Difference between revisions of "Hyperthyroidism"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (7 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{unfinished}} |
| − | + | ||
| + | Seen most commonly in the cat. Elderly cats are affected with the average age of onset being 12-13 years. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''Clinical signs'': | ||
| + | *Weight loss despite polyphagia | ||
| + | *Increased activity, nervousness (approximately 10% will show apathy) | ||
| + | *Polyuria and polydipsia | ||
| + | *Heat intolerance, panting | ||
| + | *Tachycardia >240 bpm | ||
| + | *Poor coat, matted and unkempt | ||
| + | *Palpable thyroid mass often present | ||
| + | |||
| + | Often see a [[Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy|hypertrophic cardiomyopathy]] due to chronically increased heart rate and activity. | ||
| + | |||
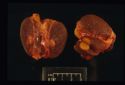
[[Image:thyroid adenoma.jpg|right|thumb|125px|<small><center>'''Thyroid adenoma'''. Courtesy of T. Scase</center></small>]] | [[Image:thyroid adenoma.jpg|right|thumb|125px|<small><center>'''Thyroid adenoma'''. Courtesy of T. Scase</center></small>]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | ''Aetiopathogenesis'': | |
| − | + | ||
| + | >98% are a functional adenoma of the thyroid gland and many will be palpable. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''Treatment:'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Surgical removal of the affected thyroid gland(s). If bilateral it is important to preserve at least one parathyroid gland to maintain calcium homeostasis. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Medical treatment: | ||
| + | *'''Carbamizole''': Interferes with thyroid hormone synthesis. | ||
| + | *'''Radioactive iodine''' therapy. Useful for intrathoracic thyroid nodules. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | *In young animals causes accelerated maturation of growth plate | |
| − | + | *In adults causes [[Bones Degenerative - Pathology#Osteoporosis (Atrophy)|osteoporosis]] | |
| − | |||
| − | + | ==Pathophysiology== | |
| − | |||
| − | == | + | ==Signalment== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==Presentation/Clinical Signs== | |
| − | + | #Weight loss | |
| − | + | #Cardiovascular effects | |
| − | + | #Palpable goitre | |
| + | #Hyperactive | ||
| + | #Polyuria | ||
| + | #Polydipsia | ||
| − | == | + | ==Diagnosis== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | #T4 Assay | ||
| + | #T4 and TSH assay | ||
| − | + | ==Treatment== | |
| − | + | #Surgical - Thyroidectomy | |
| + | #Medical - Thiamazole blocks synthesis of T3 and T4. | ||
| + | #Radioactive Iodine | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:To Do - Clinical]][[Category:Endocrine Diseases - Cat]] |
[[Category:Bones - Metabolic Pathology]] | [[Category:Bones - Metabolic Pathology]] | ||
[[Category:Thyroid Gland - Pathology]] | [[Category:Thyroid Gland - Pathology]] | ||
Revision as of 18:48, 27 February 2011
| This article is still under construction. |
Seen most commonly in the cat. Elderly cats are affected with the average age of onset being 12-13 years.
Clinical signs:
- Weight loss despite polyphagia
- Increased activity, nervousness (approximately 10% will show apathy)
- Polyuria and polydipsia
- Heat intolerance, panting
- Tachycardia >240 bpm
- Poor coat, matted and unkempt
- Palpable thyroid mass often present
Often see a hypertrophic cardiomyopathy due to chronically increased heart rate and activity.
Aetiopathogenesis:
>98% are a functional adenoma of the thyroid gland and many will be palpable.
Treatment:
Surgical removal of the affected thyroid gland(s). If bilateral it is important to preserve at least one parathyroid gland to maintain calcium homeostasis.
Medical treatment:
- Carbamizole: Interferes with thyroid hormone synthesis.
- Radioactive iodine therapy. Useful for intrathoracic thyroid nodules.
- In young animals causes accelerated maturation of growth plate
- In adults causes osteoporosis
Pathophysiology
Signalment
Presentation/Clinical Signs
- Weight loss
- Cardiovascular effects
- Palpable goitre
- Hyperactive
- Polyuria
- Polydipsia
Diagnosis
- T4 Assay
- T4 and TSH assay
Treatment
- Surgical - Thyroidectomy
- Medical - Thiamazole blocks synthesis of T3 and T4.
- Radioactive Iodine