Difference between revisions of "Bone Cysts"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
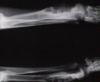
(Created page with "right|thumb|100px|<small><center>Bone cysts (Image sourced from Bristol Biomed Image Archive with permission)</center></small> *May be seen radiograp...") |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:Bone cysts dog.jpg|right|thumb|100px|<small><center>Bone cysts (Image sourced from Bristol Biomed Image Archive with permission)</center></small>]] | [[Image:Bone cysts dog.jpg|right|thumb|100px|<small><center>Bone cysts (Image sourced from Bristol Biomed Image Archive with permission)</center></small>]] | ||
*May be seen radiographically | *May be seen radiographically | ||
| − | *Must be distinguished from [[ | + | *Must be distinguished from [[Bones Hyperplastic and Neoplastic - Pathology#Neoplastic|neoplasia]] |
*Expansile lytic masses | *Expansile lytic masses | ||
*Do not appear aggressive | *Do not appear aggressive | ||
*'''Subchondral cysts''' | *'''Subchondral cysts''' | ||
**Common in horses and pigs | **Common in horses and pigs | ||
| − | **Usually manifestations of [[Joints Developmental - Pathology#Osteochondrosis|osteochondrosis]] and [[Degenerative | + | **Usually manifestations of [[Joints Developmental - Pathology#Osteochondrosis|osteochondrosis]] and [[Joints Degenerative - Pathology#Degenerative joint disease (DJD)|DJD]] |
*'''Simple cysts''' | *'''Simple cysts''' | ||
**May contain clear colourless fluid, or serosanguinous | **May contain clear colourless fluid, or serosanguinous | ||
Revision as of 11:58, 3 March 2011
- May be seen radiographically
- Must be distinguished from neoplasia
- Expansile lytic masses
- Do not appear aggressive
- Subchondral cysts
- Common in horses and pigs
- Usually manifestations of osteochondrosis and DJD
- Simple cysts
- May contain clear colourless fluid, or serosanguinous
- Wall of dense fibrous tissue, woven or lamellar bone
- Aneurysmal bone cysts
- Expansie lesions
- Arise from disturbance of vascular tissue of bone marrow
- Grossly:
- Appear as blood filled sponge
- Spaces separated by fibrous trabeculae
- Histologically:
- Proliferation of undifferentiated mesenchymal cell with multinucleated osteoclast-like cells
- Haemorrhage and haemosiderosis
- Radiography is essential to help differentiate with cavity of a neoplasm