Difference between revisions of "Tick Life Cycle"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:Ticks mating.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Ixodes ricinus'' mating - Wikimedia Commons]] | [[Image:Ticks mating.jpg|thumb|right|150px|''Ixodes ricinus'' mating - Wikimedia Commons]] | ||
| + | [[Image:Ixodidae life cycle.jpg|thumb|right|200px|Life cycle of Ixodidae family ticks - CDC, Wikimedia Commons]] | ||
*Ticks are temporary parasites so only spend a short period of their lives on the host species | *Ticks are temporary parasites so only spend a short period of their lives on the host species | ||
Revision as of 10:58, 8 July 2010
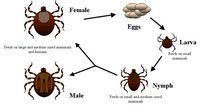
- Ticks are temporary parasites so only spend a short period of their lives on the host species
- When larvae are seeking a host they are known as seed ticks
- Both hard and soft ticks have the same life cycle
- Egg → larva → nymph → adult
- Soft ticks feed little and often and on many hosts
Hard ticks
- Classified depending on the number of host species they parasitise during their life cycle
- Take one blood meal at each life cycle stage which lasts several days
- One-host ticks
- Each stage feeds and develops on one host (the same host)
- E.g. Boophillus spp.
- Two-host ticks
- Larvae and nymphs feed on one host
- Adults feed on a second host
- E.g. Hyalomma
- Three-host ticks
- Each stage feeds and develops on a different host
- E.g. Ixodes spp.