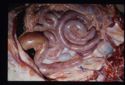
The myocardium provides the bulk of the heart tissue, and enables the co-ordinated contraction needed for efficient pumping of blood to the body.
Cardiac muscle is intermediate in appearance between skeletal muscle and visceral muscle with characteristics of both:
- Contracts with the force of skeletal muscle.
- Contracts continually like visceral muscle.
Cardiac muscle cells are long, striated, cylindrical cells with one or sometimes two nuclei. Cells contain a sarcoplasmic reticulum which slowly leak calcium ions into the cytoplasm, allowing automatic contractions without the need for external input. The rate of contractions is modulated by external autonomic and hormonal inputs. The sino-atrial node is the pace-maker of the heart as its rate of automatic firing is the greatest.
Intercellular junctions are known as intercalated discs and provide anchorage. They also allow the rapid progression of contractile stimuli throughout the heart muscle, making a functional syncytium.
The ventricular muscle is much thicker than that of the atria, and the atrial myocardium has a more fibrous component.
Blood supply is from the coronary arteries, sinuses beind the leaflets of the aortic valve allow entry of blood into the coronary system at diastole.
Disease of the myocardium may be incidental at post mortem and cause no clinical signs, or may be clinically evident. Disease must be severe and widespread to lead to observable clinical signs. Myocardial disease most often leads to heart failure.
The heart cannnot regenerate by hyperplasia and so responds with hypertrophic change in order to maintain normal function.
Steatosis
Hyaline Degeneration
Lipofuscinosis
Myocardial Mineralisation
Inflammatory-Myocarditis
Most often due to an infective agent. In most cases myocarditis is a result of a generalised infection, myocarditis is rarely an isolated primary condition. Classified as:
Acute Suppurative
Follows from the dissemination of septic emboli form suppurative foci therefore always follows pyaemia. Original septic foci may be:
- Joint ill.
- Umbilical abcess.
- Metritis.
- Mastitis.
- Valvular endocarditis.
May also be a result of extension from the endocarium or pericardium.
Acute non-suppurative
Usually results from a septicaemia or viraemia E.g Parvovirus infection in puppies. Also includes:
- Foot and Mouth Disease.
- Leptospirosis.
- Pasteurellosis.
Parvovirus Infection of puppies:
Parvovirus affects rapidly dividing cells which are found in the GI tract, and in the growing pup, the myocardium. Myocardial cells divide up to approximately 2 weeks of age and so this is when the infection has an effect although clinical signs may not become apparent until later in life.
Two cardiac syndromes exist:
- Sudden death, 3-8 weeks: Cardiac failure with pulmonary oedema etc. Histologically see multifocal myocardial necrosis due to viral replication within the myocardium. May see large basophilic intranuclear inclusion bodies.
- Puppies >8 weeks: See dyspoea, weakness, collapse and death within 24 hours. In this case cardiac failure occurs due to myocardial fibrosis.
Chronic
Myofibrils replaced by fibrous tissue during healing. May be a sequale of previous acute myocarditis.
Parasites
Parasites also may cause myocarditis. parasitic larvae may encyst in the myocardium, including:
- Cysticercosis.
- Sarcocystis.
- Toxoplasmosis.
Vascular pathology
Haemorrhage
Haemorrhage into the myocardium is seen with septicaemic disease. Also seen with:
Mulberry Heart Disease.
Occurs in pigs fed a diet deficient in Vitamin E/Selenium. Exact aetiology unknown but the lack of free radical scavenging allows haemorrhage into the myocardium. Characteristic linear and ecchymotic haemorrages are seen under the visceral pericarium and haermorrhage extends between the fibres, leading to myocardial degeneration.
Clinically seen as sudden death in pigs 3-4 months of age. The fastest growing pigs are affected the most so disease is seen in those with the best condition.
Thrombosis
Myocardial infarction rare in animals. May be seen with septicaemias.
Pages in category "Myocardial Pathology"
The following 12 pages are in this category, out of 12 total.