Intestinal Arterial Thromboembolism
Revision as of 15:23, 16 December 2010 by Bara (talk | contribs) (Text replace - "Category:Intestinal Pathology - Dog" to "Category:Intestinal Diseases - Dog")
- Non-strangulation infarction.
- There is often a functional obstruction at point of infarction.
- Relatively rare as the bowel has a good anastomosing blood supply.
Horses
- E.g. Strongylus vulgaris larvae migrating in cranial mesenteric artery in horse
- Cause arteritis with thickening of wall
- Due to fibrin and debris deposition and hypersensitivity reaction
- Leads to vasoconstriction
- May occlude lumen and encourage thromboemboli.
- Can cause ischaemic necrosis of a segment of small intestine
- Is less common now that Strongylus vulgaris infections are declining.
- Cause arteritis with thickening of wall
- E.g. equine salmonellosis.
Small Animals
- Especially dogs
- Road traffic accidents produce and infact in the gut.
- Renal disease also causes infarction.
- Particularly nephrotic syndrome.
- Anticoagulant proteins are lost in the urine, leading to a prothrombic state in the ciruclation.
Pathology
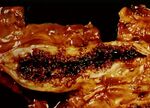
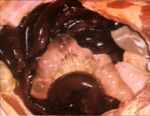
- Similar to that caused by venous congestion.
- See sharply delineated dark areas in bowel that are flaccid with loss of tone.
- These become necrotic followed later by peritonitis.