Host invasion by microorganisms
Introduction
Infection is a primary cause of disease. Three pathways of infection are identified: bacterial, viral, and parasitic. In all three cases, microorganisms can display similar characteristics. They can manifest as primary (obligate) pathogens or secondary (opportunistic) pathogens, the former of which always corresponds to disease, and the latter of which depends on prerequisites being fulfilled before causing disease. As such, secondary pathogens can be found in healthy animals, but they lie in wait until a primary cause compromises the immune system and then manifest symptoms. Secondary pathogens can even masquerade as commensal organisms, or those which operate in harmony with the animal, until they become pathogenic.
Microorganisms can enter the body by three routes: contact (typically dermatological infection), aerosol (typically respiratory infection), or orofecal (typically enteric infection). Infection can be either exogenous (via entry to epithelial surfaces) or endogenous (intracellular, extracellular, or vesicular).
Viruses
Structure
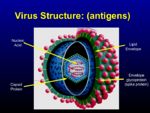
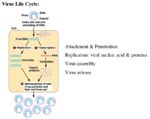
Viruses are very simple structures that do not carry any cellular machinery of their own. They depend on host cells to replicate and flourish. As such, their structure is streamlined, containing only:
- Genetic material, which consists solely of viral RNA
- Capsid proteins surrounding the RNA
- A lipid envelope
- Envelope glycoproteins (or spike proteins)
All of these elements can be recognized by the host as foreign material, and will provoke an immune response. Viruses have an advantage if they are able to penetrate host cell walls in that they are then capable of masquerading as host cells. The immune system must then counter by killing off host cells it recognizes as infected.