Difference between revisions of "Traumatic Reticulitis"
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
| − | Due to their unselective feeding habits, cattle may ingest a variety of foreign bodies. Heavier metallic objects consumed can become lodged in the [[The Reticulum - Anatomy & Physiology|reticulum]], and may penetrate the reticular wall under the influence of the continuous [[The Reticulum - Anatomy & Physiology#Ruminoreticular contraction|reticular movements]] and forces caused by pregnancy and parturition. | + | Due to their unselective feeding habits, cattle may ingest a variety of foreign bodies. Cattle cannot spit out metallic agents (e.g. screws, nails, pieces of wire, bottle tops)once in their mouths, and so ingest them. Heavier metallic objects consumed can become lodged in the [[The Reticulum - Anatomy & Physiology|reticulum]], and may penetrate the reticular wall under the influence of the continuous [[The Reticulum - Anatomy & Physiology#Ruminoreticular contraction|reticular movements]] and forces caused by pregnancy and parturition. |
Pathological changes depend on the direction of penetration; this is usually in an anterior-ventral direction. Pyogenic bacteria escape from the [[The Reticulum - Anatomy & Physiology|reticulum]], causing localised [[Peritonitis|peritonitis]] and local fibrinous adhesions. | Pathological changes depend on the direction of penetration; this is usually in an anterior-ventral direction. Pyogenic bacteria escape from the [[The Reticulum - Anatomy & Physiology|reticulum]], causing localised [[Peritonitis|peritonitis]] and local fibrinous adhesions. | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
Signs are often vague, but adult cattle will show a drop in milk production and fecal output is decreased. The rectal temperature is often mildly increased. The heart rate is often increased, and respiration is usually shallow and rapid. Initially, the cow exhibits abdominal pain with an arched back; and a reluctance to move often with abducted elbows. | Signs are often vague, but adult cattle will show a drop in milk production and fecal output is decreased. The rectal temperature is often mildly increased. The heart rate is often increased, and respiration is usually shallow and rapid. Initially, the cow exhibits abdominal pain with an arched back; and a reluctance to move often with abducted elbows. | ||
Affected animals will also grunt in response to the "bar test". | Affected animals will also grunt in response to the "bar test". | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ====Pathology==== | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Very thick-walled, pus-filled abscesses form around points of penetration, which may be multiple. | |
| + | The foreign object may be found in one of these abscesses, or free in the reticular lumen | ||
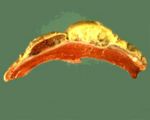
| + | If the pericardium is penetrated it becomes thickened with oedema, and purulent fluid containing fibrin clots accumulates in the sac giving a “bread and butter heart” which is classical traumatic reticulitis. | ||
| − | + | [[Image:traumatic pericarditis.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Traumatic pericarditis (Courtesy of BioMed Image Archive)]] | |
| − | |||
Large abscesses in the dorsal part of the [[Liver - Anatomy & Physiology|liver]] may erode into posterior vena cava to produce thrombosis. | Large abscesses in the dorsal part of the [[Liver - Anatomy & Physiology|liver]] may erode into posterior vena cava to produce thrombosis. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Treatment== | ==Treatment== | ||
Revision as of 16:53, 11 August 2010
| This article is still under construction. |
Description
Due to their unselective feeding habits, cattle may ingest a variety of foreign bodies. Cattle cannot spit out metallic agents (e.g. screws, nails, pieces of wire, bottle tops)once in their mouths, and so ingest them. Heavier metallic objects consumed can become lodged in the reticulum, and may penetrate the reticular wall under the influence of the continuous reticular movements and forces caused by pregnancy and parturition.
Pathological changes depend on the direction of penetration; this is usually in an anterior-ventral direction. Pyogenic bacteria escape from the reticulum, causing localised peritonitis and local fibrinous adhesions. Penetration of the diaphragm and pericardium results in pericarditis. Penetration of the heart itself results in myocarditis and endocarditis. Penetration of the lungs and pleura can occur resulting in pneumonia and pleurisy. Liver and splenic abscesses also occasionally occur following penetration of either organ.
Signalment
More frequently affects adult dairy cows but does also affect beef animals. More comon in cows grazing a pasture where there has been previous building.
Diagnosis
Clinical Signs
Signs are often vague, but adult cattle will show a drop in milk production and fecal output is decreased. The rectal temperature is often mildly increased. The heart rate is often increased, and respiration is usually shallow and rapid. Initially, the cow exhibits abdominal pain with an arched back; and a reluctance to move often with abducted elbows. Affected animals will also grunt in response to the "bar test".
Pathology
Very thick-walled, pus-filled abscesses form around points of penetration, which may be multiple. The foreign object may be found in one of these abscesses, or free in the reticular lumen If the pericardium is penetrated it becomes thickened with oedema, and purulent fluid containing fibrin clots accumulates in the sac giving a “bread and butter heart” which is classical traumatic reticulitis.
Large abscesses in the dorsal part of the liver may erode into posterior vena cava to produce thrombosis.