| This article is still under construction. |
| Also known as: | EPM Equine protozoal myelitis |
Description
A progressive, infectious,[1]neurological disease of horses, endemic in the USA[2] and only encountered elsewhere in imported equids.[3] EPM is one of the most frequently diagnosed neurological conditions of the Western Hemisphere[4] and the principal differential for multifocal, asymmetric progressive central nervous system (CNS) disease.[1] As it can resemble any neurological disorder, EPM must be considered in any horse with neurological signs if it resides in the Americas or if it has been imported from that area[2][5] The disease is not contagious.[1]
Aetiology
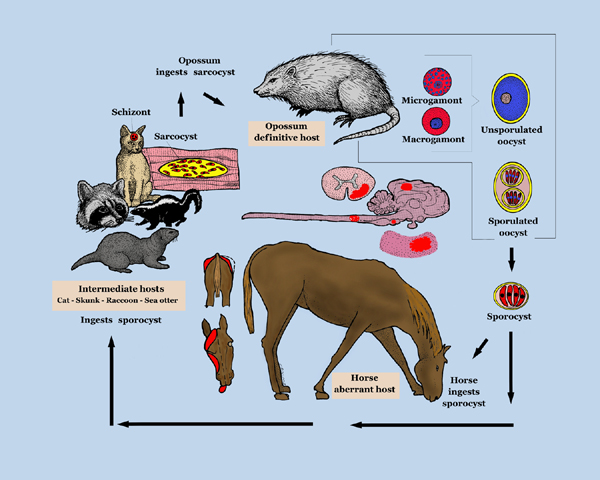
EPM results from infection of the CNS by the apicomplexan parasite Sarcocystis neurona or, less frequently, its close relative Neospora hughesi.[6][7] These protozoans develop within neurons[4] causing immediate or inflammatory-mediated neuronal damage. The organisms migrate randomly through the brain and spinal cord causing asymmetrical lesions of grey and white matter and thus multifocal lower and upper motor neuron deficits.[1]
Signalment
Mostly Standardbreds and Thoroughbreds aged 1-6years.[1] Foal infection may be possible.[2]
Differential Diagnoses
Prognosis
Depends on duration and severity of neurological signs[3] but clinical resolution is more likely if the condition is diagnosed and treated early.[2] With standard therapy, involving 6-8months of ponazuzril or pyrimethamine-sulfadiazine (V), there is a recovery rate of around 25% and an improvement in 60-75% of cases.[8] A good prognosis might be expected if there is an improvement in clinical signs within two weeks of commencing anti-protozoal and anti-inflammatory treatment (V). The prognosis will be guarded to poor[1] for a horse with severe irreversible neuronal damage or one that has not been diagnosed or treated appropriately (V).
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 Pasquini, C, Pasquini, S, Woods, P (2005) Guide to Equine Clinics Volume 1: Equine Medicine (Third edition), SUDZ Publishing, 245-250. Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "Pasq" defined multiple times with different content Cite error: Invalid<ref>tag; name "Pasq" defined multiple times with different content Cite error: Invalid<ref>tag; name "Pasq" defined multiple times with different content Cite error: Invalid<ref>tag; name "Pasq" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Gray, L.C, Magdesian, K.G, Sturges, B.K, Madigan, J.E (2001) Suspected protozoal myeloencephalitis in a two-month-old colt. Vet Record, 149:269-273.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Vatistas, N, Mayhew, J (1995) Differential diagnosis of polyneuritis equi. In Practice, Jan, 26-29.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Furr, M (2010) Equine protozoal myeloencephalitis in Reed, S.M, Bayly, W.M. and Sellon, D.C (2010) Equine Internal Medicine (Third Edition), Saunders, Chapter 12.
- ↑ DEFRA, The Animal Health Trust, The British Equine Veterinary Association (2009) Surveillance: Equine disease surveillance, April to June 2009, The Vet Record, Oct 24:489-492.
- ↑ Dubey, J.P, Lindsay, D.S, Saville, W.J, Reed, S.M, Granstrom, D.E, Speer, C.A (2001)A review of Sarcocystis neurona and equine protozoal myeloencephalitis (EPM). Vet Parasitol, 95:89-131. In: Pusterla, N, Wilson, W.D, Conrad, P.A, Barr, B.C, Ferraro, G.L, Daft, B.M, Leutenegger, C.M (2006) Cytokine gene signatures in neural tissue of horses with equine protozoal myeloencephalitis or equine herpes type 1 myeloencephalopathy. The Vet Record, Sep 9:Papers & Articles.
- ↑ Wobeser, B.K, Godson, D.L, Rejmanek, D, Dowling, P (2009) Equine protozoal myeloencephalitis caused by Neospora hughesi in an adult horse in Saskatchewan. Can Vet J, 50(8):851-3.
- ↑ MacKay, R.J (2006) Equine protozoa myeloencephalitis: treatment, prognosis and prevention. Clin Tech Equine Pract, 5:9-16. In: Furr, M (2010) Equine protozoal myeloencephalitis in Reed, S.M, Bayly, W.M. and Sellon, D.C (2010) Equine Internal Medicine (Third Edition), Saunders, Chapter 12.
| Differential | Differentiating signs | Tests to rule out |