Difference between revisions of "Avian Respiration - Anatomy & Physiology"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | |||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
Revision as of 11:19, 14 August 2008
|
|
Introduction
The avian respiratory system contains some fundamental changes to the mammalian system.
Avian Nasopharynx and Oropharynx
- The nostrils of the bird, which lead into the nasal cavity, may have a flap of horn to protect them, known as the Operculum.
- The Oral Cavity and the Nasal Cavity of the bird are interconnecting via a slit in the hard palate called the Choana. Birds lack a soft palate.
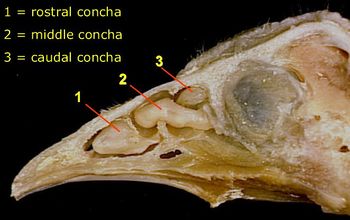
- There are Rostral, Middle and Caudal Conchae arising from the lateral wall, filling part of the nasal cavity.
- Rostral Conchae - Vestibular Region - lined with Stratified Squamous Epithelium
- Middle Conchae - Respiratory Region - lined with Respiratory Epithelium.
- Caudal Conchae - Olfactory Region - lined with olfactory epithelium.
- The Infraorbital Sinus is a triangular cavity under the skin, rostroventral to the eye.
- Some marine birds have a Salt Gland (nasal gland) which excretes sodium.
Avian Larynx
- The larynx is on the floor of the oropharynx supported by Cricoid and paried Arytenoid Cartilages which are different in structure to those in mammals.
- There is no Epiglottis.
- There are no vocal folds - birds vocalise using a syrinx.
Avian Trachea
- The avian trachea is composed of tightly stacked cartilages which are shaped similarly to signet rings. These are complete with no dorsal space as in the mammalian trachea. They overlap considerably.
- The trachea can be palpated on the right side of the neck; it runs alongside the oesophagus.
- The trachea is lined with Respiratory Epithelium.
- The trachea bifurcates as in mammals. The syrinx is formed by this terminal part of the trachea.
Avian Lungs
- The lungs of birds are relatively small, unlobed and do not have the capacity to expand.
- The lungs are positioned in the craniodorsal region of the body, and are deeply indented by both the thoracic vertebrae and ribs.
- Birds do not have a pleural cavity as the lungs do not expand, thus it is not necessary.
Air Sacs
Links
References
- Dyce, K.M., Sack, W.O. and Wensing, C.J.G. (2002) Textbook of Veterinary Anatomy. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Saunders.