Difference between revisions of "Periodontal Disease"
Ggaitskell (talk | contribs) |
Ggaitskell (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 82: | Line 82: | ||
Treatment of periodontitis is two stage – periodontal therapy performed under general anaesthesia, and the most important stage is then follow up home care following an oral hygiene program. | Treatment of periodontitis is two stage – periodontal therapy performed under general anaesthesia, and the most important stage is then follow up home care following an oral hygiene program. | ||
| − | + | ===Gingivitis=== | |
Gingivitis is by definition reversible. Removal or adequate reduction of plaque will restore inflamed gingivae to health. Once clinically healthy gingivae have been achieved, these can be maintained by daily removal or reduction in the accumulation of plaque. In short, the treatment of gingivitis is to restore the inflamed tissues to clinical health and then to maintain clinically healthy gingivae, thus preventing periodontitis. Treatment involves performing a dental scale and polish with the purpose of professional periodontal therapy in the gingivitis patient being to remove dental deposits, mainly calculus (which is not removed by toothbrushing). Once the teeth have been cleaned it remains up to the owner to remove the plaque that re-accumulates on a daily basis. | Gingivitis is by definition reversible. Removal or adequate reduction of plaque will restore inflamed gingivae to health. Once clinically healthy gingivae have been achieved, these can be maintained by daily removal or reduction in the accumulation of plaque. In short, the treatment of gingivitis is to restore the inflamed tissues to clinical health and then to maintain clinically healthy gingivae, thus preventing periodontitis. Treatment involves performing a dental scale and polish with the purpose of professional periodontal therapy in the gingivitis patient being to remove dental deposits, mainly calculus (which is not removed by toothbrushing). Once the teeth have been cleaned it remains up to the owner to remove the plaque that re-accumulates on a daily basis. | ||
| Line 96: | Line 96: | ||
| − | + | ===Periodontitis=== | |
Untreated gingivitis may progress to periodontitis. In most instances in a practice situation, periodontitis is irreversible. It is important to remember that periodontitis is a site-specific disease, i.e. it may affect one or more sites of one or several teeth. The aim of treatment is thus to prevent development of new lesions at other sites and to prevent further tissue destruction at sites which are already affected. Treatment consists of a dental scale and polish and root surface debridement. Teeth with severe periodontitis will need to be extracted and periodontal surgery may be necessary. | Untreated gingivitis may progress to periodontitis. In most instances in a practice situation, periodontitis is irreversible. It is important to remember that periodontitis is a site-specific disease, i.e. it may affect one or more sites of one or several teeth. The aim of treatment is thus to prevent development of new lesions at other sites and to prevent further tissue destruction at sites which are already affected. Treatment consists of a dental scale and polish and root surface debridement. Teeth with severe periodontitis will need to be extracted and periodontal surgery may be necessary. | ||
| Line 112: | Line 112: | ||
Educate the owner of the disease process and also educate them on good daily dental home care such as tooth brushing and diet. Regular examinations to assess the condition of the teeth are vital and the owner needs to be made aware of this. | Educate the owner of the disease process and also educate them on good daily dental home care such as tooth brushing and diet. Regular examinations to assess the condition of the teeth are vital and the owner needs to be made aware of this. | ||
| − | + | ===Periodontal Pockets=== | |
With pocket depths below 5mm, dental scaling and polishing should be performed, and then subgingival curettage and the placement of an antibiotic gel in the pocket may help rejuvenate the periodontal tissues and reduce pocket depth. | With pocket depths below 5mm, dental scaling and polishing should be performed, and then subgingival curettage and the placement of an antibiotic gel in the pocket may help rejuvenate the periodontal tissues and reduce pocket depth. | ||
Revision as of 16:56, 14 April 2014
Includes: Gingivitis — Periodontitis — Periodontal Pockets
Introduction
Periodontal disease is essentially an inflammatory response by the supporting structures of the teeth known as the periodontium. These structures include the gingiva, periodontal ligaments, cementum and alveolar bone. It is the most common dental disease in dogs and cats and the major cause of tooth loss in both species. There are numerous factors that contribute to the formation of the disease but the primary agent is dental plaque. Plaque accumulates at the gingival margin, partly due to insufficient oral hygiene.
Periodontal disease is the result of the inflammatory response to dental plaque, i.e. oral bacteria, and is limited to the periodontium. It is probably the most common disease seen in small animal practice, with the great majority of dogs and cats over the age of 3 years having a degree of disease that warrants intervention.
Periodontal disease is a collective term for a number of plaque-induced inflammatory lesions that affect the periodontium. It is a unique infection in that it is not associated with a massive bacterial invasion of the tissues. Gingivitis is inflammation of the gingiva and is the earliest sign of disease. Individuals with untreated gingivitis may develop periodontitis. The inflammatory reactions in periodontitis result in destruction of the periodontal ligament and alveolar bone. The result of untreated periodontitis is ultimately exfoliation of the affected tooth. Thus, gingivitis is inflammation that is not associated with destruction (loss) of supporting tissue – it is reversible. In contrast, periodontitis is inflammation where the tooth has lost a variable degree of its support (attachment) – it is irreversible. Infection of the periodontium may cause discomfort to the affected animal. There is also strong evidence that a focus of infection in the oral cavity has been associated with disease of distant organs. Consequently, prevention and treatment of periodontal diseases is, contrary to common belief, not a cosmetic issue, but a general health and welfare issue.
Initially, the bacterial flora tend to be non-motile aerobes or facultative anaerobes. However, as the supply of oxygen is reduced by supragingival plaque accumulation and pocket formation, the bacterial flora become more motile and anaerobic. Important bacterial flora responsible include Porphyromonas gingivalis, Bacteroides asaccharolyticus, Fusobacterium nucleatum, Actinomyces viscosus and Actinomyces odontolyticus.
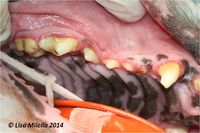
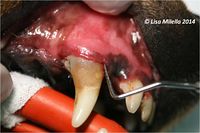
Gingival inflammation starts because of dental calculus (tartar) from diets high in minerals and diets consisting of soft rather than hard crunchy food. Dental plaque becomes calcified and whole crown may become covered in brown chalky material. Calculus gives brittle dirty brown covering to tooth which may not affect enamel at all but may produce mild gingivitis round edge and the gum may start to recede. This exposes more of crown, may reach level of dentine and infection may enter the alveolus and loosen ligaments holding tooth in and ultimately the tooth will become loose and fall out.
Gingivitis - Reversible inflammation of the marginal gingival tissues that does not affect the periodontal ligament or the alveolar bone.
Periodontitis - Inflammation and irreversible destruction of the tooth's supporting structures that includes the gingiva, periodontal ligament, alveolar bone and root cementum. It usually occurs after years of plaque accumulation and gingivitis. The epithelial attachments of the tooth regress apically and there is absorption of the associated alveolar bone, resulting in permanent loss of tooth support.
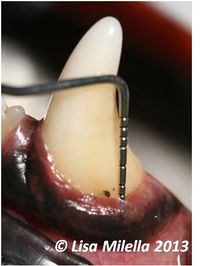
Periodontal pocket - this describes the area of tissue destruction left by periodontitis. It is an attachment loss due to destruction of the fibres and bone that support the tooth which results in a pathological deepening of the gingival sulcus.
Aetiology
The primary cause of gingivitis and periodontitis is accumulation of dental plaque on the tooth surfaces. Calculus (tartar) is only a secondary aetiological factor.
Dental plaque is a biofilm composed of aggregates of bacteria and their by-products, salivary components, oral debris, and occasional epithelial and inflammatory cells. Plaque accumulation starts within minutes on a clean tooth surface. The initial accumulation of plaque occurs supragingivally but will extend into the sulcus and populate the subgingival region if left undisturbed. The formation of plaque involves two processes, namely the initial adherence of bacteria and then the continued accumulation of bacteria due to a combination of bacterial multiplication and further aggregation of bacteria to those cells that are already attached.
As soon as a tooth becomes exposed to the oral cavity, its surfaces are covered by the pellicle (an amorphous coating of salivary proteins and glycoproteins). The pellicle alters the charge and free energy of the tooth surfaces, which increases the efficiency of bacterial adhesion. Certain specific bacteria can adhere directly to the pellicle. These bacteria produce extracellular polysaccharides, which then aggregate other bacteria that are not otherwise able to adhere. The plaque associated with healthy gingiva is mainly comprised of aerobic and facultative anaerobic bacteria. As gingivitis develops, plaque extends subgingivally. Aerobes consume oxygen and a low redox potential is created, which makes the environment more suitable for the growth of anaerobic species. The aerobic population does not decrease, but with increasing numbers of anaerobes, the aerobic/anaerobic ratio decreases. The subgingival florae associated with periodontitis are predominantly anaerobic bacteria.
Dental calculus (tartar) is mineralized plaque. However, a layer of plaque always covers calculus. Both supragingival and subgingival plaque becomes mineralized. Supragingival calculus per se does not exert an irritant effect on the gingival tissues. The main importance of calculus in periodontal disease seems to be its role as a plaque-retentive surface. This is supported by well-controlled animal and clinical studies that have shown that the removal of subgingival plaque on top of subgingival calculus will result in healing of periodontal lesions and the maintenance of healthy periodontal tissues.
Pathogenesis
The pathogenic mechanisms involved in periodontal disease include:
- Direct injury by plaque microorganisms
- Indirect injury by plaque microorganisms via inflammation
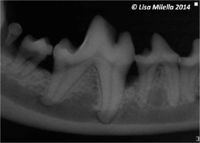
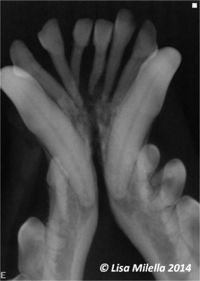
The microbiota in periodontal pockets is in a continual state of flux; periodontitis is a dynamic infection caused by a combination of bacterial vectors that change over time. As a result, the molecular events that trigger and sustain the inflammatory reactions constantly change. Many microbial products have little or no direct toxic effect on the host. However, they possess the potential to activate inflammatory reactions that cause the tissue damage. It is now well accepted that it is the host’s response to the plaque bacteria, rather than microbial virulence per se, that directly causes the tissue damage. In gingivitis, the plaque-induced inflammation is limited to the soft tissue of the gingiva. As periodontitis occurs, the inflammatory destruction of the coronal part of the periodontal ligament allows apical migration of the epithelial attachment and the formation of a pathological periodontal pocket (i.e. periodontal probing depths around the tooth increase). If the inflammatory disease is permitted to progress, the crestal portion of the alveolar process begins to resorb. Alveolar bone destruction type and extent are diagnosed radiographically.
Disease progression is generally an episodic occurrence rather than a continuous process. Tissue destruction occurs as acute bursts of disease activity followed by relatively quiescent periods. The acute burst is clinically characterized by rapid deepening of the periodontal pocket as periodontal ligament fibres and alveolar bone are destroyed by the inflammatory reactions. The quiescent phase is not associated with clinical or radiographic evidence of disease progression. However, complete healing does not occur during this quiescent phase, because subgingival plaque remains on the root surfaces and inflammation persists in the connective tissue. The inactive phase can last for extended periods. Other conditions, such as physical or psychological stress and malnutrition, may impair protective responses, such as the production of antioxidants and acute phase proteins, and can aggravate periodontitis, but do not actually cause destructive tissue inflammation.
A genetic predisposition to destructive inflammation of the periodontium may be important in some individuals.
Signalment
Pure bred cats are particularly susceptible and include: Burmese, Persian, Siamese and Maine Coon. The disease affects majority of cats over two years of age.
Certain breeds of dogs are thought to be susceptible to an aggressive form of the disease and include: Greyhound and Maltese. Small breed dogs are more prone to tooth crowding, predisposing the animal to the initiation and rapid progression of the disease.
Clinical Signs
Clinical signs include fetid breath odour (halitosis), excessive salivation, blood in saliva, dysphagia, pain on mastication and difficulty eating. There may also be loose teeth. The animal may be lethargic and show signs of weight loss and poor grooming (cats).
Diagnosis
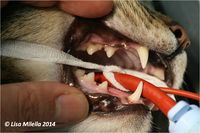
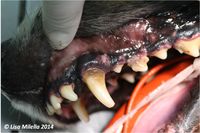
An oral examination should be performed. This is the most important part of the diagnostic procedure and should include inspection of extraoral structures (looking for swelling, atrophy or asymmetry), such as face, lips, muscles of mastication, temporomandibular joints, salivary glands, lymph nodes, maxillae and mandibles. Intraoral structures such as the dentition, gingiva, mucosa, tongue, tonsils and dental occlusion should also be thoroughly examined. On visual inspection of the intraoral structures, an animal with periodontitis may demonstrate oral mucosal ulceration, inflammed and bleeding gingiva, loss of normal gingival contour, purulent discharge from the periodontal pocket, gingival recession, loose teeth and presence of variable quantities of plaque and calculus on the tooth surface.
Periodontal disease is associated with loss of the attachment apparatus of the tooth. Clinically this is hard to detect and there is no correlation between the amount of calculus seen on the tooth and the degree of destruction. Loss of attachment usually involves the periodontal ligament, bone, root cementum and gingiva. Clinically, mobile teeth may be evident and some teeth may have evidence of gingival recession and root exposure indicating that there is periodontal disease but for a full assessment, an examination has to be performed under general anaesthesia. A periodontal probe is used to assess the depth of the gingival sulcus and whether there is loss of bone or periodontal ligament. A probing depth greater than 3mm in most dogs would be considered abnormal. This does vary based on the tooth and the size of the dog. Any depth over 0.5mm in cats would be considered abnormal. The periodontal probe is used to assess the degree of gingivitis, measure the pocket depth, check whether the tooth is mobile, whether there is bone loss between the roots (furcation exposure) and measure the amount of gingival recession. The whole circumference of the tooth needs to be evaluated.
There are a number of methods that grade the severity of periodontal disease. It must be remembered though that different teeth in the mouth may be affected by different severities of the disease and even around each tooth, the degree of attachment loss may vary. Grading is based on the extent of attachment loss as this is indicative of periodontal destruction.
- Grade 0 = Healthy Gingiva
- Grade 1 = Established gingivitis
- Grade 2 = Mild periodontitis (<25% attachment loss based on radiographs)
- Grade 3 = Moderate periodontitis (25-50% attachment loss based on radiographs)
- Grade 4 = Severe periodontitis (>50% attachment loss)
Oral radiography should be used to assess periodontal disease. Cases of periodontitis will show generalised horizontal and vertical alveolar bone loss in focal areas. Radiographic signs of periodontal disease include resorption/rounding of the alveolar margin, widening of the periodontal space, loss of the lamina dura (cortical bone of the alveolus) and alveolar bone destruction. Find more information about radiographic interpretation of periodontal disease.
Treatment
The treatment of periodontal disease is aimed at controlling the cause of the inflammation, i.e. dental plaque. Conservative or cause-related periodontal therapy consists of removal of plaque and calculus, along with any other remedial procedures required, under general anaesthesia, in combination with daily maintenance of oral hygiene. In other words, the treatment of periodontal disease has two components:
- Maintenance of oral hygiene.
- Professional periodontal therapy.
Maintenance of oral hygiene is performed by the owner and is often called home care. Its effectiveness depends on the motivation and technical ability of the owner and the cooperation of the animal.
Treatment of periodontitis is two stage – periodontal therapy performed under general anaesthesia, and the most important stage is then follow up home care following an oral hygiene program.
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is by definition reversible. Removal or adequate reduction of plaque will restore inflamed gingivae to health. Once clinically healthy gingivae have been achieved, these can be maintained by daily removal or reduction in the accumulation of plaque. In short, the treatment of gingivitis is to restore the inflamed tissues to clinical health and then to maintain clinically healthy gingivae, thus preventing periodontitis. Treatment involves performing a dental scale and polish with the purpose of professional periodontal therapy in the gingivitis patient being to remove dental deposits, mainly calculus (which is not removed by toothbrushing). Once the teeth have been cleaned it remains up to the owner to remove the plaque that re-accumulates on a daily basis.
Treatment of gingivitis relies heavily on owner compliance. It is important to stress to the owner that the disease is reversible and treatment and control may prevent this disease from becoming peridontitis, which is a lot more severe. The owner should receive information on good daily dental home care such as tooth brushing and diet.
Summary for Treatment of Gingivitis:
- Educating the owner to understand the disease process.
- Training and motivating the owner to perform daily home care.
- Instituting a daily home care regimen by the owner – ideally, toothbrushing with a pet toothpaste in conjunction with a dental hygiene product.
- Professional periodontal therapy (supra- and subgingival scaling and polishing) under general anaesthesia to remove dental deposits (plaque and calculus).
- Regular check-ups to ensure that the owner is following recommendations and to boost the owner’s motivation.
Periodontitis
Untreated gingivitis may progress to periodontitis. In most instances in a practice situation, periodontitis is irreversible. It is important to remember that periodontitis is a site-specific disease, i.e. it may affect one or more sites of one or several teeth. The aim of treatment is thus to prevent development of new lesions at other sites and to prevent further tissue destruction at sites which are already affected. Treatment consists of a dental scale and polish and root surface debridement. Teeth with severe periodontitis will need to be extracted and periodontal surgery may be necessary.
Professional periodontal therapy removes dental deposits above and below the gingival margin. It then rests with the owner to ensure that plaque does not reaccumulate. Meticulous supragingival plaque control, by means of daily toothbrushing and adjunctive antiseptics when indicated, will prevent migration of the plaque below the gingival margin. If the subgingival tooth surfaces are kept clean, the sulcular epithelium will reattach.
Summary for Treatment of Periodontitis:
- Educating the owner to understand the disease process.
- Training and motivating the owner to perform daily home care.
- Instituting a daily toothbrushing regimen by the owner.
- Professional periodontal therapy – this includes supra- and subgingival scaling and polishing, rootplaning and extraction of unsalvageable teeth under general anaesthesia.
- Regular check-ups to ensure that the owner is following recommendations and to boost the owner’s motivation.
- Periodontal surgery may be indicated (if the owner has shown the ability to maintain adequate plaque control).
Educate the owner of the disease process and also educate them on good daily dental home care such as tooth brushing and diet. Regular examinations to assess the condition of the teeth are vital and the owner needs to be made aware of this.
Periodontal Pockets
With pocket depths below 5mm, dental scaling and polishing should be performed, and then subgingival curettage and the placement of an antibiotic gel in the pocket may help rejuvenate the periodontal tissues and reduce pocket depth.
With pocket depths greater that 5mm, surgery is needed to either expose the root for treatment or extract. Gingival flaps or bony replacement procedures for infrabony pockets can be used to decrease pocket depths in areas of alveolar bone loss.
| Periodontal Disease Learning Resources | |
|---|---|
 Test your knowledge using flashcard type questions |
Veterinary Dentistry Q&A 11 |
References
Tutt, C., Deeprose, J. and Crossley, D. (2007) BSAVA Manual of Canine and Feline Dentistry (3rd Edition) BSAVA
Merck & Co (2008) The Merck Veterinary Manual Merial
Lobprise, H. (2007) Blackwell's five minute consult clinical companion: small animal dentistry Wiley-Blackwell