Difference between revisions of "Oviduct - Anatomy & Physiology"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Fiorecastro (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (23 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
| − | The Oviduct is the tube that links the ovary to the uterus and which the ovulated | + | The Oviduct is the tube that links the ovary to the uterus and which the ovulated oocyte travels down to become fertilised by sperm present in the female tract. It is also refered to as the Fallopian tube, Uterine tube or Ovarian tube. |
| − | |||
==Structure== | ==Structure== | ||
The oviduct is devided into 3 anatomical regions: | The oviduct is devided into 3 anatomical regions: | ||
| − | * | + | |
| − | * | + | === Infundibulum === |
| − | * | + | * The cranial ovarian end of the oviduct. |
| − | ** The formation of a | + | * It comprises of numerous fimbrae and the opening into the oviduct tube, the ostium. |
| + | |||
| + | === Ampulla === | ||
| + | |||
| + | * The longest region of the oviduct occupying more than half of its total length and also has the largest diameter. | ||
| + | * This is the site of fertilisation. | ||
| + | * It is distinguished by its many mucosal folds. | ||
| + | * The ampulla is joined to the isthmus via the Ampullary-Isthmus junction. | ||
| + | * This junction is important in the mare as it acts as a regulatory checkpoint allowing only fertilised ova to pass any further along the oviduct and into the uterus. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Isthmus === | ||
| + | |||
| + | * The caudal end of the oviduct joined to the uterus. | ||
| + | * The Isthmus is thicker walled than the ampulla and smaller in diameter. | ||
| + | * Its folded mucosa forms a functional reservoir for sperm in the female tract. | ||
| + | * Sperm in the female tract reach the isthmus of the oviduct and bind to the mucosal epithelial cells, forming a functional reservoir. | ||
| + | * The sperm are only released from the isthmus mucosa by the action of paracrine signals from an ova travelling down the oviduct. | ||
| + | ** The formation of a functional reservoir is a possible supporting mechanism of [[Fertilisation - Anatomy & Physiology|Block to polyspermy]], as only a few sperm are released from the isthmus mucosa at any one time. This results in only a few sperm being in the vicinity of the ova at a time and so in a position of fertilising the ova. | ||
| + | |||
| + | * The oviducts open into the uterine horn through the uterine ostium. | ||
| + | * This marks the site of the uterotubal junction. | ||
| + | * This junction is gradual in ruminants and pigs, but abrupt in the horse and carnivores. | ||
| + | * In the horse and carnivores, the uterine ostium is located on top of a papilla, which forms a barrier against ascending infections. | ||
==Function== | ==Function== | ||
| + | |||
*A connecting tube structure between the uterus and ovary where fertilisation occurs. | *A connecting tube structure between the uterus and ovary where fertilisation occurs. | ||
*To provide regulation check points for unfertilised oocytes. | *To provide regulation check points for unfertilised oocytes. | ||
| Line 33: | Line 46: | ||
==Histology== | ==Histology== | ||
| − | + | <center><gallery widths=150px> | |
| + | Image:Fimbrae.jpg|Histological Section of the Oviduct to show Fimbriae of the Infundibulum- Courtesy of J.Bredl, Copyright RVC 2008 | ||
| + | Image:Oviduct Ampulla.jpg|Histological Cross-Section of the Oviduct to show the Ampulla- Courtesy of J.Bredl, Copyright RVC 2008 | ||
| + | Image:Isthmus.jpg|Histological Cross-Section of the Oviduct to show the Isthmus- Courtesy of J.Bredl, Copyright RVC 2008 | ||
| + | </gallery></center> | ||
=== Infundibulum === | === Infundibulum === | ||
*Fimbriae | *Fimbriae | ||
| − | |||
** Finger like projections that aid the Infundibulum in gliding over the surface of the ovary. This action enhances the chances of the ovulated Oocyte being captured by the Infundibulum, as ovulation in domestic species does not occur in any one place. The exception to this being the mare, where ovulation always occurs from the ovulation fossa. | ** Finger like projections that aid the Infundibulum in gliding over the surface of the ovary. This action enhances the chances of the ovulated Oocyte being captured by the Infundibulum, as ovulation in domestic species does not occur in any one place. The exception to this being the mare, where ovulation always occurs from the ovulation fossa. | ||
| Line 44: | Line 60: | ||
*Ciliated Columna Epithelium | *Ciliated Columna Epithelium | ||
*Thin muscularis layer | *Thin muscularis layer | ||
| − | *Fern like mucosal folds | + | *Fern-like mucosal folds |
=== Isthmus === | === Isthmus === | ||
| Line 51: | Line 67: | ||
*Thick muscularis layer divided into inner circular layer and outer longditudinal layer | *Thick muscularis layer divided into inner circular layer and outer longditudinal layer | ||
*few mucosal folds | *few mucosal folds | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Vasculature== | ==Vasculature== | ||
*Tubal branch of the ovarian artery. | *Tubal branch of the ovarian artery. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {{Template:Learning | ||
| + | |powerpoints = [[Female Reproductive Tract Histology resource|Histology of the female reproductive tract]] | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Webinars== | ||
| + | <rss max="10" highlight="none">https://www.thewebinarvet.com/urogenital-and-reproduction/webinars/feed</rss> | ||
| − | + | [[Category:Female Reproduction]] | |
| + | [[Category:Bullet Points]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:16, 5 January 2023
Introduction
The Oviduct is the tube that links the ovary to the uterus and which the ovulated oocyte travels down to become fertilised by sperm present in the female tract. It is also refered to as the Fallopian tube, Uterine tube or Ovarian tube.
Structure
The oviduct is devided into 3 anatomical regions:
Infundibulum
- The cranial ovarian end of the oviduct.
- It comprises of numerous fimbrae and the opening into the oviduct tube, the ostium.
Ampulla
- The longest region of the oviduct occupying more than half of its total length and also has the largest diameter.
- This is the site of fertilisation.
- It is distinguished by its many mucosal folds.
- The ampulla is joined to the isthmus via the Ampullary-Isthmus junction.
- This junction is important in the mare as it acts as a regulatory checkpoint allowing only fertilised ova to pass any further along the oviduct and into the uterus.
Isthmus
- The caudal end of the oviduct joined to the uterus.
- The Isthmus is thicker walled than the ampulla and smaller in diameter.
- Its folded mucosa forms a functional reservoir for sperm in the female tract.
- Sperm in the female tract reach the isthmus of the oviduct and bind to the mucosal epithelial cells, forming a functional reservoir.
- The sperm are only released from the isthmus mucosa by the action of paracrine signals from an ova travelling down the oviduct.
- The formation of a functional reservoir is a possible supporting mechanism of Block to polyspermy, as only a few sperm are released from the isthmus mucosa at any one time. This results in only a few sperm being in the vicinity of the ova at a time and so in a position of fertilising the ova.
- The oviducts open into the uterine horn through the uterine ostium.
- This marks the site of the uterotubal junction.
- This junction is gradual in ruminants and pigs, but abrupt in the horse and carnivores.
- In the horse and carnivores, the uterine ostium is located on top of a papilla, which forms a barrier against ascending infections.
Function
- A connecting tube structure between the uterus and ovary where fertilisation occurs.
- To provide regulation check points for unfertilised oocytes.
- The mucosal glands produce oviduct secretions integral for:
- Supporting the unfertilised oocyte
- Supporting spermatozoa in the oviduct
- Increasing the fertilising capabilities of the spermatozoa
- Development of the early embryo
Anatomical Boundaries
- The Oviduct is suspended from the abdominal wall by the mesosalpnix broad ligament.
Histology
Infundibulum
- Fimbriae
- Finger like projections that aid the Infundibulum in gliding over the surface of the ovary. This action enhances the chances of the ovulated Oocyte being captured by the Infundibulum, as ovulation in domestic species does not occur in any one place. The exception to this being the mare, where ovulation always occurs from the ovulation fossa.
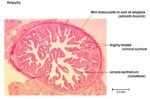
Ampulla
- Ciliated Columna Epithelium
- Thin muscularis layer
- Fern-like mucosal folds
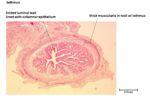
Isthmus
- Simple columna Epithelium
- Thick muscularis layer divided into inner circular layer and outer longditudinal layer
- few mucosal folds
Vasculature
- Tubal branch of the ovarian artery.
| Oviduct - Anatomy & Physiology Learning Resources | |
|---|---|
 Selection of relevant PowerPoint tutorials |
Histology of the female reproductive tract |
Webinars
Failed to load RSS feed from https://www.thewebinarvet.com/urogenital-and-reproduction/webinars/feed: Error parsing XML for RSS