Difference between revisions of "Pericarditis"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
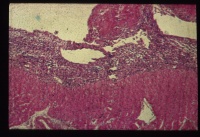
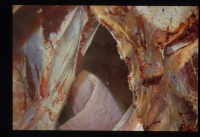
| − | + | [[Image:Pericarditis-histo.jpg|right|thumb|200px|<small><center>'''Pericarditis'''. Courtesy of A. Jefferies</center></small>]] | |
Pericarditis is common in cattle and uncommon in horses and small animals. It usually is caused by an infective agent, causing inflammatory fluid to gather in the pericardial sac. As with non-inflammatory accumulation of fluid in the pericardial sac, the main complication of the condition, as well as severe systemic infection, is the restriction of ventricular movement. Clinical signs seen are therefore those of circulatory failure along with pyrexia and a general depression. | Pericarditis is common in cattle and uncommon in horses and small animals. It usually is caused by an infective agent, causing inflammatory fluid to gather in the pericardial sac. As with non-inflammatory accumulation of fluid in the pericardial sac, the main complication of the condition, as well as severe systemic infection, is the restriction of ventricular movement. Clinical signs seen are therefore those of circulatory failure along with pyrexia and a general depression. | ||
| − | |||
| − | The spread of the infectious agent may be haematogenous, | + | The spread of the infectious agent may be haematogenous, followed by generalised infection. This is most often seen in cattle and pigs. It can also occur as an extension of infection from surrounding tissues; for example from the lungs, pleura, mediastinum or rarely, extension of infection from myocardium. The most common cause of the condition in cattle is from traumatic penetration of the pericardium from foreign bodies from the oesophagus or reticulum; [[Traumatic_Reticulitis|traumatic reticulo-peritonitis]]. Fractured ribs; e.g. road trafic accidents (RTAs) in small animals and equine sport injuries can also cause the condition. |
Pericarditis can be subdivided into two main categories; fibrinous pericarditis and suppurative pericarditis. | Pericarditis can be subdivided into two main categories; fibrinous pericarditis and suppurative pericarditis. | ||
| − | + | == Fibrinous Pericarditis == | |
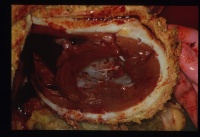
| − | + | [[Image:Fibrinous pericarditis.jpg|right|thumb|200px|<small><center>'''Fibrinous pericarditis'''. Courtesy of A. Jefferies</center></small>]] | |
| − | + | This is the most common form of pericarditis. Grey strands of fibrin cover the epicardium and a small amount of fluid only, will accumulate. Close apposition of the parietal and visceral pericardium layers allows adhesion formation within approximately 7-10 days. Such adhesions may resolve with little residual pathology or may become focal or diffuse adhesive pericarditis lesions. Such little fluid accumulation will not compromise the function of the heart. This condition is most commonly caused by the haematogenous spread of organisms. Common bacteria include [[:Category:Pasteurella and Mannheimia species|''Pasturella'' species]], [[:Category:Haemophilus species|''Haemophilus ''species]] and [[:Category:Streptococcus species|''Streptococcus'' species]]. | |
| − | == Fibrinous | ||
| − | + | Fibrinous pericarditis produces a crackling sound on auscultation. | |
| − | + | == Suppurative Pericarditis == | |
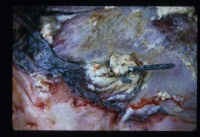
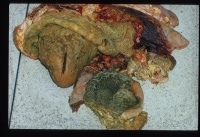
| + | [[Image:traumatic pericarditis 2.jpg|right|thumb|200px|<small><center>'''Traumatic pericarditis'''. Courtesy of A. Jefferies</center></small>]] | ||
| + | [[Image:traumatic reticulitis.jpg|right|thumb|200px|<small><center>'''Traumatic pericarditis'''. Courtesy of A. Jefferies</center></small>]] | ||
| + | [[Image:Traumatic pericarditis 4.jpg|right|thumb|200px|<small><center>'''Traumatic pericarditis'''. Courtesy of A. Jefferies</center></small>]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | Purulent pericarditis indicates the presence of pyogenic organisms e.g. [[:Category:Staphylococcus species|''Staphylococcal'' species]]. It is most commonly seen in cattle as a result of traumatic penetration of the pericardial sac with a sharp metallic object or ''wire''. This is [[Traumatic_Reticulitis|Traumatic reticulo-peritonitis]] causing [[Traumatic Pericarditis]]. It is most commonly due to the indiscriminate feeding of cattle. Objects become lodged in the rumen and are then forced by ruminal contractions into the reticulum and cranially into the diaphragm and pericardium. They may also penetrate the liver. Large amount of purulent material, up to 4 litres, can accumulate in the pericardium, causing severe constriction of the ventricles. | |
| − | + | Death usually occurs before organisation of the exudate forming a constrictive pericarditis. Toxaemia becomes apparent in the early stages of the condition. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Death usually occurs before organisation of the exudate | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Clinical Signs == | == Clinical Signs == | ||
| − | Signs include signs of right sided heart failure such as jugular pulses, ascites and hepatomegaly. The | + | Signs include signs of [[Heart Failure, Right-Sided|right sided heart failure]] such as jugular pulses, ascites and hepatomegaly. The physical examination will reveal muffled heart sounds and variable pulse quality. In cases of 'wire' the cow may elicit a pain response upon pressure being exerted in between the front limbs. If the pericarditis is of an infectious cause, then pyrexia will also be observed. |
| − | + | == Diagnosis == | |
| + | Clinical signs, animal species and history are very suggestive of the condition. This is usually diagnostic in cattle. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
In small animals or horses, echocardiography is usually performed, along with pericardiocentesis for a definitive diagnosis. | In small animals or horses, echocardiography is usually performed, along with pericardiocentesis for a definitive diagnosis. | ||
| + | == Treatment and Control == | ||
| + | Drainage of the pericardium can be attempted and systemic [[antibiotics]] can be administered for cases of suppurative disease. Where economically viable, the wire can be removed from the cow by ruminal surgery, where the veterinarian will perform a rumenotomy and then reach into the reticulum and manually remove the wire. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Most farmers will tend to prefer the option of slaughtering the animal on welfare grounds. | Most farmers will tend to prefer the option of slaughtering the animal on welfare grounds. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Prognosis == | == Prognosis == | ||
| − | The condition can resolve without any further clinical significance. As described above, death is a common outcome in the suppurative form of the disease. Adhesions may occur, due to organisation of fibrin, leading to a 'bread and butter' appearance. As the condition worsens, if not treated, gradual constriction may | + | The condition can resolve without any further clinical significance. As described above, death is a common outcome in the suppurative form of the disease. Adhesions may occur, due to organisation of fibrin, leading to a 'bread and butter' appearance. As the condition worsens, if not treated, gradual constriction may end up causing [[Cardiac Tamponade|cardiac tamponade]]. |
| + | ==Test yourself with the Pericardial Pathology Flashcards== | ||
| + | [[Pericardial Pathology Flashcards]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | {{review}} | ||
[[Category:Pericardial_Pathology]] | [[Category:Pericardial_Pathology]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Cardiovascular Diseases - Cattle]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Cardiac Diseases - Dog]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Cardiac Diseases - Cat]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Cardiovascular Diseases - Horse]] | ||
[[Category:Cardiovascular System - Inflammatory Pathology]] | [[Category:Cardiovascular System - Inflammatory Pathology]] | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Expert_Review]] |
Revision as of 11:44, 29 April 2011
Introduction
Pericarditis is common in cattle and uncommon in horses and small animals. It usually is caused by an infective agent, causing inflammatory fluid to gather in the pericardial sac. As with non-inflammatory accumulation of fluid in the pericardial sac, the main complication of the condition, as well as severe systemic infection, is the restriction of ventricular movement. Clinical signs seen are therefore those of circulatory failure along with pyrexia and a general depression.
The spread of the infectious agent may be haematogenous, followed by generalised infection. This is most often seen in cattle and pigs. It can also occur as an extension of infection from surrounding tissues; for example from the lungs, pleura, mediastinum or rarely, extension of infection from myocardium. The most common cause of the condition in cattle is from traumatic penetration of the pericardium from foreign bodies from the oesophagus or reticulum; traumatic reticulo-peritonitis. Fractured ribs; e.g. road trafic accidents (RTAs) in small animals and equine sport injuries can also cause the condition.
Pericarditis can be subdivided into two main categories; fibrinous pericarditis and suppurative pericarditis.
Fibrinous Pericarditis
This is the most common form of pericarditis. Grey strands of fibrin cover the epicardium and a small amount of fluid only, will accumulate. Close apposition of the parietal and visceral pericardium layers allows adhesion formation within approximately 7-10 days. Such adhesions may resolve with little residual pathology or may become focal or diffuse adhesive pericarditis lesions. Such little fluid accumulation will not compromise the function of the heart. This condition is most commonly caused by the haematogenous spread of organisms. Common bacteria include Pasturella species, Haemophilus species and Streptococcus species.
Fibrinous pericarditis produces a crackling sound on auscultation.
Suppurative Pericarditis
Purulent pericarditis indicates the presence of pyogenic organisms e.g. Staphylococcal species. It is most commonly seen in cattle as a result of traumatic penetration of the pericardial sac with a sharp metallic object or wire. This is Traumatic reticulo-peritonitis causing Traumatic Pericarditis. It is most commonly due to the indiscriminate feeding of cattle. Objects become lodged in the rumen and are then forced by ruminal contractions into the reticulum and cranially into the diaphragm and pericardium. They may also penetrate the liver. Large amount of purulent material, up to 4 litres, can accumulate in the pericardium, causing severe constriction of the ventricles.
Death usually occurs before organisation of the exudate forming a constrictive pericarditis. Toxaemia becomes apparent in the early stages of the condition.
Clinical Signs
Signs include signs of right sided heart failure such as jugular pulses, ascites and hepatomegaly. The physical examination will reveal muffled heart sounds and variable pulse quality. In cases of 'wire' the cow may elicit a pain response upon pressure being exerted in between the front limbs. If the pericarditis is of an infectious cause, then pyrexia will also be observed.
Diagnosis
Clinical signs, animal species and history are very suggestive of the condition. This is usually diagnostic in cattle.
In small animals or horses, echocardiography is usually performed, along with pericardiocentesis for a definitive diagnosis.
Treatment and Control
Drainage of the pericardium can be attempted and systemic antibiotics can be administered for cases of suppurative disease. Where economically viable, the wire can be removed from the cow by ruminal surgery, where the veterinarian will perform a rumenotomy and then reach into the reticulum and manually remove the wire.
Most farmers will tend to prefer the option of slaughtering the animal on welfare grounds.
Prognosis
The condition can resolve without any further clinical significance. As described above, death is a common outcome in the suppurative form of the disease. Adhesions may occur, due to organisation of fibrin, leading to a 'bread and butter' appearance. As the condition worsens, if not treated, gradual constriction may end up causing cardiac tamponade.
Test yourself with the Pericardial Pathology Flashcards
Pericardial Pathology Flashcards
| This article has been peer reviewed but is awaiting expert review. If you would like to help with this, please see more information about expert reviewing. |