Difference between revisions of "Thromboembolism"
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
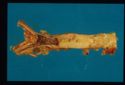
| − | + | [[Image:Sarcoma embolus.jpg|thumb|right|125px|<small><center><b>Sarcoma embolus (dog)</b>. Courtesy of T. Scase</center></small>]] | |
| − | |||
| − | [[Image:Sarcoma embolus.jpg|thumb|right| | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | == Introduction<br> == | |
| − | The | + | As the name implies, a thromboembolism is a clot (thrombus) or foreign body that blocks vessels a distance away from its original site of origin. The most significant sites of thromboembolic formation are the following: lungs, CNS, terminal aorta, kidneys. |
| − | + | In order for a thromboembolism to occur, some changes in the vasculature need to occur. These include disruption of endothelial integrity, disruption of flow, disruption of blood haemostasis amd disruption of fibrinolysis. | |
| + | The incidence of thromboembolism greatly increases with certain diseases including heart disease, neoplasia, blood disorders, parasitic diseases and hyperadrenocortiscm. | ||
| − | + | <br> | |
| − | == | + | == Clinical Signs<br> == |
| − | + | The '5 P's' are the characteristic clinical signs of thromboembolism. These are pain, paresis, pallor, pulselessness and polar (cold extremities). <span style="font-weight: bold;" /><span style="font-weight: bold;" /><span style="font-weight: bold;" /><span style="font-weight: bold;" />Long term clinical effects include necrosis of the affected area. Specific clinical signs relating to the thromboembolism being in a particular area include acute onset neurological problems, renal failure if clot in kidneys and dyspnoea if it is in the lungs.<br> | |
| − | + | <br> | |
| − | == | + | == Diagnosis<br> == |
| + | |||
| + | All findings and diagnostic procedures are heavily dependent on the site affected.<br> | ||
| − | + | Blood tests may reveal hyperkalemia, acidosis, increased lactate, azotemia and elevated serum creatine phospohokinase. Radiography, Echocardiography and Angiography may also be used to diagnose a thromboembolism.<br> | |
| − | + | <br> | |
| − | + | == Treatment == | |
| − | + | It is important to treat the underlying conditions. Pain relief is vital and must be very strong, e.g. morphine. I.V. fluids will also need to be given as supportive treatment. Anticoagulants: Heparin or Aspirin should also be given. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <br> | |
| − | + | == Prognosis<br> == | |
| − | + | This is grave in most cases.<br> | |
| − | + | <br> | |
| − | + | == References<br> == | |
| − | Nelson, R.W. and Couto, C.G. (2009) | + | Ettinger, S.J. and Feldman, E. C. (2000) Textbook of Veterinary Internal Medicine Diseases of the Dog and Cat Volume 2 (Fifth Edition) W.B. Saunders Company<br>Ettinger, S.J, Feldman, E.C. (2005) Textbook of Veterinary Internal Medicine (6th edition, volume 2)W.B. Saunders Company<br>Fossum, T. W. et. al. (2007) Small Animal Surgery (Third Edition) Mosby Elsevier <br>Merck & Co (2008) The Merck Veterinary Manual (Eighth Edition) Merial<br>Nelson, R.W. and Couto, C.G. (2009) Small Animal Internal Medicine (Fourth Edition) Mosby Elsevier. <br> |
| + | <br> | ||
| + | Literature Search | ||
| − | + | [[Image:CABI logo.jpg|left|90px]] | |
| − | + | <br> Use these links to find recent scientific publications via CAB Abstracts (log in required unless accessing from a subscribing organisation). <br><br><br> [http://www.cabi.org/cabdirect/FullTextPDF/2008/20083206605.pdf '''Feline thromboembolism.''' Moïse, N. S.; The North American Veterinary Conference, Gainesville, USA, Small animal and exotics. Proceedings of the North American Veterinary Conference, Volume 22, Orlando, Florida, USA, 2008, 2008, pp 229-232 - '''Full Text Article'''] | |
| − | [[Category:Arterial_Pathology]] [[Category: | + | [[Category:Arterial_Pathology]] [[Category:To_Do_-_Review]] [[Category:Vascular_Diseases_-_Dog]] [[Category:Vascular_Diseases_-_Cat]] |
| − | |||
Revision as of 13:02, 15 March 2011
Introduction
As the name implies, a thromboembolism is a clot (thrombus) or foreign body that blocks vessels a distance away from its original site of origin. The most significant sites of thromboembolic formation are the following: lungs, CNS, terminal aorta, kidneys.
In order for a thromboembolism to occur, some changes in the vasculature need to occur. These include disruption of endothelial integrity, disruption of flow, disruption of blood haemostasis amd disruption of fibrinolysis. The incidence of thromboembolism greatly increases with certain diseases including heart disease, neoplasia, blood disorders, parasitic diseases and hyperadrenocortiscm.
Clinical Signs
The '5 P's' are the characteristic clinical signs of thromboembolism. These are pain, paresis, pallor, pulselessness and polar (cold extremities). Long term clinical effects include necrosis of the affected area. Specific clinical signs relating to the thromboembolism being in a particular area include acute onset neurological problems, renal failure if clot in kidneys and dyspnoea if it is in the lungs.
Diagnosis
All findings and diagnostic procedures are heavily dependent on the site affected.
Blood tests may reveal hyperkalemia, acidosis, increased lactate, azotemia and elevated serum creatine phospohokinase. Radiography, Echocardiography and Angiography may also be used to diagnose a thromboembolism.
Treatment
It is important to treat the underlying conditions. Pain relief is vital and must be very strong, e.g. morphine. I.V. fluids will also need to be given as supportive treatment. Anticoagulants: Heparin or Aspirin should also be given.
Prognosis
This is grave in most cases.
References
Ettinger, S.J. and Feldman, E. C. (2000) Textbook of Veterinary Internal Medicine Diseases of the Dog and Cat Volume 2 (Fifth Edition) W.B. Saunders Company
Ettinger, S.J, Feldman, E.C. (2005) Textbook of Veterinary Internal Medicine (6th edition, volume 2)W.B. Saunders Company
Fossum, T. W. et. al. (2007) Small Animal Surgery (Third Edition) Mosby Elsevier
Merck & Co (2008) The Merck Veterinary Manual (Eighth Edition) Merial
Nelson, R.W. and Couto, C.G. (2009) Small Animal Internal Medicine (Fourth Edition) Mosby Elsevier.
Literature Search
Use these links to find recent scientific publications via CAB Abstracts (log in required unless accessing from a subscribing organisation).
Feline thromboembolism. Moïse, N. S.; The North American Veterinary Conference, Gainesville, USA, Small animal and exotics. Proceedings of the North American Veterinary Conference, Volume 22, Orlando, Florida, USA, 2008, 2008, pp 229-232 - Full Text Article