adrenocortical neoplasia with adrenalectomy of the affected gland(s) or mitotane therapy. | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
Terminate the oestrus cycle with hormonal therapy (HCG), mate with a vasectomized male or an ovariohysterectomy. Hormonal therapy may not be effective in the moderate to severely affected case, therefore perform an ovariohysterectomy as soon as the patient is stable. | Terminate the oestrus cycle with hormonal therapy (HCG), mate with a vasectomized male or an ovariohysterectomy. Hormonal therapy may not be effective in the moderate to severely affected case, therefore perform an ovariohysterectomy as soon as the patient is stable. | ||
Ferrets have no discernable blood types, therefore it is possible to use multiple donors when performing blood transfusions. Provide other supportive care as needed. Attempt to stimulate the bone marrow with anabolic steroids or synthetic erythropoietin used at feline dosages. | Ferrets have no discernable blood types, therefore it is possible to use multiple donors when performing blood transfusions. Provide other supportive care as needed. Attempt to stimulate the bone marrow with anabolic steroids or synthetic erythropoietin used at feline dosages. | ||
| − | |l2= Hyperoestrogenism | + | |l2= Hyperoestrogenism - Ferret |
</FlashCard> | </FlashCard> | ||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
rect 0 0 860 850 [[Small Mammals Q&A 19|Next question]] | rect 0 0 860 850 [[Small Mammals Q&A 19|Next question]] | ||
desc none}} | desc none}} | ||
| + | |||
[[Category: Small Mammals Q&A]] | [[Category: Small Mammals Q&A]] | ||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 15:08, 16 August 2011
| This question was provided by Manson Publishing as part of the OVAL Project. See more Small Mammals questions |
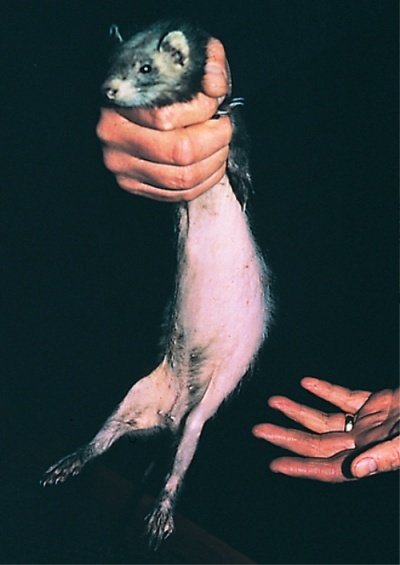
A two-year-old ferret jill is dull, lethargic and has a generalised alopecia.
| Question | Answer | Article | |
| What are your differential diagnoses for the alopecia? | Adrenocortical disease (hyperplasia or neoplasia) and hyperestrogenism are the most likely differential diagnoses.
In the ferret, disease of the adrenal gland is not related to the pituitary as in other species. It is usually a disease of ferrets three years of age and older, although it has been reported in animals as young as 18 months. Ferrets affected with adrenal disease may be either intact or neutered. The alopecia in adrenocortical disease in the ferret is caused by an increased production of androgens rather than an increase in corticosteroids as in other animals. Some neutered female ferrets will exhibit an enlarged vulva as if in estrus in response to the abnormal androgen production. Hyperestrogenism occurs when an intact jill remains unbred and in oestrus for an extended period of time. The most prominent sign of oestrus is vulvar swelling. The effects of prolonged exposure to high levels of endogenous oestrogen are alopecia and bone marrow suppression. Signs include petechial hemorrhages on the skin and mucous membranes, pallor, lethargy and generalized weakness. |
Link to Article | |
| How would you treat these conditions? | Manage adrenocortical neoplasia with adrenalectomy of the affected gland(s) or mitotane therapy.
Obtain a CBC and platelet count on ferrets with hyperoestrogenism to determine the extent of disease. If the PCV is 15% or lower, the prognosis for recovery is grave. Terminate the oestrus cycle with hormonal therapy (HCG), mate with a vasectomized male or an ovariohysterectomy. Hormonal therapy may not be effective in the moderate to severely affected case, therefore perform an ovariohysterectomy as soon as the patient is stable. Ferrets have no discernable blood types, therefore it is possible to use multiple donors when performing blood transfusions. Provide other supportive care as needed. Attempt to stimulate the bone marrow with anabolic steroids or synthetic erythropoietin used at feline dosages. |
Link to Article | |