Difference between revisions of "Soft Palate"
(→Avian) |
|||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
{{OpenPages}} | {{OpenPages}} | ||
[[Category:Oral Cavity - Anatomy & Physiology]] | [[Category:Oral Cavity - Anatomy & Physiology]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 16:44, 31 August 2014
Introduction
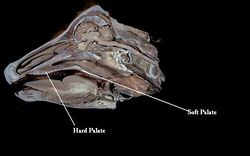
The soft palate (velum palatine) is located caudally to the hard palate and is composed of muscle. It is involved in tasting food and in deglutition.
Structure and Function
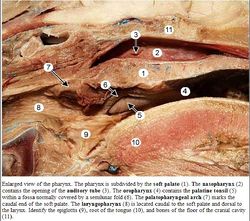
The soft palate is made of striated palatine muscle and has very folded mucosa. It contacts the epiglottis caudally.
Musculature and Innervation
The soft palate transmits sensation and taste via the glossopharyngeal (CN IX) nerve.
Palatine muscle
The origin of the palatine muscle is the hard palate transeverse ridges and the insertion site is the soft palate. The muscle shortens the palate and recieves major innervation from the vagus nerve (CN X) and minor innervation from the glossopgaryngeal nerve (CN IX).
Tensor velli palatini muscle
The origin of the tensor velli palatini muscle is near the tympanic bulla on the temporal bone. The insertion site is the lateral aponeurosis. It tenses the soft palate.
Levator velli palatini muscle
The origin of the levator velli palatini muscle is near the tympanic bulla on the temporal bone. The insertion site is the lateral aponeurosis. It raises the soft palate and recieves major innervation from the vagus nerve (CN X) and minor from the glossopgaryngeal nerve (CN IX).
Palatopharyngeus muscle
The palatopharyngeus muscle closes the palatopharyngeal arch, and therefore lifts the soft palate. It recieves major innervation from the vagus nerve (CN X) and minor innervation from the glossopgaryngeal nerve (CN IX).
Histology
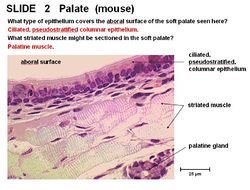
The soft palate contains respiratory mucosa - ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium on the aboral surface. There is stratified squamous epithelium on the oral surface. The soft palate also contains palatine salivary glands.
Species Differences
Porcine
The soft palate does not contact the epiglottis as the porcine soft palate is raised higher in the oral cavity than in other species.
Equine
The tight laryngeal cuff around the laryngeal entrance, and therefore the soft palate cannot be raised for long periods of time and thus horses are nasal breathers. Laryngeal cuffing prevents vomiting.
Canine
As brachiocephalic breeds have a shortened skull length, the soft palate can often obstruct air flow into the larynx causing breathing difficulties.
Avian
Birds lack a soft palate.
| Soft Palate Learning Resources | |
|---|---|
 Test your knowledge using flashcard type questions |
Soft Palate Anatomy & Physiology Flashcards Facial muscle |
 Selection of relevant PowerPoint tutorials |
Histology of the oral cavity - part 1 features the soft palate |
Error in widget FBRecommend: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt6979cb2b6872e9_41088018 Error in widget google+: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt6979cb2b7a4ce8_54567264 Error in widget TwitterTweet: unable to write file /var/www/wikivet.net/extensions/Widgets/compiled_templates/wrt6979cb2b8b5fc7_10562983
|
| WikiVet® Introduction - Help WikiVet - Report a Problem |