Difference between revisions of "Proventriculus - Anatomy & Physiology"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
m |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | {{toplink | |
| − | + | |backcolour =BCED91 | |
| − | + | |linkpage =Alimentary - Anatomy & Physiology | |
| + | |linktext =Alimentary System | ||
| + | |maplink = Alimentary (Concept Map)- Anatomy & Physiology | ||
| + | |pagetype =Anatomy | ||
| + | |sublink1=Avian Digestive Tract - Anatomy & Physiology | ||
| + | |subtext1=AVIAN DIGESTIVE TRACT | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | <br> | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
Revision as of 22:04, 2 September 2008
|
|
Introduction
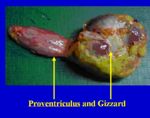
The proventriculus is also referred to as the glandular stomach. It is connected by the isthmus to the gizzard.
Structure and Function
- A storage organ in fish and flesh eating birds
- Appropriate to a soft diet
- Secretes digestive enzymes
- Contacts the left lobe of the liver ventrally and laterally
- Related dorso-caudally to the spleen
- More cranial than the gizzard
- Lies to the left of the midline of the bird
- Spindle/fusiform shaped
- Roughly 4cm long
- Lumen diameter similar to the oesophagus
- No oesophageal sphincter
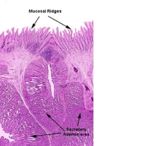
Histology
- Mucous cells
- Columnar epithelium
- Basophilic
- Papillae- through which collecting ducts from glands run
- Lamina propria run into the papillae
- Hydrochloric acid and pepsin produced
- Glands in the submucosa
- Single tubular glands are grouped into lobules with a common opening into a papillae
- Serous membrane of mesothelial cells attached to the outer longitudinal layer of muscle
- 3 layers of lamina muscularis
- No parietal cells