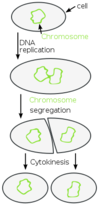
Bacterial Replication
Replication normally occurs by binary fission and ranges from every 20 mins (e.g. Staphylococci) to 2 weeks (e.g. leprosy bacillus)
- Variation can occur either by mutations in their DNA, or by lateral gene transfer:
- Transformation- small, naked pieces of DNA are directly transferred between bacteria, e.g. S pneumoniae
- Transduction- viruses known as bacteriophages transfer the DNA, many genes encoding toxins are transferred this way
- Conjugation- DNA is transferred in the form of plasmids, genes encoding antibiotic resistance are typically transferred this way.
Typical requirements of bacteria
- Atmospheric requirements:
- Obligate aerobe- e.g. B. bronchoseptica
- Facultative (optional) anaerobe-e.g. E. coli
- Obligate anaerobe- e.g. F. necrophorum
- Microaerophil- e.g. C. jejuni
- Aerotolerant- e.g. S. dysgalactiae
- pH- most pathogens require a neutral pH, although some need acidic/alkali environments:
- Acidophilic- Lactobacillus
- Alkophilic- Vibrio
Replication of E. coli [1]
| Bacterial Replication Learning Resources | |
|---|---|
To reach the Vetstream content, please select |
Canis, Felis, Lapis or Equis |