Difference between revisions of "Tendons - Horse Anatomy"
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
'''''Superficial Digital Flexor Tendon (SDFT)''''' | '''''Superficial Digital Flexor Tendon (SDFT)''''' | ||
| − | *'''Origin''': Superficial digital flexor muscle on the medial humeral epicondlye | + | *'''Origin''': Superficial digital flexor muscle on the medial [[Bones and Cartilages - Horse Anatomy#Humerus|humeral]] epicondlye |
*'''Insertion''': [[Phalanges - Horse Anatomy#Middle Phalanx|Middle phalanx]] | *'''Insertion''': [[Phalanges - Horse Anatomy#Middle Phalanx|Middle phalanx]] | ||
*'''Action''': Flexes the proximal and middle phalangeal joints, stabilises [[Joints and Ligaments - Horse Anatomy#Thoracic Limb|metacarpophalangeal]] joint | *'''Action''': Flexes the proximal and middle phalangeal joints, stabilises [[Joints and Ligaments - Horse Anatomy#Thoracic Limb|metacarpophalangeal]] joint | ||
| − | The SDFT arises from the superficial digital flexor muscle at the level of the [[Joints and Ligaments - Horse Anatomy#Thoracic Limb|carpus]]. At this level, the tendon combines with the accessory ligament ('''superior check ligament'''). The tendon passes distally on the caudal aspect of the limb, running through the '''carpal canal''' to the metacarpus. The SDFT and DDFT run within a synovial structure termed the '''carpal sheath'''. | + | The SDFT arises from the superficial digital flexor muscle at the level of the [[Joints and Ligaments - Horse Anatomy#Thoracic Limb|carpus]]. At this level, the tendon combines with the accessory ligament ('''superior check ligament'''). The tendon passes distally on the caudal aspect of the limb, running through the '''carpal canal''' to the [[Bones and Cartilages - Horse Anatomy#Metacarpals and Metatarsals|metacarpus]]. The SDFT and DDFT run within a synovial structure termed the '''carpal sheath'''. |
Just proximal to the [[Joints and Ligaments - Horse Anatomy#Thoracic Limb|metacarpophalangeal]] joint, the SDFT forms a ring-like structure which wraps around the DDFT. This structure is known as the '''manica flexoria'''. | Just proximal to the [[Joints and Ligaments - Horse Anatomy#Thoracic Limb|metacarpophalangeal]] joint, the SDFT forms a ring-like structure which wraps around the DDFT. This structure is known as the '''manica flexoria'''. | ||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
'''''Deep Digital Flexor Tendon (DDFT)''''' | '''''Deep Digital Flexor Tendon (DDFT)''''' | ||
| − | *'''Origin''': Deep digital flexor muscle on the medial humeral epicondyle, radius and ulna | + | *'''Origin''': Deep digital flexor muscle on the medial [[Bones and Cartilages - Horse Anatomy#Humerus|humeral]] epicondyle, [[Bones and Cartilages - Horse Anatomy#Radius and Ulna|radius and ulna]] |
*'''Insertion''': [[Phalanges - Horse Anatomy#Distal Phalanx|Distal phalanx]]. | *'''Insertion''': [[Phalanges - Horse Anatomy#Distal Phalanx|Distal phalanx]]. | ||
*'''Action''': Flexes the [[Phalanges - Horse Anatomy#Distal Phalanx|distal phalanx]]. | *'''Action''': Flexes the [[Phalanges - Horse Anatomy#Distal Phalanx|distal phalanx]]. | ||
| − | The deep digital flexor tendon arises as three bellies from its origin on the medial humeral epicondyle, fusing to form a common tendon just proximal to the [[Joints and Ligaments - Horse Anatomy#Thoracic Limb|carpus]] on the caudal aspect of the limb. The single tendon passes distally, enclosed in the '''carpal sheath''', through the '''carpal canal'''. In the mid-metacarpal region, the tendon is enforced by an accessory ligament ('''inferior check ligament'''). At the [[Joints and Ligaments - Horse Anatomy#Thoracic Limb|metacarpophalangeal]] (fetlock) joint, the DDFT passes though the '''manica flexoria''' and over the sesamoid groove. In the mid –region of the [[Phalanges - Horse Anatomy#Proximal Phalanx|proximal phalanx]], the DDFT runs between the branches of the SDFT and over the flexor cortex of the [[Phalanges - Horse Anatomy#Distal Sesamoid (Navicular) Bone|distal sesamoid]] ('''navicular''') bone to insert on the flexor cortex of the [[Phalanges - Horse Anatomy#Distal Phalanx|distal phalanx]]. | + | The deep digital flexor tendon arises as three bellies from its origin on the medial [[Bones and Cartilages - Horse Anatomy#Humerus|humeral]] epicondyle, fusing to form a common tendon just proximal to the [[Joints and Ligaments - Horse Anatomy#Thoracic Limb|carpus]] on the caudal aspect of the limb. The single tendon passes distally, enclosed in the '''carpal sheath''', through the '''carpal canal'''. In the mid-metacarpal region, the tendon is enforced by an accessory ligament ('''inferior check ligament'''). At the [[Joints and Ligaments - Horse Anatomy#Thoracic Limb|metacarpophalangeal]] (fetlock) joint, the DDFT passes though the '''manica flexoria''' and over the sesamoid groove. In the mid –region of the [[Phalanges - Horse Anatomy#Proximal Phalanx|proximal phalanx]], the DDFT runs between the branches of the SDFT and over the flexor cortex of the [[Phalanges - Horse Anatomy#Distal Sesamoid (Navicular) Bone|distal sesamoid]] ('''navicular''') bone to insert on the flexor cortex of the [[Phalanges - Horse Anatomy#Distal Phalanx|distal phalanx]]. |
The '''navicular bursa''' is the space formed between the DDFT and the [[Phalanges - Horse Anatomy#Distal Sesamoid (Navicular) Bone|distal sesamoid]] ('''navicular''') bone, which is filled with synovial fluid. It extends beyond the borders of the distal sesamoid bone proximally, distally and laterally. | The '''navicular bursa''' is the space formed between the DDFT and the [[Phalanges - Horse Anatomy#Distal Sesamoid (Navicular) Bone|distal sesamoid]] ('''navicular''') bone, which is filled with synovial fluid. It extends beyond the borders of the distal sesamoid bone proximally, distally and laterally. | ||
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
'''''Suspensory Ligament (SL)''''' | '''''Suspensory Ligament (SL)''''' | ||
| − | *'''Origin''': Proximal region of third metacarpal (cannon bone) and distal row of carpal bones | + | *'''Origin''': Proximal region of [[Bones and Cartilages - Horse Anatomy#Metacarpals and Metatarsals|third metacarpal]](cannon bone) and distal row of [[Bones and Cartilages - Horse Anatomy#Carpal Bones|carpal bones]] |
*'''Insertion''': Proximal sesamoids, joins common digital extensor tendon | *'''Insertion''': Proximal sesamoids, joins common digital extensor tendon | ||
*'''Action''': Prevents fetlock hyperextension and limits palmar flexion | *'''Action''': Prevents fetlock hyperextension and limits palmar flexion | ||
| − | The suspensory ligament (middle interosseous muscle) is an entirely tendinous structure. The SL originates on the proximal aspect of the third metacarpal (cannon) and distal carpal bones. It lies within the groove between the second and fourth | + | The suspensory ligament (middle interosseous muscle) is an entirely tendinous structure. The SL originates on the proximal aspect of the [[Bones and Cartilages - Horse Anatomy#Metacarpals and Metatarsals|third metacarpal]](cannon) and distal [[Bones and Cartilages - Horse Anatomy#Carpal Bones|carpal bones]]. It lies within the groove between the second and fourth [[Bones and Cartilages - Horse Anatomy#Metacarpals and Metatarsals|metacarpals]](splint bones), deep to the SDFT and DDFT. Running distally, it bifurcates into two extensor branches which insert on the proximal sesamoid bones. Each branch extends laterally and medially, either side of the [[Joints and Ligaments - Horse Anatomy#Thoracic Limb|metacarpophalangeal]] (feltlock) joint, to join the common digital extensor tendon. The major function of the SL is as part of the '''suspensory apparatus'''. It provides support to the [[Joints and Ligaments - Horse Anatomy#Thoracic Limb|metacarpophalangeal]](fetlock) joint by preventing hyperextension and also limits palmar flexion. |
[[Image:Equine thoracic limb tendons ML.jpg|200px|thumb|right|'''Tendons of the thoracic limb, mediolateral view''']] | [[Image:Equine thoracic limb tendons ML.jpg|200px|thumb|right|'''Tendons of the thoracic limb, mediolateral view''']] | ||
Revision as of 08:17, 31 October 2012
| This article is still under construction. |
Introduction
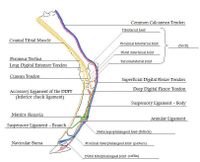
Tendons are composed of bundles of collagen, predominantly type I, surrounding parallel rows of fibroblasts known as tenocytes. Tenocytes synthesize the collagen fibres that they surround. Many collagen fibres make up a fascicle. Within the fascicle, collagen fibres are parallel with a ‘crimp’ waveform. This arrangement allows lateral cohesion between fibres, preventing slippage between fibres or fibrils. The ‘crimp’ straightens when the tendon is loaded and then recoils when the load is removed; this allows the elastic function of tendons. There are no muscles in the equine digit, instead there are the tendons of insertion of the two extensor muscles and the two flexor muscles of the digit.
Thoracic Limb
Extensors
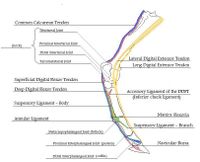
Common Digital Extensor Tendon
- Origin: Common digital extensor muscle on the lateral humeral epicondyle
- Insertion: Extensor process of distal phalanx
- Action: Extends carpus and digit
The common digital extensor tendon passes over the dorsolateral aspect of the carpus , continuing distally over the dorsal metacarpus. The branches of the interosseous muscle (suspensory ligament) join the common digital extensor tendon before its insertion on the extensor process of the distal phalanx. A minor branch inserts on the middle phalanx and some fibres insert on the hoof cartilages. The common digital extensor tendon is surrounded by the extensor retinaculum and a protective synovial sheath. The tendon sheath begins approximately 10cm proximal to the carpus, extending distally to the level of the metacarpus.
Lateral Digital Extensor Tendon
- Origin: Lateral digital extensor muscle on the lateral humeral epicondyle
- Insertion: Dorsolateral aspect of proximal phalanx
- Action: Extends the carpus and metacarpophalangeal joint
The lateral digital extensor muscle arises from the lateral humeral epicondyle and forms the lateral digital extensor tendon on the lateral aspect of the antebrachium; caudal to the common digital extensor tendon. The tendon is enclosed within a synovial sheath as it extends distally over the metacarpus to insert on the dorsolateral aspect of the proximal phalanx.
Flexors
The digital flexor tendons are surrounded by synovial sheaths, which serve a protective function; allowing frictionless movement as the tendons traverse the bony prominences of the carpus and metacarpophalangeal (fetlock) joint.
- Carpal Sheath
Arises approximately 10cm proximal to the carpus and extends to mid-metacarpal region.
- Digital Sheath
Arises at the distal metacarpus, approximately 5cm proximal to the metacarpophalangeal joint and extends to the middle of the middle phalanx.
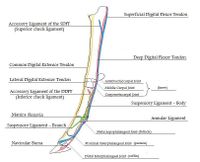
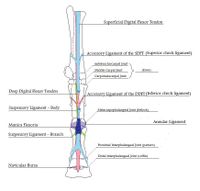
Superficial Digital Flexor Tendon (SDFT)
- Origin: Superficial digital flexor muscle on the medial humeral epicondlye
- Insertion: Middle phalanx
- Action: Flexes the proximal and middle phalangeal joints, stabilises metacarpophalangeal joint
The SDFT arises from the superficial digital flexor muscle at the level of the carpus. At this level, the tendon combines with the accessory ligament (superior check ligament). The tendon passes distally on the caudal aspect of the limb, running through the carpal canal to the metacarpus. The SDFT and DDFT run within a synovial structure termed the carpal sheath. Just proximal to the metacarpophalangeal joint, the SDFT forms a ring-like structure which wraps around the DDFT. This structure is known as the manica flexoria.
From the distal metacarpus to the level of the middle phalanx, the SDFT and DDFT are enclosed by another synovial structure, the digital sheath. The SDFT divides into two branches at the distal end of the proximal phalanx. The branches insert on the lateral and medial eminences of the middle phalanx, a minority of fibres also insert on the lateral aspect of the proximal phalanx.
Deep Digital Flexor Tendon (DDFT)
- Origin: Deep digital flexor muscle on the medial humeral epicondyle, radius and ulna
- Insertion: Distal phalanx.
- Action: Flexes the distal phalanx.
The deep digital flexor tendon arises as three bellies from its origin on the medial humeral epicondyle, fusing to form a common tendon just proximal to the carpus on the caudal aspect of the limb. The single tendon passes distally, enclosed in the carpal sheath, through the carpal canal. In the mid-metacarpal region, the tendon is enforced by an accessory ligament (inferior check ligament). At the metacarpophalangeal (fetlock) joint, the DDFT passes though the manica flexoria and over the sesamoid groove. In the mid –region of the proximal phalanx, the DDFT runs between the branches of the SDFT and over the flexor cortex of the distal sesamoid (navicular) bone to insert on the flexor cortex of the distal phalanx.
The navicular bursa is the space formed between the DDFT and the distal sesamoid (navicular) bone, which is filled with synovial fluid. It extends beyond the borders of the distal sesamoid bone proximally, distally and laterally. The distal parts of the superficial and deep digital flexor tendons are supported by three annular ligaments:
- Palmar annular ligament
- Proximal digital annular ligament
- Distal digital annular ligament
Suspensory Ligament (SL)
- Origin: Proximal region of third metacarpal(cannon bone) and distal row of carpal bones
- Insertion: Proximal sesamoids, joins common digital extensor tendon
- Action: Prevents fetlock hyperextension and limits palmar flexion
The suspensory ligament (middle interosseous muscle) is an entirely tendinous structure. The SL originates on the proximal aspect of the third metacarpal(cannon) and distal carpal bones. It lies within the groove between the second and fourth metacarpals(splint bones), deep to the SDFT and DDFT. Running distally, it bifurcates into two extensor branches which insert on the proximal sesamoid bones. Each branch extends laterally and medially, either side of the metacarpophalangeal (feltlock) joint, to join the common digital extensor tendon. The major function of the SL is as part of the suspensory apparatus. It provides support to the metacarpophalangeal(fetlock) joint by preventing hyperextension and also limits palmar flexion.
Pelvic Limb
Extensors
Long Digital Extensor Tendon
- Origin: Long digital extensor muscle proximal and dorsolateral to the tarsus (hock)
- Insertion: Extensor process of distal phalanx
- Action: Extends the digit, flexes the tarsus
The long digital extensor tendon extends distally on the dorsolateral aspect of the tarsus and metatarsus , surrounded by a synovial sheath from mid-tarsus to 3-4cm distal to the tarsus . The branches of the interosseous muscle (suspensory ligament) join this tendon before its insertion on the extensor process of the distal phalanx. The long digital extensor tendon is joined by the lateral digital extensor tendon in the proximal metatarsal region.
Lateral Digital Extensor Tendon
- Origin: Lateral digital extensor muscle proximal and lateral to the tarsus (hock)
- Insertion: Dorsal proximal phalanx
- Action: Aids long digital extensor in digit extension and tarsal flexion
The lateral digital extensor tendon passes over the lateral aspect of the hock , held in place by the extensor retinaculum and surrounded by a protective synovial sheath. It joins the long digital extensor tendon in the proximal metatarsal region.
Flexors
Cunean Tendon
- Origin: Cranial tibial muscle in the distal tibia/proximal talus region
- Insertion: Medially on the fused first and second tarsal bones
- Action: Aids tarsal flexion
In the horse, the medial insertion of the cranial tibial muscle (tibialis cranialis) is known as the cunean tendon. There is an associated synovial fluid-filled space known as the cunean bursa, which is also species specific.
Common Calcaneal Tendon
- Origin: Caudal to the stifle joint
- Insertion: Calcanean tuberosity
- Action of components:
- Biceps femoris: Extends the hip , abducts the limb, extends the stifle , flexes the stifle (via caudal aspect) and extends the hock
- Abductor cruris caudalis: Abducts proximal limb and flexes the stifle
- Semitendinosus: Extends the hip , adducts and draws back the limb, extends the stifle and hock
- Semimembranosus: Extends the hip , adducts and draws back the limb, rotates limb inward, extends the stifle and hock
- Gastrocnemius: Flexes the stifle and extends the hock
The common calcaneal tendon is the continuation of the ‘hamstring’ group of muscles (biceps femoris, abductor cruris caudalis, semitendinosus, semimembranosus, gastrocnemius and SDFT) on the caudal aspect of the proximal limb.
The synovial fluid-filled calcanean bursa lies between the SDFT and the calcanean tuberosity.
Peroneus Tertius
- Origin: Extensor fossa of femur
- Insertion: Dorsal insertion on the proximal region of the third metatarsal (cannon) and third tarsal bones. Lateral insertion on the calcaneus and fourth tarsal bone (lateral splint)
- Action: Passively flexes the tarsus when the stifle is flexed
The peroneus tertius is an entirely tendinous structure in the horse, forming an important component of the reciprocal apparatus . It acts to passively flex the tarsus when the stifle is flexed. The tendon forms a loop, through which the tendon of the tibialis cranialis passes. It then bifurcates at the level of the talus into dorsal and lateral branches. The dorsal branch passes deep to the cunean tendon to insert on the third metatarsal (cannon) and third tarsal bones. The lateral branch extends distally, deep to the long digital extensor tendon and runs laterally distal to the lateral ridge of the trochlea of the talus. This lateral branch then bifurcates to insert on the calcaneus and fourth tarsal (splint) bone.
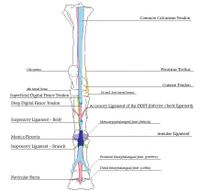
Superficial Digital Flexor Tendon
- Origin: Proximal/mid-tibia
- Insertion: Calcanean tuberosity and middle phalanx
- Action: Extends the digit, assists in extending the hock and flexing the stifle as part of the reciprocal apparatus
The superficial digital flexor tendon is a major component of the common calcaneal tendon, which forms part of the reciprocal apparatus. The SDFT arises from the superficial digital flexor muscle in the proximal/mid-tibial region and passes around the gastrocnemius tendon caudally. At the point of the hock, the SDFT widens to form a cap over the calcanean tuberosity. The calcanean bursa is a synovial fluid-filled space formed between the calcanean tuberosity and the SDFT. Distal to the calcaneus, the SDFT continues as arranged in the thoracic limb to its point of insertion on the middle phalanx. In contrast to the thoracic limb, there is no accessory ligament of the SDFT in the pelvic limb.
Deep Digital Flexor Tendon (DDFT)
- Origin: Deep digital flexor muscle, distal to the tarsus
- Insertion: Flexor cortex of distal phalanx
- Action: Flexes the distal phalanx
The DDFT runs on the plantar aspect of the metatarsus distally, over the distal sesamoid (navicular bone). Its passage over the navicular bone is facilitated by the synovial fluid-filled navicular bursa before inserting on the flexor cortex of the distal phalanx. The accessory (check) ligament connects the DDFT to the third metatarsal. This forms part of the stay apparatus by removing tension from the main body of the DDFT.
Suspensory Ligament
- Origin: Third metatarsal (cannon) and distal tarsal bones
- Insertion: Proximal sesamoids, joins long digital extensor tendon
- Action: Prevents fetlock hyperextension and limits plantar flexion
Originating from the proximal aspect of the third metatarsal (cannon) and distal tarsal bones, the SL of the pelvic limb is relatively thinner and longer than that of the forelimb. It lies within the metatarsal groove deep to the DDFT. Continuing distally it bifurcates into two extensor branches, as in the thoracic limb, which insert on the proximal sesamoid bones. Identical to in the thoracic limb, medial and lateral branches then join the long digital extensor tendon.
References
- Baxter, G.M., Manual of Equine Lameness (2011), Wiley-Blackwell
- Baxter, G.M., Adams, Adams and Stashak’s Lameness in Horses, 6th Edition (2011), Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins
- Konig, H.E., Liebich, H.G. Veterinary Anatomy of Domestic Mammals: Textbook and Colour Atlas (2009), Schattauer
- Pasquini, C, Spurgeon, T.L., An Anatomy of Domestic Animals: A Systemic and Regional Approach, 10th Edition (2003), Bowker