Reticulum - Anatomy & Physiology
Revision as of 13:37, 6 September 2010 by Bara (talk | contribs) (Text replace - "[[Oesophageal groove|" to "[[Oesophageal Groove|")
|
|
Introduction
The reticulum is the second chamber of the ruminant stomach. It has regular contractions which precede the biphasic ruminal contraction for digestion of food particles.
Mechanical digestion and microbial fermentation occur to breakdown food particles for absorption. Volatile fatty acids are the major product of ruminant digestion.
Structure
- Covered by greater omentum
- The rumino-reticular fold often gets object lodged. When the rumen contracts, the object can be pushed through the reticulum wall into the pericardium and heart.
- Opening at the cardia into both the reticulum and the rumen is called the reticuluar groove (see oseophageal groove). The reticular groove also opens into the omasum.
- Cranial to the rumen
- Ribs 6-8
- From cardia to the diaphragm
- Lies above the xiphoid process of the sternum
- Serosa covers the surface
Function
- Waste removal
- Movement
- Simpler products of digestion are assilimated directly, others continue down the digestive tract for further digestion
- See rumination
- See eructation
Ruminoreticular contraction
- Primary mixes food
- Mixing cycle of ruminoreticulum
- 2 contractions of the reticulum (2nd most powerful) which continues over the rumen
- Ingesta flows from the reticulum to cranial ruminal sac to reticulum (or ventral sac)
- Every 60 seconds
- Secondary lets gas out
- See eructation
- Ingesta flows from ventral blind sac to dorsal blind sac to dorsal sac (eructation) to ventral sac
Vasculature
- Cranial mesenteric artery
- Celiac artery
- Right and left ruminal arteries
Innervation
- Dorsal vagus (CN X) (most important)
- Ventral vagus (CN X)
Lymphatics
- Numerous small lymph nodes are scattered in the grooves
- The lymph drains to larger atrial nodes between the cardia and omasum, then to the cistera chyli
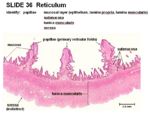
Histology
- Keratinised stratified squamous epithelium
- No glands
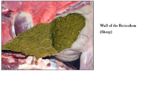
- Honeycomb appearance of short and tall folds
- Mucosal layer thrown into folds
- The folds gradually merge into papillae where the reticulum meets the rumen
- Lamina muscularis present as discrete bands of smooth muscle (not continuous)
- Conical papillae, also called secondary papillae, on folds providing a rough surface to increase food breakdown
- 2 thick layers of tunica muscularis- inner circular and outer longitudinal
- The upper keratinised layer protects against abrasion
- The deeper layers metabolise volatile fatty acids
Species Differences
Small Ruminants
- Larger reticulum compared to cattle
- In sheep and goats the ridges of the reticular cells are lower and have more prominant serrated edges than in cattle
- The papillated ruminal mucosa expands over a greater proportion of the reticulum
Test yourself with the Stomachs of the Ruminant flashcards
Links
The Rumen - Anatomy & Physiology
The Omasum - Anatomy & Physiology
The Abomasum- Anatomy & Physiology
Video
Pot 52 Lateral view of the Abdomen of a young Ruminant
Pot 175 Sections of the Ruminant Stomach
Left sided topography of the Ovine Abdomen and Thorax