Difference between revisions of "Equine Internal Medicine Q&A 07"
Ggaitskell (talk | contribs) (Created page with "{{Template:Manson Mair}} centre|500px<br> <br /> '''You are asked to examine a three-year-old Thoroughbred mare with a history of...") |
|||
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
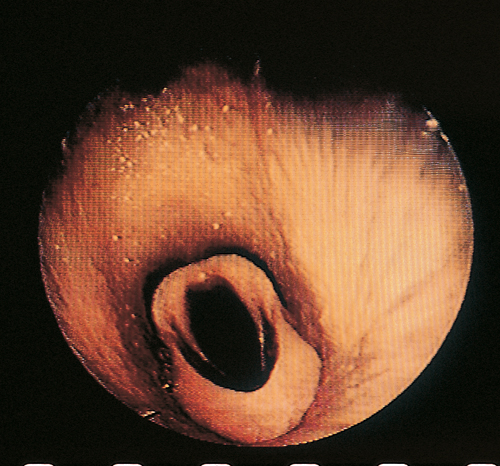
Epiglottic entrapment. <br><br> | Epiglottic entrapment. <br><br> | ||
The epiglottis is covered by the entrapping membrane, thereby obscuring the serrated edge and its surface vasculature. | The epiglottis is covered by the entrapping membrane, thereby obscuring the serrated edge and its surface vasculature. | ||
| − | |l1= | + | |l1= |
|q2=Describe two basic methods for surgical correction. | |q2=Describe two basic methods for surgical correction. | ||
|a2= The entrapped epiglottis can be approached through a ventral midline laryngotomy, after which the aryteno-epiglottic tissue is resected. <br><br> | |a2= The entrapped epiglottis can be approached through a ventral midline laryngotomy, after which the aryteno-epiglottic tissue is resected. <br><br> | ||
Alternatively, the aryteno-epiglottic fold can be approached through the mouth or nose, after which the fold is divided in the midline using either a hook with a cutting edge on the inside of the hook, or transendoscopically using Nd:YAG laser, or transendoscopically using monopolar electrosurgical cutting equipment. <br><br> | Alternatively, the aryteno-epiglottic fold can be approached through the mouth or nose, after which the fold is divided in the midline using either a hook with a cutting edge on the inside of the hook, or transendoscopically using Nd:YAG laser, or transendoscopically using monopolar electrosurgical cutting equipment. <br><br> | ||
Transendoscopical treatment can be performed in the standing animal. | Transendoscopical treatment can be performed in the standing animal. | ||
| − | |l2= | + | |l2= |
|q3=What postoperative complications may occur? | |q3=What postoperative complications may occur? | ||
|a3= | |a3= | ||
Dorsal displacement of the soft palate may occur, especially after resection of the aryteno-epiglottic fold. This is most likely to occur if dorsal displacement of the soft palate was observed prior to surgery, or if the epiglottis is hypoplastic or deformed. | Dorsal displacement of the soft palate may occur, especially after resection of the aryteno-epiglottic fold. This is most likely to occur if dorsal displacement of the soft palate was observed prior to surgery, or if the epiglottis is hypoplastic or deformed. | ||
| − | |l3= | + | |l3= |
| + | |||
| + | |||
</FlashCard> | </FlashCard> | ||
Revision as of 17:50, 31 May 2011
| This question was provided by Manson Publishing as part of the OVAL Project. See more Equine Internal Medicine questions |
You are asked to examine a three-year-old Thoroughbred mare with a history of intermittent coughing and exercise intolerance. The cough is said to be most pronounced when the horse is eating. The animal is clinically healthy but during light exercise you hear an abnormal noise during both inspiration and expiration. Endoscopic examination reveals the lesion shown in the image.
| Question | Answer | Article | |
| What is your diagnosis? | Epiglottic entrapment. |
[[|Link to Article]] | |
| Describe two basic methods for surgical correction. | The entrapped epiglottis can be approached through a ventral midline laryngotomy, after which the aryteno-epiglottic tissue is resected. Alternatively, the aryteno-epiglottic fold can be approached through the mouth or nose, after which the fold is divided in the midline using either a hook with a cutting edge on the inside of the hook, or transendoscopically using Nd:YAG laser, or transendoscopically using monopolar electrosurgical cutting equipment. |
[[|Link to Article]] | |
| What postoperative complications may occur? | Dorsal displacement of the soft palate may occur, especially after resection of the aryteno-epiglottic fold. This is most likely to occur if dorsal displacement of the soft palate was observed prior to surgery, or if the epiglottis is hypoplastic or deformed. |
[[ |Link to Article]] | |