Difference between revisions of "CNS Vasculature - Anatomy & Physiology"
Fiorecastro (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (29 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
== Circle of Willis == | == Circle of Willis == | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Blood is supplied to the brain by the ''internal carotid artery'' in dogs and horses whilst in other domestic species the main blood supply is from branches of the ''maxillary artery''. The Circle of Willis (also called the ''cerebral arterial circle'' or ''arterial circle of Willis'') is a circle of arteries that supply blood to the brain. The Circle of Willis is made up of the following arteries; | |
| − | * | + | |
| − | * | + | *Left and right inferior cerebral arteries |
| − | * | + | *Anterior communicating artery |
| − | * | + | *Left and right internal carotid arteries |
| + | *Left and right posterior cerebral arteries | ||
| + | *Left and right posterior communicating arteries | ||
The arrangement of the Circle of Willis means that if one part of the circle becomes blocked or narrowed (stenosed), or one of the arteries supplying the circle is stenosed, blood flow from the other blood vessels can continue to provide a continuous supply of blood to the brain. | The arrangement of the Circle of Willis means that if one part of the circle becomes blocked or narrowed (stenosed), or one of the arteries supplying the circle is stenosed, blood flow from the other blood vessels can continue to provide a continuous supply of blood to the brain. | ||
| − | + | <br> <u>Note</u>: The basilar artery and middle cerebral arteries, though they supply the brain, are not considered part of the circle. | |
| − | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| − | + | === Rete Mirable === | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | ==Rete Mirable== | ||
[[Image:Carotidretesheep.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Carotid Rete of the Sheep. Sophie Stenner, RVC 2008]] | [[Image:Carotidretesheep.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Carotid Rete of the Sheep. Sophie Stenner, RVC 2008]] | ||
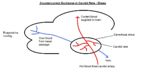
| − | The | + | The Rete Mirabile is a complex network of arteries and veins lying very close to each other and depends on a countercurrent blood flow between the arterioles and venuoles (blood flowing in opposite directions). It exchanges heat, ions, or gases between vessel walls so that the two bloodstreams within the rete maintain a gradient. The image shows the countercurrent exchange in the carotid rete mirable (carotid rete) of a sheep controlling the temperature of blood supplied to the brain. |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| − | |||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| − | ==Species Differences | + | ==Species Differences== |
| − | The blood supply to the brain has major differences depending on species. Across all species, there are | + | The [[#Vasculature|blood supply to the brain]] has major differences depending on species. Across all species, there are four 4 potential channels supplying the cerebral arterial circle. These are; |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | '''1. The internal carotid artery''' | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | '''2. The basiliar artery''' | |
| − | ===Dog | + | '''3. The anastomosing ramus from the maxillary artery to the internal carotid artery''' |
| − | [[Image:Calfvssheepblood.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Calf vs Sheep blood supply | + | |
| − | + | '''4. The connection of the vertibral artery to the internal carotid artery''' | |
| − | + | ||
| + | ==== Dog, man and many other species ==== | ||
| + | |||
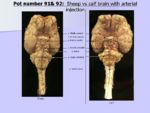
| + | [[Image:Calfvssheepblood.jpg|thumb|right|150px|Calf vs Sheep blood supply comparism. RVC 2008]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''Channels 1 + 2''' supply the arterial circle. | ||
| + | *Neither channel has a '''[[#Rete_Mirable|rete mirable]]'''. | ||
| + | *Internal carotid blood reaches all of the cerebral hemisphere '''except for it's most caudal part'''. | ||
| + | *'''Vertebral blood''' supplies the the remainder of the cerebral hemisphere and the rest of the brain. | ||
| − | ===Sheep and | + | ==== Sheep and cat ==== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | *'''Only channel 3''' supplies the arterial circle. | |
| − | + | *Channel 3 has a '''rete mirable'''. | |
| − | + | *'''Channel 2 carries blood away''' from the arterial circle. | |
| − | + | *Maxillary blood is distributed to all of the brain except the caudal part of medulla oblongata, which is supplied by vertibral blood. | |
| − | |||
| − | == | + | ==== Ox ==== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | === | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | *'''Channels 3 + 4''' both supply the arterial circle. | |
| + | *Each has a '''rete mirable'''. | ||
| + | *'''Channel 2 carries blood away''' from the arterial circle. | ||
| + | *A mixture of maxillary and vertibral blood reaches '''all parts of the brain'''. | ||
| − | [[Category:Nervous_System_-_Anatomy_&_Physiology]] [[Category: | + | [[Category:Nervous_System_-_Anatomy_&_Physiology]] [[Category:To_Do_-_A&P]] |
Revision as of 16:48, 5 March 2011
Circle of Willis
Blood is supplied to the brain by the internal carotid artery in dogs and horses whilst in other domestic species the main blood supply is from branches of the maxillary artery. The Circle of Willis (also called the cerebral arterial circle or arterial circle of Willis) is a circle of arteries that supply blood to the brain. The Circle of Willis is made up of the following arteries;
- Left and right inferior cerebral arteries
- Anterior communicating artery
- Left and right internal carotid arteries
- Left and right posterior cerebral arteries
- Left and right posterior communicating arteries
The arrangement of the Circle of Willis means that if one part of the circle becomes blocked or narrowed (stenosed), or one of the arteries supplying the circle is stenosed, blood flow from the other blood vessels can continue to provide a continuous supply of blood to the brain.
Note: The basilar artery and middle cerebral arteries, though they supply the brain, are not considered part of the circle.
Rete Mirable
The Rete Mirabile is a complex network of arteries and veins lying very close to each other and depends on a countercurrent blood flow between the arterioles and venuoles (blood flowing in opposite directions). It exchanges heat, ions, or gases between vessel walls so that the two bloodstreams within the rete maintain a gradient. The image shows the countercurrent exchange in the carotid rete mirable (carotid rete) of a sheep controlling the temperature of blood supplied to the brain.
Species Differences
The blood supply to the brain has major differences depending on species. Across all species, there are four 4 potential channels supplying the cerebral arterial circle. These are;
1. The internal carotid artery
2. The basiliar artery
3. The anastomosing ramus from the maxillary artery to the internal carotid artery
4. The connection of the vertibral artery to the internal carotid artery
Dog, man and many other species
- Channels 1 + 2 supply the arterial circle.
- Neither channel has a rete mirable.
- Internal carotid blood reaches all of the cerebral hemisphere except for it's most caudal part.
- Vertebral blood supplies the the remainder of the cerebral hemisphere and the rest of the brain.
Sheep and cat
- Only channel 3 supplies the arterial circle.
- Channel 3 has a rete mirable.
- Channel 2 carries blood away from the arterial circle.
- Maxillary blood is distributed to all of the brain except the caudal part of medulla oblongata, which is supplied by vertibral blood.
Ox
- Channels 3 + 4 both supply the arterial circle.
- Each has a rete mirable.
- Channel 2 carries blood away from the arterial circle.
- A mixture of maxillary and vertibral blood reaches all parts of the brain.