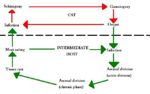
Tissue cyst-forming coccidia
| This article is still under construction. |
|
|
Toxoplasma
- 1 major pathogenic species called Toxoplasma gondii
- Causes disease in a wide range of animal species including humans
- Important cause of abortion in sheep
- Zoonotic
- Can cause abortion
- Can cause congenitally aquired defects
- Forms a sporulated oocyst which is only 10μm
- Contains 2 sporocysts with 4 sporozoites
- Transmission through ingesting the intermediate host or via the faecal-oral route
Life Cycle
- Complex
- Usually indirect
- Gametogeny (sexual stage) is host specific for felids
- Any warm blooded animal can act as a facultative intermediate host
- Asexual reproduction occurs in the intermediate host forming tissue cysts
- Intermediate host swallows sporulated oocysts or tissue cysts
- Can be transferred between intermediate hosts by carnivorism
Toxoplasma can cause acute interstitial pancreatitis in systemic toxoplasmosis
Sarcocystis
- Most infections are asymptomatic
- Heavy infections are causes of chronic wasting in large animals, hide sondemnation and downgrading of carcasses
- Sarcocystis should be differentiated from other tissue-cyst forming coccidia
- There are many species of Sarcocystis
- Sporulated oocyst has 2 sporocysts containing 4 sporozoites
- Naked oocyst usually seen in faeces as the oocyst wall is very delicate
- Indirect life cycle
- Life cycle alternates between the final and the obligatory intermediate host
- Only one final and one intermediate host
Neospora
- 2 main species
- Neospora caninum in the dog
- Neospora hughesi in the horse
- Sporulated oocysts measuring just 10μm
- Oocyst contains 2 sporocysts with 4 sporozoites
- Route of transmission not fully understood
- Often misdiagnosed as Toxoplasma gondii
- Sarcocystis cysts have thicker walls
- Infection diagnosed by IFAT, ELISA or PCR
- Identification of lesions and organisms in tissue using immunohistochemical staining
- Eliminate other causes of abortion first
Life cycle
- Life cycle similar to Toxoplasma gondii
- Limited range of warm-blooded intermediate hosts
- Asexual reproduction occurs in intermediate host forming tissue cysts
- Host range of sexual stage is unknown for N.caninum
- Intermediate host for N.hughesi is the horse, but the definitive host is unknown
- Final host
- Dogs pass oocysts
- Role not fully understood in pathogenesis
- 5 day prepatent period
- Other wild canids may also act as final definitive hosts
- Intermediate host
- Mostly cattle
- Natural infection has been documented in other herbivores
- Transmission
- Transplacental infection occurs in all intermediate hosts and in the canine final host
- Transplacental can occur in successive pregnancies
- In cattle, vertical transmission occurs
- Post-natal infection occurs but is less common
- Transplacental infection occurs in all intermediate hosts and in the canine final host
Pathogenesis
- Dogs
- Occurs mainly in puppies
- Causes ascending paralysis, especially of hind limbs, with muscle wasting
- Causes sudden collapse due to myocarditis
- More than puppy in a litter may be affected, although this may not occur simultaneously
- Successive litters affected
- Cattle
- Commenest cause of infectious abortion in dairy cattle
- Congenitally infected calves can have encephalomyelitis and paresis
- Abortion usually occurs between 5-7 months of gestation but can occur as early as 3 months
- No other clinical signs in the cow
- Repeat abortions possible in same cow (persistently infected)
- Horses
- Myeloencephalitis
- Transplacental infection occurs
- Disease only diagnosed in USA
Prevention and Control
- Do not allow dogs access to calving cows, placental membranes and aborted or dead calves
- Do not allow dogs to defecate in cattle feeding areas
- Identify and cull seropositive cattle, or do not breed from them or their progeny
- Select seronegative cattle for breeding
- Vaccinate
- Only in the USA
- Neoguard or Intervet
- Killed protozoal vaccine for healthy, preganant cows
- Dosed in first 3 weeks of pregnancy and then every 3-4 weeks during gestation
- Revaccination with 2 doses during each subsequent pregnancy