Liver - Anatomy & Physiology
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
BACK TO ALIMENTARY - ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY
Introduction
The liver (hepar) is an extremely important organ in the body of mammals and vertebrates which provides functions essential for life. It is the largest internal organ and has numerous functions including production of bile and protein, fat and carbohydrate metabolism.
The size of the liver varies due to its role in metabolism. In carnivores the liver weighs about 3-5% of body weight, in omnivores 2-3% and in herbivores 1.5%. the liver is much heavier in young animals rather than older animals as it atropies with age.
Structure
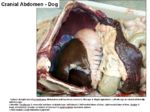
- Cranial part of the abdomen
- Immediately caudal to the diaphragm
- Cranial to the stomach and intestines
- Generally the bulk of the liver on the right of the midline
- Divided into lobes by fissures
- Cranially the liver is convex, called the diaphragmatic surface
- Caudally the liver is concave, called the visceral surface
- Caudate lobe has a renal impression from the right kidney
- Passgaes or notches on the median plane allow the caudal vena cava and oesophagus to pass by
- The gallbladder is located between the right medial and quadrate lobes
- Reticular fibres (collagen type III, proteoglycans and glycoproteins) support the hepatocytes and walls of the sinusoids
- The hiatus is
Lobes of the Liver
- Left lateral
- Left medial
- Right lateral
- Right medial
- Quadrate
- Caudate
- Papillary
Function
Vasculature
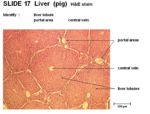
- Blood flows from the portal areas into the central vein
- Central vein lined by simple squamous epithelium
Innervation
Lymphatics
Histology
- Connective tissue capsule around each lobule
- Thin mesothelium covers connective tissue layer
- The larger liver cells are called lobules
- Each lobule contains an opening for the central vein and contains portal areas
- Lobules composed of liver cords called hepatocytes
- Sinusoids present between hepatocytes containing red blood cells
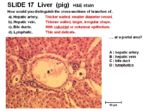
- Portal area present in lobules
- Hepatic artery- thick walls, small diameter
- Hepatic vein- thin walls, large and irregular shape
- Bile ducts- cuboidal or columnar epithelium
- Lymphatics- small and delicate
- Hepatocytes are the smaller liver cells in the lobules
- Contain glycogen granules
- Kupfer macrophages present near the lining of the sinusoids
Species Differences
Canine
- Conical bluntly