Difference between revisions of "Contagious Bovine Pleuropneumonia"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Redirected page to Mycoplasma mycoides subsp. mycoides) |
|||
| (4 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | # | + | (CBPP) |
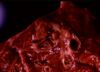
| + | [[Image:Contagious bovine pleuropneumonia.jpg|right|thumb|100px|<small><center>Contagious bovine pleuropneumonia (Image sourced from Bristol Biomed Image Archive with permission)</center></small>]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | *Aerosol transmission by close contact with clinically or subclinically affected animals | ||
| + | *Severity depends on strain and host susceptibility | ||
| + | *Slow spread of infection | ||
| + | *50% morbidity; mortality rate high in severe outbreaks | ||
| + | *Large colony type causes pleuropneumonia, mastitis, septicaemia and polyarthritis | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Clinical signs | ||
| + | **Acute onset fever, anorexia, depression, lowered milk yield, hyperpnoea, coughing and a mucopurulent nasal discharge | ||
| + | **Dyspnoea occurs with abducted elbows and extended necks and an expiratory grunt | ||
| + | **Can be fatal within 1-3 weeks | ||
| + | **Calves may suffer from [[Infectious Arthritis#In Cattle|arthritis]], synovitis and endocarditis | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Gross pathology | ||
| + | **Marbled appearance to lungs with consolidated grey and red lobules separated by emphysematous areas | ||
| + | **Serofibrinous pleural fluid | ||
| + | **Necrotic foci surrounded by fibrous capsules in chronic cases act as source of infection | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Diagnosis | ||
| + | **Clinical signs and post-mortem appearance | ||
| + | **PCR on pleural fluid, lung tissue, regional lymph nodes or bronchoalveolar lavage fluid | ||
| + | **Fluorescent antibody test | ||
| + | **Serological tests such as serum agglutination, haemagglutination, complement fixation, ELISA | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Treatment and control | ||
| + | **Slaughter of affected cattle in counries where the disease is exotic | ||
| + | **Movement restrictions, quaranteen and slaughter of carrier animals in endemic countries | ||
| + | *''M. mycoides'' subsp. 'mycoides'' causes septicaemia, pleuropneumonia, arthritis and mastitis in goats | ||
| + | **Vaccination in endemic regions | ||
| + | *Caused by [[Mycoplasma mycoides subsp. mycoides|''Mycoplasma mycoides'']], small colony variant | ||
| + | *Causes a fibrinonecrotic [[Pneumonia Overview#Infectious causes of pneumonia|pneumonia]] and [[Pleuritis|fibrinous pleuritis]] | ||
| + | *Also affects caudodorsal areas | ||
| + | *[[Bronchopneumonia|Bronchopneumonia]] -> [[Lobar Pneumonia|lobar pneumonia]] | ||
| + | *Sequestra are common | ||
| + | *NB: similarity to pneumonic pasteurellosis but CBPP has more pronounced marbled effect | ||
| + | *Interstitial septa are markedly widened by fibrinous exudate and the necrotic areas may have a fibrous capsule | ||
| + | *Large colony variant will cause a similar disease in goats | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Respiratory Diseases - Cattle]][[Category:To_Do_-_Kate]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Respiratory_Bacterial_Infections]] | ||
Revision as of 10:04, 10 March 2011
(CBPP)
- Aerosol transmission by close contact with clinically or subclinically affected animals
- Severity depends on strain and host susceptibility
- Slow spread of infection
- 50% morbidity; mortality rate high in severe outbreaks
- Large colony type causes pleuropneumonia, mastitis, septicaemia and polyarthritis
- Clinical signs
- Acute onset fever, anorexia, depression, lowered milk yield, hyperpnoea, coughing and a mucopurulent nasal discharge
- Dyspnoea occurs with abducted elbows and extended necks and an expiratory grunt
- Can be fatal within 1-3 weeks
- Calves may suffer from arthritis, synovitis and endocarditis
- Gross pathology
- Marbled appearance to lungs with consolidated grey and red lobules separated by emphysematous areas
- Serofibrinous pleural fluid
- Necrotic foci surrounded by fibrous capsules in chronic cases act as source of infection
- Diagnosis
- Clinical signs and post-mortem appearance
- PCR on pleural fluid, lung tissue, regional lymph nodes or bronchoalveolar lavage fluid
- Fluorescent antibody test
- Serological tests such as serum agglutination, haemagglutination, complement fixation, ELISA
- Treatment and control
- Slaughter of affected cattle in counries where the disease is exotic
- Movement restrictions, quaranteen and slaughter of carrier animals in endemic countries
- M. mycoides subsp. 'mycoides causes septicaemia, pleuropneumonia, arthritis and mastitis in goats
- Vaccination in endemic regions
- Caused by Mycoplasma mycoides, small colony variant
- Causes a fibrinonecrotic pneumonia and fibrinous pleuritis
- Also affects caudodorsal areas
- Bronchopneumonia -> lobar pneumonia
- Sequestra are common
- NB: similarity to pneumonic pasteurellosis but CBPP has more pronounced marbled effect
- Interstitial septa are markedly widened by fibrinous exudate and the necrotic areas may have a fibrous capsule
- Large colony variant will cause a similar disease in goats