Difference between revisions of "Epiglottis"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
The epiglottis can return to its normal size and shape after distortion due to the vast amount of elastic fibres present within. | The epiglottis can return to its normal size and shape after distortion due to the vast amount of elastic fibres present within. | ||
| − | [[Image:Epiglottic | + | [[Image:Epiglottic cartilage.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Epiglottic Cartilage - Copyright RVC]] |
| + | |||
==Histology== | ==Histology== | ||
[[Image:Epiglottis histology.jpg|right|thumb|150px|Epiglottis Histology - Copyright RVC]] | [[Image:Epiglottis histology.jpg|right|thumb|150px|Epiglottis Histology - Copyright RVC]] | ||
Revision as of 13:03, 31 July 2008
Introduction
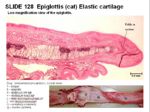
The epiglottis is a flap of elastic cartilage covered by mucous membrane. It forms the rostral boundary of the larynx and prevents food particles from entering the trachea.
The epiglottis can return to its normal size and shape after distortion due to the vast amount of elastic fibres present within.
Histology
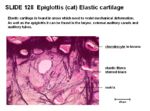
- Covered by mucous membrane
- Irregular elastic fibres
- Dense network of branching fibres around the chondrocytes
- Less dense branching fibres towards the perichondrium
Species Differences
Avian
- No epiglottis