Difference between revisions of "Diaphragm - Anatomy & Physiology"
Fiorecastro (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (2 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
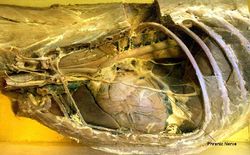
[[Image:DogThorax.jpg|right|thumb|250px|''Dog Thorax, contents of Thoracic Cavity removed. ©University of Nottingham 2008'']] | [[Image:DogThorax.jpg|right|thumb|250px|''Dog Thorax, contents of Thoracic Cavity removed. ©University of Nottingham 2008'']] | ||
| + | |||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
Because of the shorter thorax, the diaphragm is steeper in the '''ruminant''' compared to the '''horse'''. '''Avian''' species do not possess a diaphragm. Air moves in and out of their lungs via [[Avian Respiration - Anatomy & Physiology#Air Sacs|air sacs]]. | Because of the shorter thorax, the diaphragm is steeper in the '''ruminant''' compared to the '''horse'''. '''Avian''' species do not possess a diaphragm. Air moves in and out of their lungs via [[Avian Respiration - Anatomy & Physiology#Air Sacs|air sacs]]. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{citation|initiallast = Dyce|initialfirst = K.M|2last = Sack|2first = W.O|finallast = Wensing|finalfirst = C.J.G|year = 2002|title = Textbook of Veterinary Anatomy|ed =3rd|city = Philadelphia|pub = Saunders}} | {{citation|initiallast = Dyce|initialfirst = K.M|2last = Sack|2first = W.O|finallast = Wensing|finalfirst = C.J.G|year = 2002|title = Textbook of Veterinary Anatomy|ed =3rd|city = Philadelphia|pub = Saunders}} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Category:Musculoskeletal System - Anatomy & Physiology]][[Category:Respiratory System - Anatomy & Physiology]] | [[Category:Musculoskeletal System - Anatomy & Physiology]][[Category:Respiratory System - Anatomy & Physiology]] | ||
[[Category:A&P Done]] | [[Category:A&P Done]] | ||
Revision as of 16:53, 14 January 2011
Introduction
The Diaphragm is a dome-shaped musculotendinous sheet separating the thoracic and abdominal cavities. It is convex on its cranial surface. In the neutral position between full inspiration and full expiration, the most cranial part of the diaphragm is in line with the 6th rib.
Structure
The muscular part of the diaphragm is peripheral, surrounding the central tendinous area. The muscular part has sections which arise from the xiphoid process of the sternum, vertebral column and caudal ribs.
Openings within the diaphragm
The diaphragm has three openings:
- Aortic Hiatus - the most dorsal opening, contains the aorta, azygous vein and thoracic duct
- Oesophageal Hiatus - contains the oesophagus, dorsal and ventral vagal trunks
- Caval Foramen - lies within the central tendinous region of the diaphragm and contains the caudal vena cava. This opening does not allow movement, the diaphragm is fused with the vessel wall.
Function
During inspiration, the diaphragm contracts to increase the volume of the thoracic cavity, decreasing its pressure, thus drawing air in. The diaphragm relaxes for expiration.
Innervation
The diaphragm is supplied by the phrenic nerve.
Species differences
Because of the shorter thorax, the diaphragm is steeper in the ruminant compared to the horse. Avian species do not possess a diaphragm. Air moves in and out of their lungs via air sacs.
References
Dyce, K.M., Sack, W.O. and Wensing, C.J.G. (2002) Textbook of Veterinary Anatomy. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Saunders.