Difference between revisions of "Gall Bladder - Anatomy & Physiology"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Fiorecastro (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (38 intermediate revisions by 9 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | <big><center>[[Liver - Anatomy & Physiology|'''BACK TO THE LIVER''']]</center></big> | |
| + | |||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
| − | The | + | The gallbladder stores bile produced in the [[Liver - Anatomy & Physiology|liver]]. Bile is important in the digestion of lipids. |
| + | |||
| + | ==Structure== | ||
| + | |||
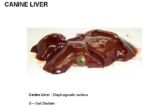
| + | [[Image:Canine Gallbladder Anatomy.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Location of the Canine Gallbladder - Copyright RVC 2008]] | ||
| + | *Lies between the right medial and quadrate lobes of the [[Liver - Anatomy & Physiology|liver]] | ||
| − | + | *Partly attached | |
| − | + | *Partly free | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Function== | ==Function== | ||
| − | + | *Stores bile | |
| + | |||
| + | *Concentrates bile by absorption through the folded mucosal wall | ||
| + | |||
==Innervation== | ==Innervation== | ||
| − | + | *Parasympathetic nerves | |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Histology== | ||
| + | |||
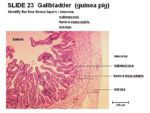
| + | [[Image:Guinea-pig Gallbladder Hsitology.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Histology of the Guinea-pig Gallbladder - Copyright RVC 2008]] | ||
| + | *Highly folded mucosa | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Reduced submucosa | ||
| + | |||
| + | *No lamina muscularis | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Simple columnar epithelium | ||
| + | |||
| + | *No glands | ||
| + | |||
==Species Differences== | ==Species Differences== | ||
'''Equine''' | '''Equine''' | ||
| − | + | *The horse has no gallbladder | |
'''Rodents''' | '''Rodents''' | ||
| − | + | *Rats do not have a gallbladder | |
| − | |||
'''Canine''' | '''Canine''' | ||
| + | *In some dogs, the gallbladder is so deeply embedded it makes contact with the diaphragm and contacts the parietal surface | ||
| − | + | *Thinest layers of tunica muscularis | |
'''Bovine''' | '''Bovine''' | ||
| + | *Thickest layers of tunica muscularis | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Links== | ==Links== | ||
| − | + | [[Liver - gall bladder|Pathology of the Gall Bladder]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 15:20, 10 July 2008
Introduction
The gallbladder stores bile produced in the liver. Bile is important in the digestion of lipids.
Structure
- Lies between the right medial and quadrate lobes of the liver
- Partly attached
- Partly free
Function
- Stores bile
- Concentrates bile by absorption through the folded mucosal wall
Innervation
- Parasympathetic nerves
Histology
- Highly folded mucosa
- Reduced submucosa
- No lamina muscularis
- Simple columnar epithelium
- No glands
Species Differences
Equine
- The horse has no gallbladder
Rodents
- Rats do not have a gallbladder
Canine
- In some dogs, the gallbladder is so deeply embedded it makes contact with the diaphragm and contacts the parietal surface
- Thinest layers of tunica muscularis
Bovine
- Thickest layers of tunica muscularis