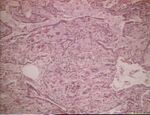
Lipid pneumonia (Image sourced from Bristol Biomed Image Archive with permission) - Associated with inhalation of oil, paraffin, etc.
- Reaction dominated by macrophages which fill the alveoli and interstitial thickening (mononuclear cells and fibrosis)
- Tends to acumulate in ventral regions bilterally
- Occurs subclinically in cats, sometimes dogs, unrelated to aspiration
- Gross lesion:
- Multifocal, firm, white nodules
- Microscopic lesions:
- Macrophages full of lipid forming foam within alveoli
- Interstitial lymphocyte and plasma cell infiltration, fibrosis
